Human Body Handbook
... waste (CO2). So, the brain tells the heart to increase the flow of blood to deliver more nutrients and pump the waste away. If you run or jump and then stop and touch your fingers to a pulse point—located on your wrist, neck, and upper arms— you can feel your heart working. Your pulse is the number ...
... waste (CO2). So, the brain tells the heart to increase the flow of blood to deliver more nutrients and pump the waste away. If you run or jump and then stop and touch your fingers to a pulse point—located on your wrist, neck, and upper arms— you can feel your heart working. Your pulse is the number ...
Chapter 4-2: Worm Lesson
... the earthworm remains out in the heat of the sunthe earthworm suffocates and dies. Although earthworms have only a simple nervous system, they are very sensitive to their environment. An earthworm's nervous system consists of a brain found in the head region, two nerves that pass around the intestin ...
... the earthworm remains out in the heat of the sunthe earthworm suffocates and dies. Although earthworms have only a simple nervous system, they are very sensitive to their environment. An earthworm's nervous system consists of a brain found in the head region, two nerves that pass around the intestin ...
Introduction to Evolution
... 2.compare your definition with your neighbour • try and write a consensus one you both agree on • if this is difficult, try to make notes on where the problems might come from ...
... 2.compare your definition with your neighbour • try and write a consensus one you both agree on • if this is difficult, try to make notes on where the problems might come from ...
respiratory, urinary
... the walls of the alveoli from sticking together when they collapse during exhalation. If you have two wet pieces of paper and stick them together, they are hard to pull apart without ripping. Put soapy water between them, and you can pull them apart. The reason this is important is because surfactan ...
... the walls of the alveoli from sticking together when they collapse during exhalation. If you have two wet pieces of paper and stick them together, they are hard to pull apart without ripping. Put soapy water between them, and you can pull them apart. The reason this is important is because surfactan ...
PINK DISEASE SUPPORT GROUP PO Box 5120, Eagleby, Qld
... makes it difficult to get air out, so it becomes trapped in the lungs. The air tubes or airways may be narrowed due to swelling and mucus and this also makes it difficult to get air out. Air trapping makes it harder work to breathe and breathing can feel uncomfortable. 2. Stiff Lungs: For people wit ...
... makes it difficult to get air out, so it becomes trapped in the lungs. The air tubes or airways may be narrowed due to swelling and mucus and this also makes it difficult to get air out. Air trapping makes it harder work to breathe and breathing can feel uncomfortable. 2. Stiff Lungs: For people wit ...
Our Human Body - On-site student activities
... or for small groups of students to use. A larger selection of themes may be used by larger groups of students. The information collected on the student record sheets should be used as reference material for the follow-up Classroom Activities, or for further research of the subject back at school. Al ...
... or for small groups of students to use. A larger selection of themes may be used by larger groups of students. The information collected on the student record sheets should be used as reference material for the follow-up Classroom Activities, or for further research of the subject back at school. Al ...
Lab: Shark (Dogfish) Dissection Squalus acanthias
... The muscles revealed by skinning the side of the shark are arranged in W-shaped bundles. What is the name of these muscles and what is their purpose? The “scales” you see are called dermal denticles, (literally “skin teeth”). Draw an example of the dermal denticles ...
... The muscles revealed by skinning the side of the shark are arranged in W-shaped bundles. What is the name of these muscles and what is their purpose? The “scales” you see are called dermal denticles, (literally “skin teeth”). Draw an example of the dermal denticles ...
3 -Humans
... Your digestive system starts from your mouth. But even after you have swallowed the food, it is not really inside your body. The gut or the digestive system is a long tube about 8-9m long which runs from your mouth to anus. In your mouth food is broken down into smaller pieces with the help of teeth ...
... Your digestive system starts from your mouth. But even after you have swallowed the food, it is not really inside your body. The gut or the digestive system is a long tube about 8-9m long which runs from your mouth to anus. In your mouth food is broken down into smaller pieces with the help of teeth ...
BC Science 8 CH02
... 1. Carbohydrates are the body’s fastest source of _________________________________. 2. Examples of foods containing carbohydrates are ________________________________ and ________________________________________________________________________. 3. ________________________________________ help build ...
... 1. Carbohydrates are the body’s fastest source of _________________________________. 2. Examples of foods containing carbohydrates are ________________________________ and ________________________________________________________________________. 3. ________________________________________ help build ...
Name - grade8structureoflivingthings
... 12. Use a Clorox Wipe to clean: all used tools, the blue mat, gray dissecting tray, lab table. 13. Return all clean materials to the drawer you got them from. Part D: What I learned Summary Questions 14. Compare the organs in the frog to what you saw at the Bodies Exhibit. How are they similar and d ...
... 12. Use a Clorox Wipe to clean: all used tools, the blue mat, gray dissecting tray, lab table. 13. Return all clean materials to the drawer you got them from. Part D: What I learned Summary Questions 14. Compare the organs in the frog to what you saw at the Bodies Exhibit. How are they similar and d ...
