Simulation of Charged Particle Orbits in Fusion
... 90◦ , and allows us to determine |C| by adding the squares of vy and vz . If we define the perpendicular velocity to be v⊥ ≡ (vy2 + vz2 )1/2 , we get ...
... 90◦ , and allows us to determine |C| by adding the squares of vy and vz . If we define the perpendicular velocity to be v⊥ ≡ (vy2 + vz2 )1/2 , we get ...
FORCE and MOTION
... free fall accelerates. Every second something is in free fall, it accelerates by 9.8 meters per second. So if an object free falls for two seconds, it would be traveling at 19.6 meters per second. If a piece of paper and a marble are in free fall, they will fall at the same speed, so they should hit ...
... free fall accelerates. Every second something is in free fall, it accelerates by 9.8 meters per second. So if an object free falls for two seconds, it would be traveling at 19.6 meters per second. If a piece of paper and a marble are in free fall, they will fall at the same speed, so they should hit ...
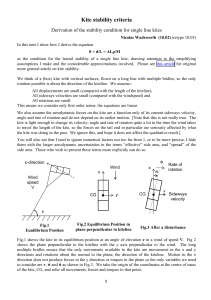
Kite stability criteria
... turn it towards its original direction. The equations of motion to be solved are now (1), (2A) and (3) and the analytical solution is even more complicated. Basically the solution is a damped (or overdamped) oscillatory approach to the equilibrium state if the kite is stable and an oscillation of in ...
... turn it towards its original direction. The equations of motion to be solved are now (1), (2A) and (3) and the analytical solution is even more complicated. Basically the solution is a damped (or overdamped) oscillatory approach to the equilibrium state if the kite is stable and an oscillation of in ...
MasteringPhysics: Assignmen
... equation states that the work done on a unit volume of fluid by the surrounding fluid is equal to the sum of the change in potential and kinetic energy per unit volume that occurs during the flow. This is nothing more than the statement of conservation of mechanical energy for an ideal fluid flowing ...
... equation states that the work done on a unit volume of fluid by the surrounding fluid is equal to the sum of the change in potential and kinetic energy per unit volume that occurs during the flow. This is nothing more than the statement of conservation of mechanical energy for an ideal fluid flowing ...
Chapter 8 Oscillations
... the right as shown above right and released from rest so that it swings as a simple pendulum with small amplitude. Assume that both spheres undergo simple harmonic motion 11. Which of the following is true for both spheres? (A) The maximum kinetic energy is attained as the sphere passes through its ...
... the right as shown above right and released from rest so that it swings as a simple pendulum with small amplitude. Assume that both spheres undergo simple harmonic motion 11. Which of the following is true for both spheres? (A) The maximum kinetic energy is attained as the sphere passes through its ...
Slides for Motion and Forces
... Static friction acts on objects that are not moving. Have you ever wondered why it is so hard to start moving a heavy object like a dresser or couch, but then once it starts moving it is easier? That is because you have to overcome the force of static friction! Static friction holds the couch in pla ...
... Static friction acts on objects that are not moving. Have you ever wondered why it is so hard to start moving a heavy object like a dresser or couch, but then once it starts moving it is easier? That is because you have to overcome the force of static friction! Static friction holds the couch in pla ...
Interim Assessment Sample Question
... Develop student’s ability to solve for force or acceleration through Guided Practice using real world problems, for example, a 1500 kg car accelerates at 5 m/s2, what is the force pushing the car forward? (3B) ...
... Develop student’s ability to solve for force or acceleration through Guided Practice using real world problems, for example, a 1500 kg car accelerates at 5 m/s2, what is the force pushing the car forward? (3B) ...
FREE Sample Here
... b. (ii) and (iii) c. (iii) and (iv) d. Choose this answer if all the statements are true. ANS: D ...
... b. (ii) and (iii) c. (iii) and (iv) d. Choose this answer if all the statements are true. ANS: D ...
Calculation of an Atomically Modulated Friction Force in Atomic-Force Microscopy.
... on B. In that case, C is given by the elastic constants of A at the interface (7], hence cannot be changed independently. Since c is rather large in many materials, zero friction should be observed for moderate applied loads in the absence of wear and plastic deformations. For a multiatom «tip» whic ...
... on B. In that case, C is given by the elastic constants of A at the interface (7], hence cannot be changed independently. Since c is rather large in many materials, zero friction should be observed for moderate applied loads in the absence of wear and plastic deformations. For a multiatom «tip» whic ...
PHYS 1111 Introductory Physics – Mechanics, Waves
... re-taking it at a later time. Tutors are available either for free through the UGA Tutoring Program at Tutors: Milledge Hall, http://tutor.uga.edu, or for pay through the Physics Department, http://www.physast.uga.edu/tutors. NOTE: In physics, learning can be frustrating and nonlinear. Often you hav ...
... re-taking it at a later time. Tutors are available either for free through the UGA Tutoring Program at Tutors: Milledge Hall, http://tutor.uga.edu, or for pay through the Physics Department, http://www.physast.uga.edu/tutors. NOTE: In physics, learning can be frustrating and nonlinear. Often you hav ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.