The Laws (of motion) - stupidchicken comic
... Consider two isolated particles m1 and m2 before and after they collide. Before the collision, the velocities of the two particles are v1i and v2i; after collision, the velocities are v1f and v2f. ...
... Consider two isolated particles m1 and m2 before and after they collide. Before the collision, the velocities of the two particles are v1i and v2i; after collision, the velocities are v1f and v2f. ...
Slide 1
... A 650-kg elevator starts from rest. It moves upward for 3.00 s with constant acceleration until it reaches its cruising speed of 1.75 in/s. (a) What is the average power of the elevator motor during this time interval? (b) How does this power compare with the motor power when the elevator moves at i ...
... A 650-kg elevator starts from rest. It moves upward for 3.00 s with constant acceleration until it reaches its cruising speed of 1.75 in/s. (a) What is the average power of the elevator motor during this time interval? (b) How does this power compare with the motor power when the elevator moves at i ...
Newtons Laws 2014 ppt
... A hockey player hits a hockey puck across the ice. 10 seconds after he hits it, it is still moving down the ice. Is the puck in equilibrium? Yes! Even though it is still moving, there is no net force being exerted on it, so it is moving at a constant velocity and only inertia is allowing it to ...
... A hockey player hits a hockey puck across the ice. 10 seconds after he hits it, it is still moving down the ice. Is the puck in equilibrium? Yes! Even though it is still moving, there is no net force being exerted on it, so it is moving at a constant velocity and only inertia is allowing it to ...
2003 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 14
... • Principle of work and energy can be applied to the entire system by adding the kinetic energies of all particles and considering the work done by all external and internal forces. ...
... • Principle of work and energy can be applied to the entire system by adding the kinetic energies of all particles and considering the work done by all external and internal forces. ...
Force and Newton` s Laws Study Guide
... A characteristic of a moving object that is related to the mass and velocity of the object. 32. When a rocket is launched, are the forces acting on it balanced or unbalanced? How do you know? The forces are unbalanced. I know because the rocket is accelerating and increasing in altitude. If the forc ...
... A characteristic of a moving object that is related to the mass and velocity of the object. 32. When a rocket is launched, are the forces acting on it balanced or unbalanced? How do you know? The forces are unbalanced. I know because the rocket is accelerating and increasing in altitude. If the forc ...
Microsoft Powerpoint
... Like the normal force, the friction and tension forces are all manifestations of the electromagnetic force They all are the result of attractive (and repulsive) forces of atoms and molecules within an object (normal and tension) or at the interface of two objects Applications of Newton’s 2nd La ...
... Like the normal force, the friction and tension forces are all manifestations of the electromagnetic force They all are the result of attractive (and repulsive) forces of atoms and molecules within an object (normal and tension) or at the interface of two objects Applications of Newton’s 2nd La ...
experimenting with forces
... you can feel the heat caused by friction. The warmth you feel when you rub your hands together is caused by friction. Only when an object is moving through empty space will it continue to move without slowing down. That is why Earth never stops circling around the Sun. Earth doesn’t experience any f ...
... you can feel the heat caused by friction. The warmth you feel when you rub your hands together is caused by friction. Only when an object is moving through empty space will it continue to move without slowing down. That is why Earth never stops circling around the Sun. Earth doesn’t experience any f ...
Practice Clicker Questions: Momentum, Impulse, Work and Energy
... Practice Problem Set 3 Momentum Impulse Energy ...
... Practice Problem Set 3 Momentum Impulse Energy ...
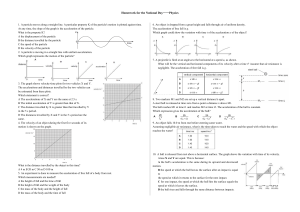
Homework for the National Day——Physics 1. A particle moves
... The speed v of the trolley is measured using a speed sensor for different values of the time t that the trolley has moved from rest down the slope. Fig. 2.2 shows the variation with t of v. ...
... The speed v of the trolley is measured using a speed sensor for different values of the time t that the trolley has moved from rest down the slope. Fig. 2.2 shows the variation with t of v. ...
work and energy
... at the bottom of a 40m high hill assuming zero speed at the top of the hill? PE lost = KE gained mgh = ½ mv2 2gh = v2 v = (2gh)1/2 v = (2 x 10 x 40)1/2 = (800)1/2 ...
... at the bottom of a 40m high hill assuming zero speed at the top of the hill? PE lost = KE gained mgh = ½ mv2 2gh = v2 v = (2gh)1/2 v = (2 x 10 x 40)1/2 = (800)1/2 ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.