Newton`s Laws Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the choice that
... ____ 25. A hockey stick hits a puck on the ice. Identify an action-reaction pair in this situation. a. The stick exerts a force on the puck; the puck exerts a force on the stick. b. The stick exerts a force on the puck; the puck exerts a force on the ice. c. The puck exerts a force on the stick; the ...
... ____ 25. A hockey stick hits a puck on the ice. Identify an action-reaction pair in this situation. a. The stick exerts a force on the puck; the puck exerts a force on the stick. b. The stick exerts a force on the puck; the puck exerts a force on the ice. c. The puck exerts a force on the stick; the ...
ch08_LecturePPT
... rotational velocity of 5 rev/s about a vertical axis. The rotational inertia of the wheel is 2 kg·m2 about its center and the rotational inertia of the student and wheel and platform about the rotational axis of the platform is 6 kg·m2. What is the initial angular momentum of the system? a) ...
... rotational velocity of 5 rev/s about a vertical axis. The rotational inertia of the wheel is 2 kg·m2 about its center and the rotational inertia of the student and wheel and platform about the rotational axis of the platform is 6 kg·m2. What is the initial angular momentum of the system? a) ...
Practice Final
... A) 0.654 mph B) 39.2 mph C) 780 mph D) 1430 mph E) 2350 mph 5) How fast will a motorcycle starting at rest go after 5 seconds if its acceleration is 3 m/s2? A) 7 m/s B) 12 m/s C) 15 m/s D) 18 m/s E) none of these 6) How long does it take for a sport car at rest to reach 27 m/s if its acceleration is ...
... A) 0.654 mph B) 39.2 mph C) 780 mph D) 1430 mph E) 2350 mph 5) How fast will a motorcycle starting at rest go after 5 seconds if its acceleration is 3 m/s2? A) 7 m/s B) 12 m/s C) 15 m/s D) 18 m/s E) none of these 6) How long does it take for a sport car at rest to reach 27 m/s if its acceleration is ...
Conservation of Momentum Notes
... • The total momentum of an isolated system of bodies remains constant. • (Isolated system: meaning that all forces acting on the bodies are included… and the sum of the external forces applied to the system is zero. External forces like Ff or Fg.) ...
... • The total momentum of an isolated system of bodies remains constant. • (Isolated system: meaning that all forces acting on the bodies are included… and the sum of the external forces applied to the system is zero. External forces like Ff or Fg.) ...
Milestones Master Study 2017
... Newton’s Second Law - the acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the amount of force applied A. F = m a Force = mass × acceleration Newton’s Third Law - whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first ...
... Newton’s Second Law - the acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the amount of force applied A. F = m a Force = mass × acceleration Newton’s Third Law - whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first ...
Force and Motion Car and Ramp
... understanding of the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration that is explained by Newton’s second law. They first observe how changing an object’s mass affects its acceleration while force is kept constant. They then keep the mass constant but vary the force. The results will be used to e ...
... understanding of the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration that is explained by Newton’s second law. They first observe how changing an object’s mass affects its acceleration while force is kept constant. They then keep the mass constant but vary the force. The results will be used to e ...
Newtons Lesson 7
... between the object and the surface. (Neglect air resistance.) 3. In a Physics lab, Ernesto and Amanda apply a 34.5 N rightward force to a 4.52-kg cart to accelerate it across a horizontal surface at a rate of 1.28 m/s/s. Determine the friction force acting upon the cart. 4. A rightward force of 25 N ...
... between the object and the surface. (Neglect air resistance.) 3. In a Physics lab, Ernesto and Amanda apply a 34.5 N rightward force to a 4.52-kg cart to accelerate it across a horizontal surface at a rate of 1.28 m/s/s. Determine the friction force acting upon the cart. 4. A rightward force of 25 N ...
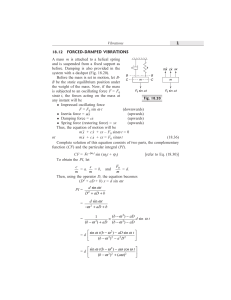
18.12 FORCED-DAMPED VIBRATIONS
... Example 18.13 A body having a mass of 15 kg is suspended from a spring which deflects 12 mm under weight of the mass. Determine the frequency of the free vibrations. What is the viscous damping force needed to make the motion aperiodic at a speed of 1 mm/s? If, when damped to this extent, a disturbi ...
