Instruction Manual/Experiments Guide
... ➃ Adjust the length of the string so that the longest arrangement of masses that you intend to use will not hit the floor before the cart has reached the end of its run. Put a loop in this end of the string. ➦ NOTE: The cart’s acceleration falls to zero when the falling mass hits the floor. ...
... ➃ Adjust the length of the string so that the longest arrangement of masses that you intend to use will not hit the floor before the cart has reached the end of its run. Put a loop in this end of the string. ➦ NOTE: The cart’s acceleration falls to zero when the falling mass hits the floor. ...
2nd Semester Final Study Guide-Clayton Answer
... Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ...
... Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ...
Slide 1
... You bend your legs when you run to reduce their rotational inertia. Bent legs are easier to swing back and forth. ...
... You bend your legs when you run to reduce their rotational inertia. Bent legs are easier to swing back and forth. ...
No Slide Title
... • Numerical measurements in science contain the value (number) and Dimension. • Dimension is the physical quantity being measured (length, mass, time, temperature, electric current) • Each dimension is measured using units and prefixes from the SI system. • The dimension must match the unit. (ex. If ...
... • Numerical measurements in science contain the value (number) and Dimension. • Dimension is the physical quantity being measured (length, mass, time, temperature, electric current) • Each dimension is measured using units and prefixes from the SI system. • The dimension must match the unit. (ex. If ...
The Concept of Collision Strength and Its Applications
... Chapter 8. We show that an Arrhenius-like formula[6] is in fact a reaction rate formula based on Thomson’s ionization theory[12]. Therefore Arrhenius’ bimolecular reaction rate theory[2, 13] and Thomson’s ionization theory[12] are unified as one theory. The exponential part of the Arrhenius formula ...
... Chapter 8. We show that an Arrhenius-like formula[6] is in fact a reaction rate formula based on Thomson’s ionization theory[12]. Therefore Arrhenius’ bimolecular reaction rate theory[2, 13] and Thomson’s ionization theory[12] are unified as one theory. The exponential part of the Arrhenius formula ...
momentum - Mrs. Brenner`s Biology
... Determine the initial momentum, pi, before the crash. Determine the final momentum, pf, after the crash. Apply the impulse-momentum theorem to obtain the force needed to stop the vehicle. Step 3: Evaluate the Answer ...
... Determine the initial momentum, pi, before the crash. Determine the final momentum, pf, after the crash. Apply the impulse-momentum theorem to obtain the force needed to stop the vehicle. Step 3: Evaluate the Answer ...
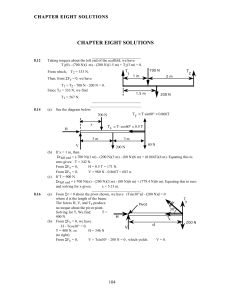
chapter eight solutions - Jay Mathy Science Wiki
... τapplied + τfriction = Iα1 with τapplied + τfriction = 36 N m. Now in six seconds, ω changes from 0 to 10 rad/s. Using ω = ω0 + α1t, we have 10 rad/s = 0 + α1(6 s), giving α1 = 1.67 rad/s2. Then, 36 N m= (1.67 rad/s2)I, or I = 21.6 kg m2. When the applied torque is removed, we have τfriction = Iα2. ...
... τapplied + τfriction = Iα1 with τapplied + τfriction = 36 N m. Now in six seconds, ω changes from 0 to 10 rad/s. Using ω = ω0 + α1t, we have 10 rad/s = 0 + α1(6 s), giving α1 = 1.67 rad/s2. Then, 36 N m= (1.67 rad/s2)I, or I = 21.6 kg m2. When the applied torque is removed, we have τfriction = Iα2. ...
FREE Sample Here
... Full file at http://TestbanksCafe.eu/Test-Bank-for-PHYSICS-1st-Edition-Ostdiek ...
... Full file at http://TestbanksCafe.eu/Test-Bank-for-PHYSICS-1st-Edition-Ostdiek ...
Momentum and Its Conservation
... The final momentum, pf, is zero. The initial momentum, pi, is the same with or without an air bag. Thus, the impulse, FΔt, also is the same. ...
... The final momentum, pf, is zero. The initial momentum, pi, is the same with or without an air bag. Thus, the impulse, FΔt, also is the same. ...
Momentum and Its Conservation
... The final momentum, pf, is zero. The initial momentum, pi, is the same with or without an air bag. Thus, the impulse, FΔt, also is the same. ...
... The final momentum, pf, is zero. The initial momentum, pi, is the same with or without an air bag. Thus, the impulse, FΔt, also is the same. ...