Chapter9_4-7_FA05
... A rocket engine emits a certain mass of fuel per unit time. This results in a force, which is called Thrust. ...
... A rocket engine emits a certain mass of fuel per unit time. This results in a force, which is called Thrust. ...
ap physics b
... straight line unless acted upon by a force. Forces that change the direction of a body’s velocity vector (versus changing the magnitude of the body’s velocity vector) are called center seeking forces or centripetal forces. A centripetal force is NOT a new kind of force, but is any naturally occurrin ...
... straight line unless acted upon by a force. Forces that change the direction of a body’s velocity vector (versus changing the magnitude of the body’s velocity vector) are called center seeking forces or centripetal forces. A centripetal force is NOT a new kind of force, but is any naturally occurrin ...
AP Momentum
... We are yet to make a distinction between a rhino moving at 5m/s and a hummingbird moving at 5m/s. Thus far, how have we handled forces that are only briefly applied such as collisions? (we pretended that doesn’t happen) ...
... We are yet to make a distinction between a rhino moving at 5m/s and a hummingbird moving at 5m/s. Thus far, how have we handled forces that are only briefly applied such as collisions? (we pretended that doesn’t happen) ...
Gravitational Fields (AIS) - Atlanta International School Moodle
... • Compared the fall of an apple with the fall of the moon. • The moon falls in the sense that it falls away from the straight line it would follow if there were no forces acting on it. • Therefore, the motion of the moon and the apple were the same motion. • Showed, everything in the universe follow ...
... • Compared the fall of an apple with the fall of the moon. • The moon falls in the sense that it falls away from the straight line it would follow if there were no forces acting on it. • Therefore, the motion of the moon and the apple were the same motion. • Showed, everything in the universe follow ...
m 1
... mathematician and geographer. He codified the Greek geocentric view of the universe, and rationalized the apparent motions of the planets as they were known in his time. Ptolemy synthesized and extended Hipparchus's system of epicycles and eccentric circles to explain his geocentric theory of the so ...
... mathematician and geographer. He codified the Greek geocentric view of the universe, and rationalized the apparent motions of the planets as they were known in his time. Ptolemy synthesized and extended Hipparchus's system of epicycles and eccentric circles to explain his geocentric theory of the so ...
momentum - BilaksPhysiks
... We are yet to make a distinction between a rhino moving at 5m/s and a hummingbird moving at 5m/s. Thus far, how have we handled forces that are only briefly applied such as collisions? (we pretended that doesn’t happen) ...
... We are yet to make a distinction between a rhino moving at 5m/s and a hummingbird moving at 5m/s. Thus far, how have we handled forces that are only briefly applied such as collisions? (we pretended that doesn’t happen) ...
PDF
... behavior of a system undergoing harmonic oscillation is essential in order to comprehend how the system will respond to more general types of excitation. Such harmonic oscillations may be in the form of free vibrations or by the action of an exciter force applied at some point of the system, as we s ...
... behavior of a system undergoing harmonic oscillation is essential in order to comprehend how the system will respond to more general types of excitation. Such harmonic oscillations may be in the form of free vibrations or by the action of an exciter force applied at some point of the system, as we s ...
Chapter 5-6
... 1. Walker3 5.P.045. [544707] Show Details In a tennis serve, a 0.070 kg ball can be accelerated from rest to 35 m/s over a distance of 0.70 m. Find the magnitude for the average force exerted by the racket on the ball during the serve. 61.3 N [Answer] Newton’s second law: F = m a To find F, we need ...
... 1. Walker3 5.P.045. [544707] Show Details In a tennis serve, a 0.070 kg ball can be accelerated from rest to 35 m/s over a distance of 0.70 m. Find the magnitude for the average force exerted by the racket on the ball during the serve. 61.3 N [Answer] Newton’s second law: F = m a To find F, we need ...
The answer is B. Newton`s 2 nd Law states that acceleration is
... acceleration? A. A car slowing from 20km/h to a stop in 10.0s. B. A car sitting still in the driveway. C. A car traveling at a constant speed of 20km/h while going around a curve. D. A car traveling at a constant speed of 100km/h on a ...
