Newton`s Second Law with Constant Mass
... Where F is the net external applied force on an object of mass m and a is the resulting acceleration. Note that F and a are vectors. This law establishes the fact that only an external unbalanced force will cause an object to move and accelerate. The purpose of this experiment is to find out what ha ...
... Where F is the net external applied force on an object of mass m and a is the resulting acceleration. Note that F and a are vectors. This law establishes the fact that only an external unbalanced force will cause an object to move and accelerate. The purpose of this experiment is to find out what ha ...
solutions to problem set 8
... The centripetal force (due to gravity) will be mg cos α, so the skier will remain on the snowball as long as gravity can hold her to that path, i.e. as long as mg cos α ≥ 2mg (1 − cos α) Any radial gravitational force beyond what is necessary for the circular motion will be balanced by the normal fo ...
... The centripetal force (due to gravity) will be mg cos α, so the skier will remain on the snowball as long as gravity can hold her to that path, i.e. as long as mg cos α ≥ 2mg (1 − cos α) Any radial gravitational force beyond what is necessary for the circular motion will be balanced by the normal fo ...
Work and Energy
... the applied force. From the expression for total work, you should now be able to write a general mathematical expression for the speed of the mass as it passes through the bottom of the arc. The photogate must be positioned carefully to determine the speed of the cylindrical mass as it swings throug ...
... the applied force. From the expression for total work, you should now be able to write a general mathematical expression for the speed of the mass as it passes through the bottom of the arc. The photogate must be positioned carefully to determine the speed of the cylindrical mass as it swings throug ...
Motion and Forces
... one force acts on an object, the forces combine and act as one force. The sum of all the forces acting on an object is called the net force. When forces act in the same direction, they add together to form one net force. Sometimes forces act in opposite directions. Imagine watching a dog pulling on ...
... one force acts on an object, the forces combine and act as one force. The sum of all the forces acting on an object is called the net force. When forces act in the same direction, they add together to form one net force. Sometimes forces act in opposite directions. Imagine watching a dog pulling on ...
9.1 Impulse and Momentum Ancient Babylonians described
... travels a distance equal to 2 times the radius of the circle. This defines the modern angular measurement of 2 radians = 360°. The unit of radians is added for “cosmetic purposes” to provide a unit analogous to the degree. The unit of one radian is equivalent to 360° / 2, or 1 rad = 57.3°. ...
... travels a distance equal to 2 times the radius of the circle. This defines the modern angular measurement of 2 radians = 360°. The unit of radians is added for “cosmetic purposes” to provide a unit analogous to the degree. The unit of one radian is equivalent to 360° / 2, or 1 rad = 57.3°. ...
3.1 Inertial and Non-inertial Frames of Reference
... your body when you stand on level ground. Now suppose that you stand on the same scale inside an elevator. When the elevator is at rest, the normal force is again the same as your weight. This is also true when the elevator is moving at a constant non-zero speed upward or downward. However, what hap ...
... your body when you stand on level ground. Now suppose that you stand on the same scale inside an elevator. When the elevator is at rest, the normal force is again the same as your weight. This is also true when the elevator is moving at a constant non-zero speed upward or downward. However, what hap ...
Introduction, Configuration space, Equations of Motion, Velocity
... course in which we spend a lot of time doing things like solving for the motion of a triple pendulum coupled by springs while sliding on an inclined plane with friction in a viscous fluid as viewed in a rotating reference frame. To be sure, we will analyze the motion of some important dynamical syst ...
... course in which we spend a lot of time doing things like solving for the motion of a triple pendulum coupled by springs while sliding on an inclined plane with friction in a viscous fluid as viewed in a rotating reference frame. To be sure, we will analyze the motion of some important dynamical syst ...
Elements of Physics Motion, Force, and Gravity
... 6. false: The third law of motion states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Opposing forces often do not balance out. 7. true 8. false: Gravitation is a universal force that affects all objects within the gravitational field. 9. false: Newton's theory of gravity holds tha ...
... 6. false: The third law of motion states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Opposing forces often do not balance out. 7. true 8. false: Gravitation is a universal force that affects all objects within the gravitational field. 9. false: Newton's theory of gravity holds tha ...
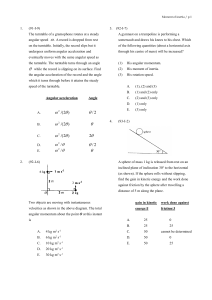
Force, Acceleration, Momentum
... to the speed v as I make the string length r shorter? A Stays constant, velocity is conserved B Slower ...
... to the speed v as I make the string length r shorter? A Stays constant, velocity is conserved B Slower ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.