Impulse and Collisions
... A net force of 30 newtons is applied to a 10 kilogram cart that is already moving at 1 meter per second. The final speed of the cart was 2 meters per second. For how long was the force applied? ...
... A net force of 30 newtons is applied to a 10 kilogram cart that is already moving at 1 meter per second. The final speed of the cart was 2 meters per second. For how long was the force applied? ...
Sample
... acceleration. The magnitude of the force that the cart exerts on the horse A) is zero newtons. B) equal to the magnitude of . C) less than the magnitude of . D) greater than the magnitude of . E) cannot be determined without knowing the mass of the horse. Answer: B Var: 1 24) An object of weight W i ...
... acceleration. The magnitude of the force that the cart exerts on the horse A) is zero newtons. B) equal to the magnitude of . C) less than the magnitude of . D) greater than the magnitude of . E) cannot be determined without knowing the mass of the horse. Answer: B Var: 1 24) An object of weight W i ...
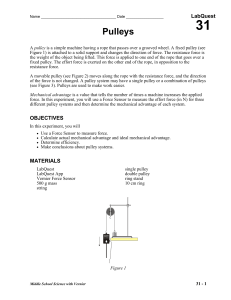
31 Pulleys
... 1. Set the range switch on the Force Sensor to 10 N. Connect the Force Sensor to LabQuest. Choose New from the File menu. If you have an older sensor that does not auto-ID, manually set up the sensor. 2. Zero the Force Sensor with its hook pointing down. a. Hold the Force Sensor in a vertical positi ...
... 1. Set the range switch on the Force Sensor to 10 N. Connect the Force Sensor to LabQuest. Choose New from the File menu. If you have an older sensor that does not auto-ID, manually set up the sensor. 2. Zero the Force Sensor with its hook pointing down. a. Hold the Force Sensor in a vertical positi ...
Motion
... • Once the scales for each axis are in place, the data points can be plotted. • After plotting the data points, draw a line connecting the points. ...
... • Once the scales for each axis are in place, the data points can be plotted. • After plotting the data points, draw a line connecting the points. ...
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS 2008 B.A./B.Sc.
... are linear dependent iff one is scalar multiple of other. Every super set of linearly dependent set of vectors is linearly dependent. The set of non-zero vectors are linearly iff one of them is scalar combination of others. ...
... are linear dependent iff one is scalar multiple of other. Every super set of linearly dependent set of vectors is linearly dependent. The set of non-zero vectors are linearly iff one of them is scalar combination of others. ...
FE5
... may be considered immovable so that all forces acting on it do no work. In any small region near the Earth's surface it is possible to choose any horizontal level and say that the system has zero PE when the object is on that level. If the object is at height h above this horizontal level the gravit ...
... may be considered immovable so that all forces acting on it do no work. In any small region near the Earth's surface it is possible to choose any horizontal level and say that the system has zero PE when the object is on that level. If the object is at height h above this horizontal level the gravit ...
Newton`s Laws
... which several objects within the system experience non-equal accelerations, and, with slight modification, situations in which some of the forces involved are velocity dependent. b.) The second approach is a simplified version of the first. When applicable, it makes the evaluation of N.S.L. problems ...
... which several objects within the system experience non-equal accelerations, and, with slight modification, situations in which some of the forces involved are velocity dependent. b.) The second approach is a simplified version of the first. When applicable, it makes the evaluation of N.S.L. problems ...
2015 Spring - Jonathan Whitmore
... A rocket with initial mass m0 (mass of the rocket plus its fuel) initially has velocity v0 = 0, in empty space. It then starts to expel fuel with (a constant) velocity vex relative to the rocket. (a) Write, and solve, the equation relating the rocket’s velocity v to its mass m at later times. Use no ...
... A rocket with initial mass m0 (mass of the rocket plus its fuel) initially has velocity v0 = 0, in empty space. It then starts to expel fuel with (a constant) velocity vex relative to the rocket. (a) Write, and solve, the equation relating the rocket’s velocity v to its mass m at later times. Use no ...
New Phenomena: Recent Results and Prospects from the Fermilab
... – Math, Torque, Angular Momentum, Energy again, but more sophisticated – The material will not be on the 3rd exam, but will help with the exam. It will all be on the ...
... – Math, Torque, Angular Momentum, Energy again, but more sophisticated – The material will not be on the 3rd exam, but will help with the exam. It will all be on the ...
SPH4U: Forces
... A force diagram uses our understanding of the interactions to construct a picture of the forces acting on a system. When you construct a force diagram: Identify the object or objects of interest – we will call these objects the system. Objects outside the system are parts of the environment. Rep ...
... A force diagram uses our understanding of the interactions to construct a picture of the forces acting on a system. When you construct a force diagram: Identify the object or objects of interest – we will call these objects the system. Objects outside the system are parts of the environment. Rep ...
Chapter 6 - AstroStop
... Collision between two objects. One not at rest initially has twice the mass. ...
... Collision between two objects. One not at rest initially has twice the mass. ...
Chapter 12
... It states that the translational acceleration of the object’s center of mass must be zero. This applies when viewed from an inertial reference frame. ...
... It states that the translational acceleration of the object’s center of mass must be zero. This applies when viewed from an inertial reference frame. ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.