... acceleration? A. A car slowing from 20km/h to a stop in 10.0s. B. A car sitting still in the driveway. C. A car traveling at a constant speed of 20km/h while going around a curve. D. A car traveling at a constant speed of 100km/h on a ...
chapter4
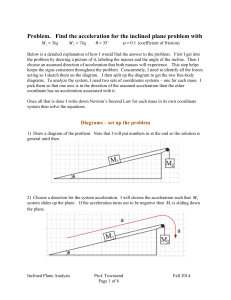
... separate free body diagrams for each object Choose a convenient coordinate system for each object The x- and y-components should be taken from the vector equation and written separately ...
... separate free body diagrams for each object Choose a convenient coordinate system for each object The x- and y-components should be taken from the vector equation and written separately ...
04_Force and Motion
... 4.5 More on Newton’s Laws: FreeBody Diagrams and Translational Equilibrium If an object is to be in translational equilibrium, there must be no net force on it. This translates into three separate requirements—that there be no force in the x-direction, the y-direction, or the z-direction. ...
... 4.5 More on Newton’s Laws: FreeBody Diagrams and Translational Equilibrium If an object is to be in translational equilibrium, there must be no net force on it. This translates into three separate requirements—that there be no force in the x-direction, the y-direction, or the z-direction. ...
Lecture 15
... 9. The period of free undamped oscillations of a mass on a spring is / 4 seconds. If the spring constant is 16 lb/ft, what is the numerical value of the weight? 10. A 4-lb weight is attached to a spring, whose spring constant is 16 lb/ft . What is period of simple harmonic motion? 11. A 24-lb weig ...
... 9. The period of free undamped oscillations of a mass on a spring is / 4 seconds. If the spring constant is 16 lb/ft, what is the numerical value of the weight? 10. A 4-lb weight is attached to a spring, whose spring constant is 16 lb/ft . What is period of simple harmonic motion? 11. A 24-lb weig ...
Student Exam Review
... a. net force, mass b. friction, speed c. inertia, gravity d. net force, inertia 93. The mass of an object times the acceleration due to gravity results in a. force b. friction c. speed d. weight 94. The four universal forces are electromagnetic force, strong nuclear force, weak nuclear force, and a. ...
... a. net force, mass b. friction, speed c. inertia, gravity d. net force, inertia 93. The mass of an object times the acceleration due to gravity results in a. force b. friction c. speed d. weight 94. The four universal forces are electromagnetic force, strong nuclear force, weak nuclear force, and a. ...
Chapter 7
... discover and describe total internal reflection. explain that tides are caused by the Moon. He tried to use stellar parallax caused by the Earth's orbit to measure the distance to the stars; the same principle as depth perception. Today this branch of research is called astrometry. suggest that the ...
... discover and describe total internal reflection. explain that tides are caused by the Moon. He tried to use stellar parallax caused by the Earth's orbit to measure the distance to the stars; the same principle as depth perception. Today this branch of research is called astrometry. suggest that the ...
Motion with a constant speed - St. Thomas the Apostle School
... • Geological evidence has shown that the Earth’s continents have moved slowly over time. • Pangea began to separate into smaller pieces . The continents are still moving today! • The Earth’s crust moves over putty like interior ...
... • Geological evidence has shown that the Earth’s continents have moved slowly over time. • Pangea began to separate into smaller pieces . The continents are still moving today! • The Earth’s crust moves over putty like interior ...
Physics218_lecture_006
... – Old: What acceleration do you need to go from 0 to 60mi/hr in 6 sec? – New: How much force does your car engine need to exert? • Use all the kinematics, vectors and calculus from ...
... – Old: What acceleration do you need to go from 0 to 60mi/hr in 6 sec? – New: How much force does your car engine need to exert? • Use all the kinematics, vectors and calculus from ...
Newton`s Laws - Ccphysics.us
... 5. Two ropes are attached to a 40-kg object. The first rope applies a force of 25 N and the second, 40 N. If the two ropes are perpendicular to each other, what is the resultant acceleration of the object? a. 1.2 m/s2 c. 25 m/s2 b. 3.0 m/s2 d. 47 m/s2 ...
... 5. Two ropes are attached to a 40-kg object. The first rope applies a force of 25 N and the second, 40 N. If the two ropes are perpendicular to each other, what is the resultant acceleration of the object? a. 1.2 m/s2 c. 25 m/s2 b. 3.0 m/s2 d. 47 m/s2 ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.