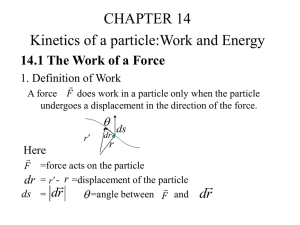
14.1 The Work of a Force
... =resultant internal force on ith particle Since work and energy are scalars both work and kinetic energy applied to each particle of the system may be added together algebraically. ...
... =resultant internal force on ith particle Since work and energy are scalars both work and kinetic energy applied to each particle of the system may be added together algebraically. ...
Name: Date:______ Period:_____ Chapter 19 Honors Study Guide
... The starting point you use to describe the motion or the position of an object 2. What is acceleration? Negative acceleration? The measure of how quickly the velocity of an object changes; when an object’s initial velocity is greater than its final velocity 3. Define speed? The distance an object mo ...
... The starting point you use to describe the motion or the position of an object 2. What is acceleration? Negative acceleration? The measure of how quickly the velocity of an object changes; when an object’s initial velocity is greater than its final velocity 3. Define speed? The distance an object mo ...
PES 1120 Spring 2014, Spendier Lecture 2/Page 1 Lecture
... 1) Showed the electric discharge from Van de Graff generator to a nearby grounded rod 2) Showed the hair stands up like charges repel! 3) Laid a stack of aluminum pie plates on the generator and turn it on. The plates will rose off one at a time by electrostatic repulsion as if they were an armada ...
... 1) Showed the electric discharge from Van de Graff generator to a nearby grounded rod 2) Showed the hair stands up like charges repel! 3) Laid a stack of aluminum pie plates on the generator and turn it on. The plates will rose off one at a time by electrostatic repulsion as if they were an armada ...
Chapter 3 - Department Of Computer Science
... The acceleration produced by an unbalance force acting on an object (or mass) is directly proportional to the magnitude of the force (a ∞ F) and in the direction of the force The acceleration of an object being acted on by an unbalance force is inversely proportional to the mass of the object (a ∞ ...
... The acceleration produced by an unbalance force acting on an object (or mass) is directly proportional to the magnitude of the force (a ∞ F) and in the direction of the force The acceleration of an object being acted on by an unbalance force is inversely proportional to the mass of the object (a ∞ ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... 3 lecture hours per week ...
... 3 lecture hours per week ...
Physics Final Exam Review Packet
... Will all objects released from rest fall at the same rate? Does air resistance make any difference? ...
... Will all objects released from rest fall at the same rate? Does air resistance make any difference? ...
The Falling Chain: - College of the Redwoods
... •The impulse force(momentum) of each link as it is stopped by the link above it (F1), and •the weight force of the links already hanging from the hook(F2). The total force (FT) exerted on the sensor is: ...
... •The impulse force(momentum) of each link as it is stopped by the link above it (F1), and •the weight force of the links already hanging from the hook(F2). The total force (FT) exerted on the sensor is: ...
Chapter 8 Practice Test Name 1. A 30 kg object is set into orbit 7.5 x
... 3. A six kg object is placed .08 meters away from a second object and experiences a .00054 N force of attraction towards the second object. What is the mass of the second object? 4. a. What gravitational attractive force does Jupiter experience towards the Sun? Mass of the Sun = 1.99 x 1030 kg Mass ...
... 3. A six kg object is placed .08 meters away from a second object and experiences a .00054 N force of attraction towards the second object. What is the mass of the second object? 4. a. What gravitational attractive force does Jupiter experience towards the Sun? Mass of the Sun = 1.99 x 1030 kg Mass ...
$doc.title
... a) momentum is conserved b) that the momentum of an object depended linearly on the velocity c) the potential energy of a system always equalled the kinetic energy d) mass is conserved in chemical reactio ...
... a) momentum is conserved b) that the momentum of an object depended linearly on the velocity c) the potential energy of a system always equalled the kinetic energy d) mass is conserved in chemical reactio ...
Physics_100_chapt_3
... Newton’3rd Law: action-reaction Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal in magnitude but opposite in direction force on the first. ...
... Newton’3rd Law: action-reaction Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal in magnitude but opposite in direction force on the first. ...
File
... c. a car moves slower and slower d. a basketball stops rolling 11. A person travels a distance of 400 miles in two hours. What is the person’s speed? Remember that ...
... c. a car moves slower and slower d. a basketball stops rolling 11. A person travels a distance of 400 miles in two hours. What is the person’s speed? Remember that ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.