... Example 18.13 A body having a mass of 15 kg is suspended from a spring which deflects 12 mm under weight of the mass. Determine the frequency of the free vibrations. What is the viscous damping force needed to make the motion aperiodic at a speed of 1 mm/s? If, when damped to this extent, a disturbi ...
No Slide Title
... So far, we used: PEgravity=mgh Only valid for h near earth’s surface. More general: PEgravity=-GMEarthm/r PE=0 at infinity distance from the center of the earth See example 7.12 for consistency between these two. Example: escape speed: what should the minimum initial velocity of a rocket be if we wa ...
... So far, we used: PEgravity=mgh Only valid for h near earth’s surface. More general: PEgravity=-GMEarthm/r PE=0 at infinity distance from the center of the earth See example 7.12 for consistency between these two. Example: escape speed: what should the minimum initial velocity of a rocket be if we wa ...
2565 Opt B Part 1
... • these are all terms which describe the turning effect produced by a force • when it acts eccentrically (to one side of) to an axis of rotation • moment = F x d ...
... • these are all terms which describe the turning effect produced by a force • when it acts eccentrically (to one side of) to an axis of rotation • moment = F x d ...
Chapter 6 - Macmillan Learning
... Questions and Problems 241 56. •Pilings are driven into the ground at a building site by dropping a 2000-kg object onto them. What change in gravitational potential energy does the object undergo if it is released from rest 18.0 m above the ground and ends up 2.00 m above the ground? 57. •A 40.0-k ...
... Questions and Problems 241 56. •Pilings are driven into the ground at a building site by dropping a 2000-kg object onto them. What change in gravitational potential energy does the object undergo if it is released from rest 18.0 m above the ground and ends up 2.00 m above the ground? 57. •A 40.0-k ...
Unbalanced forces acting on an object cause the object to
... Recall from the previous chapter that the combination of forces acting on an object is the net force. • Acceleration depends on the net force. • To increase the acceleration of an object, you must increase the net force acting on it. • An object’s acceleration is directly directl proportional to the ...
... Recall from the previous chapter that the combination of forces acting on an object is the net force. • Acceleration depends on the net force. • To increase the acceleration of an object, you must increase the net force acting on it. • An object’s acceleration is directly directl proportional to the ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 15 Thermodynamics
... rotational velocity of 5 rev/s about a vertical axis. The rotational inertia of the wheel is 2 kg·m2 about its center and the rotational inertia of the student and wheel and platform about the rotational axis of the platform is 6 kg·m2. What is the initial angular momentum of the system? a) ...
... rotational velocity of 5 rev/s about a vertical axis. The rotational inertia of the wheel is 2 kg·m2 about its center and the rotational inertia of the student and wheel and platform about the rotational axis of the platform is 6 kg·m2. What is the initial angular momentum of the system? a) ...
keplernewton - Department of Physics & Astronomy
... • Earth’s orbital period (1 year) and average distance (1 AU) tell us the Sun’s mass. • Orbital period and distance of a satellite from Earth tell us Earth’s mass. • Orbital period and distance of a moon of Jupiter tell us Jupiter’s mass. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • Earth’s orbital period (1 year) and average distance (1 AU) tell us the Sun’s mass. • Orbital period and distance of a satellite from Earth tell us Earth’s mass. • Orbital period and distance of a moon of Jupiter tell us Jupiter’s mass. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Chapter 4 Lagrangian mechanics
... in due time, especially when we get to the chapter on the connections between classical and quantum mechanics; (2) This reformulation provides powerful computational tools that can allow one to solve complex mechanics problems with greater ease. The formalism also lends itself more transparently to ...
... in due time, especially when we get to the chapter on the connections between classical and quantum mechanics; (2) This reformulation provides powerful computational tools that can allow one to solve complex mechanics problems with greater ease. The formalism also lends itself more transparently to ...
Problem 7.54 A Ball Hits a Wall Elastically
... the net force and is denoted by J . Then equation (2) can be rewritten as ...
... the net force and is denoted by J . Then equation (2) can be rewritten as ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.