Newton`s Laws - Petoskey Public Schools
... Newton’s three laws describe how things move and how this motion can be changed by other forces/objects Newton’s laws lead to the formulas that lets us express motion with math ...
... Newton’s three laws describe how things move and how this motion can be changed by other forces/objects Newton’s laws lead to the formulas that lets us express motion with math ...
10 Motion Trial Test
... What is the potential energy of the mass before it is dropped? Assuming all the potential energy of the b object is converted to kinetic energy, what is the speed of the ball as it reaches the ground? To what form or forms of energy is the c kinetic energy of the ball converted after ...
... What is the potential energy of the mass before it is dropped? Assuming all the potential energy of the b object is converted to kinetic energy, what is the speed of the ball as it reaches the ground? To what form or forms of energy is the c kinetic energy of the ball converted after ...
unit: describing motion
... 23. Define acceleration. What is the relationship between velocity and acceleration? 24. How do you calculate average acceleration? Be able to use this formula to solve problems given two of the variables. 25. Define centripetal acceleration. 26. Be able to interpret speed, velocity, distance, and a ...
... 23. Define acceleration. What is the relationship between velocity and acceleration? 24. How do you calculate average acceleration? Be able to use this formula to solve problems given two of the variables. 25. Define centripetal acceleration. 26. Be able to interpret speed, velocity, distance, and a ...
File - Physics LEAP
... There is either a change in the magnitude of the velocity a change in the direction of the velocity or both. ...
... There is either a change in the magnitude of the velocity a change in the direction of the velocity or both. ...
Newton`s Laws PowerPoint
... resist a change in its motion In order to overcome an object’s inertia, a force must be exerted on the object. Greater mass=greater inertia Newton’s 1st Law is also called the Law of Inertia Inertia ...
... resist a change in its motion In order to overcome an object’s inertia, a force must be exerted on the object. Greater mass=greater inertia Newton’s 1st Law is also called the Law of Inertia Inertia ...
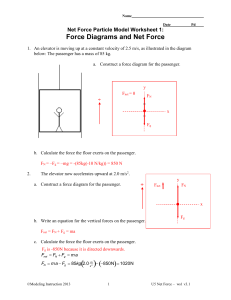
Force Diagrams and Net Force Key
... a. Which system has the greatest net force? Explain how you know. System C has the greatest net force. FN and Fg cancel out for the block moving horizontally. All of the "FT"s cancel out inside the systems because each string is pulling equally in both directions. The net force on each system is the ...
... a. Which system has the greatest net force? Explain how you know. System C has the greatest net force. FN and Fg cancel out for the block moving horizontally. All of the "FT"s cancel out inside the systems because each string is pulling equally in both directions. The net force on each system is the ...
Newton`sLaws - Redwood High School
... and of the need to have something better than a vacuum against which to react - to say that would be absurd. Of course, he only seems to lack the knowledge ladled out daily in high schools. The New York Times, January 13, 1920 Further investigation and experimentation have confirmed the findings of ...
... and of the need to have something better than a vacuum against which to react - to say that would be absurd. Of course, he only seems to lack the knowledge ladled out daily in high schools. The New York Times, January 13, 1920 Further investigation and experimentation have confirmed the findings of ...
Example - mrdsample
... on the object (slope of U(x) = 0) it must either possess only potential energy and be at rest or, it also possesses kinetic energy and must be moving at a constant velocity. x4 is a position of unstable equilibrium. If the object is displaced ever so slightly from this position, the internal forces ...
... on the object (slope of U(x) = 0) it must either possess only potential energy and be at rest or, it also possesses kinetic energy and must be moving at a constant velocity. x4 is a position of unstable equilibrium. If the object is displaced ever so slightly from this position, the internal forces ...
Monday, June 21, 2004 - UTA High Energy Physics page.
... People have been very curious about the stars in the sky, making observations for a long time. But the data people collected have not been explained until Newton has discovered the law of gravitation. Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proporti ...
... People have been very curious about the stars in the sky, making observations for a long time. But the data people collected have not been explained until Newton has discovered the law of gravitation. Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proporti ...
Answer Key Physics Study Guide A
... Know how color affects heat absorption Dark colors absorb more heat than light colors g. Analyze and measure power. P=W/t; the faster something does work, the more powerful it is. ...
... Know how color affects heat absorption Dark colors absorb more heat than light colors g. Analyze and measure power. P=W/t; the faster something does work, the more powerful it is. ...
Newton`s 2nd Law of Motion
... saying. You will then have written Newton's Second Law. The expression that you just wrote can be rewritten with an "equals to" sign. Because the expression is a proportion, all it needs is a slope. Normally we'd use the letter "m", however that one is already used--in this case it's m for mass. Let ...
... saying. You will then have written Newton's Second Law. The expression that you just wrote can be rewritten with an "equals to" sign. Because the expression is a proportion, all it needs is a slope. Normally we'd use the letter "m", however that one is already used--in this case it's m for mass. Let ...
Force and Motion Before Newton
... • Newton’s 2nd Law: When a net force (Fnet) acts on an object, it produces a change in the momentum of the object in the direction in which the force acts – A change in momentum could be a change in mass and/or velocity – Usually, mass remains constant, in which case: Fnet ma – An object accelerat ...
... • Newton’s 2nd Law: When a net force (Fnet) acts on an object, it produces a change in the momentum of the object in the direction in which the force acts – A change in momentum could be a change in mass and/or velocity – Usually, mass remains constant, in which case: Fnet ma – An object accelerat ...
Gravity_Planets_extended_ - Atlanta International School Moodle
... Energy Changes in a Gravitational Field • A mass placed in a gravitational field experiences a force. If no other force acts, the total energy will remain constant but energy might be converted from g.p.e. to k.e. • If the mass of the planet is M and the radius of the orbit of the satellite is r, t ...
... Energy Changes in a Gravitational Field • A mass placed in a gravitational field experiences a force. If no other force acts, the total energy will remain constant but energy might be converted from g.p.e. to k.e. • If the mass of the planet is M and the radius of the orbit of the satellite is r, t ...
reviewmt1
... through a distance d along the direction of the force, an amount of WORK Fd is done by the first object on the second and an amount of energy Fd is transferred from the first object to the second. Newton’s third law says that when one object exerts a force F on a second object, then the second objec ...
... through a distance d along the direction of the force, an amount of WORK Fd is done by the first object on the second and an amount of energy Fd is transferred from the first object to the second. Newton’s third law says that when one object exerts a force F on a second object, then the second objec ...
Phy 211: General Physics I
... The total linear momentum of a system will remain constant when no external net force acts upon the system, or (p1 + p2 + ...)before collision= (p1 + p2 + ...)after collision • Note: Individual momentum vectors may change due to collisions, etc. but the linear momentum for the system remains constan ...
... The total linear momentum of a system will remain constant when no external net force acts upon the system, or (p1 + p2 + ...)before collision= (p1 + p2 + ...)after collision • Note: Individual momentum vectors may change due to collisions, etc. but the linear momentum for the system remains constan ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion - pams
... Newton’s First Law: Objects in motion tend to stay in motion and objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s Second Law: Force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma). Newton’s Third Law: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. ...
... Newton’s First Law: Objects in motion tend to stay in motion and objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s Second Law: Force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma). Newton’s Third Law: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.