Forces Worksheet
... 2. What are unbalanced forces and give an example? 3. What are balanced forces and give an example? Calculate the net force on the object described in each situation. Draw a free body diagram for each and show the directions of forces as well as the total net force and direction of net force. Exampl ...
... 2. What are unbalanced forces and give an example? 3. What are balanced forces and give an example? Calculate the net force on the object described in each situation. Draw a free body diagram for each and show the directions of forces as well as the total net force and direction of net force. Exampl ...
Momentum_additional_Notes
... momentum of the first object is equal to and opposite to the change in momentum of the second object. Thus in all interactions between two isolated objects, momentum is conserved. ...
... momentum of the first object is equal to and opposite to the change in momentum of the second object. Thus in all interactions between two isolated objects, momentum is conserved. ...
Developer Notes - University of Hawaii System
... pushing up. Air might be blowing on the ball, but friction is pushing back. The ball is in equilibrium. In mathematical notation: Fnet = 0, the net force is zero, or ∑F = 0, the sum of forces is zero. If the forces on the ball didn't equal out, then the ball would start moving; it would accelerate ( ...
... pushing up. Air might be blowing on the ball, but friction is pushing back. The ball is in equilibrium. In mathematical notation: Fnet = 0, the net force is zero, or ∑F = 0, the sum of forces is zero. If the forces on the ball didn't equal out, then the ball would start moving; it would accelerate ( ...
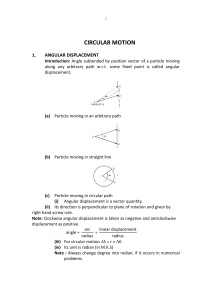
CIRCULAR MOTION
... Because Fc is always perpendicular to velocity or displacement, hence the work done by this force will always be zero. (ii) Circular motion in horizontal plane is usually uniform circular motion. (iii) There is an important difference between the projectile motion and circular motion. In projectile ...
... Because Fc is always perpendicular to velocity or displacement, hence the work done by this force will always be zero. (ii) Circular motion in horizontal plane is usually uniform circular motion. (iii) There is an important difference between the projectile motion and circular motion. In projectile ...
Worked solutions Chapter 2: Collisions and
... The dummy in car B stops in a shorter time interval and so would experience a greater stopping force. Car A: Ft = mv F A × 0.40 = 100 × –20 and F A = –5.0 103 N F B × 0.10 = 100 × –20 F B = –2.0 104 N Crumple zones reduce the magnitudes of the forces that act on the occupants of a car during ...
... The dummy in car B stops in a shorter time interval and so would experience a greater stopping force. Car A: Ft = mv F A × 0.40 = 100 × –20 and F A = –5.0 103 N F B × 0.10 = 100 × –20 F B = –2.0 104 N Crumple zones reduce the magnitudes of the forces that act on the occupants of a car during ...
The Coriolis Force in Maxwell`s Equations
... the electric sea is insignificant, and so we need to establish an alternative physical basis for ascertaining rotation. We find this in the linear polarization of the electric sea which is induced by the gravitational field. This radial effect allows us to segregate radial motion from transverse mot ...
... the electric sea is insignificant, and so we need to establish an alternative physical basis for ascertaining rotation. We find this in the linear polarization of the electric sea which is induced by the gravitational field. This radial effect allows us to segregate radial motion from transverse mot ...
acceleration ~ net force
... • Recall (Ch. 4) that in free fall, gravity is the only thing that affects a falling object. • Galileo showed that falling objects, regardless of their mass, accelerate equally. ...
... • Recall (Ch. 4) that in free fall, gravity is the only thing that affects a falling object. • Galileo showed that falling objects, regardless of their mass, accelerate equally. ...
Atwood Machine (AM)
... 3. If our data is described by “A Simplified Theory” (neglecting pulley inertia and friction), what should the slope of the plot be equal to? [1 pt] a. Fnet b. m1 – m2 c. m1 + m2 d. m1 + m2 + mp 4. If our data is described by “A Simplified Theory” (neglecting pulley inertia and friction), what shoul ...
... 3. If our data is described by “A Simplified Theory” (neglecting pulley inertia and friction), what should the slope of the plot be equal to? [1 pt] a. Fnet b. m1 – m2 c. m1 + m2 d. m1 + m2 + mp 4. If our data is described by “A Simplified Theory” (neglecting pulley inertia and friction), what shoul ...
Newton`s Wagon - Newton`s Laws
... straight line as long as it can, until air drag, rolling resistance, and gravity, all of which cause it to stop. If this seems overly simplistic, just stick with me for a minute. The reason we study motion is to get a basic understanding of scientific principles. In this experiment, the ball want ...
... straight line as long as it can, until air drag, rolling resistance, and gravity, all of which cause it to stop. If this seems overly simplistic, just stick with me for a minute. The reason we study motion is to get a basic understanding of scientific principles. In this experiment, the ball want ...
doc - Stanford Earth Sciences
... In this equation S is the remote tensile stress pulling the joint open, a is the length, and b is the breadth of the joint. Analyze the dimensions on both sides of this equation for dimensional homogeneity and point out the inconsistency. 6) The relative displacement (slip) across some faults varies ...
... In this equation S is the remote tensile stress pulling the joint open, a is the length, and b is the breadth of the joint. Analyze the dimensions on both sides of this equation for dimensional homogeneity and point out the inconsistency. 6) The relative displacement (slip) across some faults varies ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.