Document
... Simultaneous solution of the equations leads to v0 0 and a 0.40 m s2 . We now have two ways to finish the problem. One is to compute force from F = ma and then obtain the work from Eq. 7-7. The other is to find K as a way of computing W (in accordance with Eq. 7-10). In this latter approach, we ...
... Simultaneous solution of the equations leads to v0 0 and a 0.40 m s2 . We now have two ways to finish the problem. One is to compute force from F = ma and then obtain the work from Eq. 7-7. The other is to find K as a way of computing W (in accordance with Eq. 7-10). In this latter approach, we ...
Positive linear span
... Definition: Force closure means that the set of possible wrenches exhausts all of wrench space. It follows from theorem ? that a frictionless force closure requires at least 7 contacts. Or, since planar wrench space is only three-dimensional, frictionless force closure in the plane requires at ...
... Definition: Force closure means that the set of possible wrenches exhausts all of wrench space. It follows from theorem ? that a frictionless force closure requires at least 7 contacts. Or, since planar wrench space is only three-dimensional, frictionless force closure in the plane requires at ...
AOSS 321, Fall 2006 Earth Systems Dynamics 10/9/2006
... • Consider a dynamics field experiment in which one student takes a position on a merry-goround and another student takes a position above the ground in an adjacent tree. • Merry-go-round is spinning, a ball is pushed • On the Merry-go-round: the ball is deflected from its path. This is due to the C ...
... • Consider a dynamics field experiment in which one student takes a position on a merry-goround and another student takes a position above the ground in an adjacent tree. • Merry-go-round is spinning, a ball is pushed • On the Merry-go-round: the ball is deflected from its path. This is due to the C ...
9A EXPERIMENT Rotational Motion 1
... magnitude of this acceleration is equal to the magnitude of the tangential acceleration of a point on the outside surface of the central pulley. 6. Have Excel calculate the radius of the central pulley using equation (4). In addition have Excel calculate the mean value and the standard deviation of ...
... magnitude of this acceleration is equal to the magnitude of the tangential acceleration of a point on the outside surface of the central pulley. 6. Have Excel calculate the radius of the central pulley using equation (4). In addition have Excel calculate the mean value and the standard deviation of ...
pages 251-300 - Light and Matter
... example 2 The motorcyclist in figure h is moving along an arc of a circle. It looks like he’s chosen to ride the slanted surface of the dirt at a place where it makes just the angle he wants, allowing him to get the force he needs on the tires as a normal force, without needing any frictional force. ...
... example 2 The motorcyclist in figure h is moving along an arc of a circle. It looks like he’s chosen to ride the slanted surface of the dirt at a place where it makes just the angle he wants, allowing him to get the force he needs on the tires as a normal force, without needing any frictional force. ...
Lab M08: A Study of Sliding Friction PH306 24/01/08
... Whenever one object is dragged across another, sliding (kinetic) friction acts on the surface of each object. The size of the sliding frictional force is determined by the characteristics of the two surfaces and the normal force each surface exerts on the other. The sliding frictional force on each ...
... Whenever one object is dragged across another, sliding (kinetic) friction acts on the surface of each object. The size of the sliding frictional force is determined by the characteristics of the two surfaces and the normal force each surface exerts on the other. The sliding frictional force on each ...
8.1 Energy in Deforming Materials
... The discussion above which concerned particle mechanics is now generalized to that of a deforming material. Any material consists of many molecules and particles, all interacting in some complex way. There will be a complex system of internal forces acting between the molecules, even when the materi ...
... The discussion above which concerned particle mechanics is now generalized to that of a deforming material. Any material consists of many molecules and particles, all interacting in some complex way. There will be a complex system of internal forces acting between the molecules, even when the materi ...
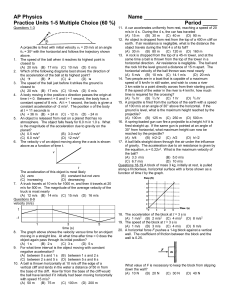
AP Physics
... m/s in 4 s. During the 4 s, the car has traveled (A) 15 m (B) 30 m (C) 40 m (D) 90 m 12. An object is dropped from rest from the top of a 400 m cliff on earth. If air resistance is negligible, what is the distance the object travels during the first 4 s of its fall? (A) 30 m (B) 80 m (C) 120 m (D) 1 ...
... m/s in 4 s. During the 4 s, the car has traveled (A) 15 m (B) 30 m (C) 40 m (D) 90 m 12. An object is dropped from rest from the top of a 400 m cliff on earth. If air resistance is negligible, what is the distance the object travels during the first 4 s of its fall? (A) 30 m (B) 80 m (C) 120 m (D) 1 ...
Chapter 4 PowerPoint
... If you drop a book, the gravitational force of Earth causes the book to accelerate, whether or not Earth is actually touching it. This is an example of a field force. Field forces are exerted without contact. Forces result from interactions; thus, each force has a specific and identifiable cause cal ...
... If you drop a book, the gravitational force of Earth causes the book to accelerate, whether or not Earth is actually touching it. This is an example of a field force. Field forces are exerted without contact. Forces result from interactions; thus, each force has a specific and identifiable cause cal ...
Physics - Study in Pakistan
... The study of physics relies on the understanding and application of a small number of basic laws and principles that govern the microscopic and macroscopic worlds. The study of physics provides students with an understanding of systems that is the basic of the development of technological applicatio ...
... The study of physics relies on the understanding and application of a small number of basic laws and principles that govern the microscopic and macroscopic worlds. The study of physics provides students with an understanding of systems that is the basic of the development of technological applicatio ...
2.Newtons_Laws
... • Suppose FNET is not zero. What will happen to the object? • The object will accelerate. • Which will accelerate more under the same FNET : – A heavy object or a light object? ...
... • Suppose FNET is not zero. What will happen to the object? • The object will accelerate. • Which will accelerate more under the same FNET : – A heavy object or a light object? ...
Physics of the tractor pull. How to use the tractor pull
... • 9.2.2.2.3 Demonstrate that whenever one object exerts force on another, a force equal in magnitude and opposite in direction is exerted by the second object back on the first object. • 9.2.3.2.2 Calculate and explain the energy, work and power involved in energy transfers in a mechanical system. • ...
... • 9.2.2.2.3 Demonstrate that whenever one object exerts force on another, a force equal in magnitude and opposite in direction is exerted by the second object back on the first object. • 9.2.3.2.2 Calculate and explain the energy, work and power involved in energy transfers in a mechanical system. • ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... Assuming identical friction, both engines do the same amount of work to get up the hill. Are the cars essentially the same ? NO. The Corvette can get up the hill quicker It has a more powerful engine. ...
... Assuming identical friction, both engines do the same amount of work to get up the hill. Are the cars essentially the same ? NO. The Corvette can get up the hill quicker It has a more powerful engine. ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.