Human Body Systems Graphic Organizer
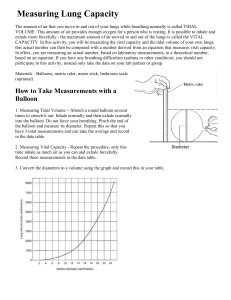
... VOLUME. This amount of air provides enough oxygen for a person who is resting. It is possible to inhale and exhale more forcefully - the maximum amount of air moved in and out of the lungs is called the VITAL CAPACITY. In this activity, you will be measuring the vital capacity and the tidal volume o ...
... VOLUME. This amount of air provides enough oxygen for a person who is resting. It is possible to inhale and exhale more forcefully - the maximum amount of air moved in and out of the lungs is called the VITAL CAPACITY. In this activity, you will be measuring the vital capacity and the tidal volume o ...
Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
... Function: Support, movement, protection, and production of blood cells Muscles of the body Function: Movement, maintenance of posture, production of body heat Brain, spinal cord, nerves through the body Function: Communication throughout body, mental activities, maintainin ...
... Function: Support, movement, protection, and production of blood cells Muscles of the body Function: Movement, maintenance of posture, production of body heat Brain, spinal cord, nerves through the body Function: Communication throughout body, mental activities, maintainin ...
7) NATURAL SELECTION: the process by which forms of life having
... from other members of its species; (an adaptation is a variation that makes an organism better suited to its environment.) 1) When environmental changes occur (biotic and/or abiotic), organisms best suited to the change will be more likely to reach the age of reproduction. This is why variation of t ...
... from other members of its species; (an adaptation is a variation that makes an organism better suited to its environment.) 1) When environmental changes occur (biotic and/or abiotic), organisms best suited to the change will be more likely to reach the age of reproduction. This is why variation of t ...
Daily Questions Unit 8- The Human Body Ch 30 Digestive and
... 1. Review Explain the function of the respiratory system 2. Use Analogies Explain how a molecule of oxygen glowing through the respiratory system is like a commuter driving home from work 3. Infer The brain’s breathing center respond to the level of carbon dioxide and not oxygen levels in the blood- ...
... 1. Review Explain the function of the respiratory system 2. Use Analogies Explain how a molecule of oxygen glowing through the respiratory system is like a commuter driving home from work 3. Infer The brain’s breathing center respond to the level of carbon dioxide and not oxygen levels in the blood- ...
living environment
... Base your answers to questions 42 and 43 on the passage below and on your knowledge of biology. …Corals come in about 1,500 known species—from soft swaying fans to stony varieties with hard skeletons that form reef bases. They are made up of polyps, tiny animals that live in colonies and feed at ni ...
... Base your answers to questions 42 and 43 on the passage below and on your knowledge of biology. …Corals come in about 1,500 known species—from soft swaying fans to stony varieties with hard skeletons that form reef bases. They are made up of polyps, tiny animals that live in colonies and feed at ni ...
Amphibians and reptiles are adapted for life on land.
... parts of the egg, which is covered by a protective shell. Reptiles reproduce sexually. The egg cell of the female joins with the sperm cell of the male in the process of fertilization. After fertilization, a protective case, or shell, forms around each egg while it is still inside the female’s body. ...
... parts of the egg, which is covered by a protective shell. Reptiles reproduce sexually. The egg cell of the female joins with the sperm cell of the male in the process of fertilization. After fertilization, a protective case, or shell, forms around each egg while it is still inside the female’s body. ...
Ten Simple Rules for Effective Computational Research
... Rule 4: Don’t Underestimate the Complexity of Your Task When developing your code, you should keep a record of your work. This could be in the form of a ‘‘logbook’’ file or a paper notebook where you store commonly used commands and other notes; another good option is an online tool such as Evernote ...
... Rule 4: Don’t Underestimate the Complexity of Your Task When developing your code, you should keep a record of your work. This could be in the form of a ‘‘logbook’’ file or a paper notebook where you store commonly used commands and other notes; another good option is an online tool such as Evernote ...
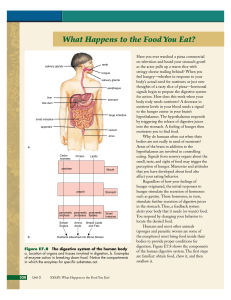
What Happens to the Food You Eat?
... digestive function. As you chew, the surface area of your food increases greatly. Increased surface area means that the chemical reactions involved in digestion can occur more quickly. In addition, chewing moistens the food with saliva. Salivary glands located under your tongue secrete saliva. The m ...
... digestive function. As you chew, the surface area of your food increases greatly. Increased surface area means that the chemical reactions involved in digestion can occur more quickly. In addition, chewing moistens the food with saliva. Salivary glands located under your tongue secrete saliva. The m ...
Frog Lab - saddlespace.org
... 30. The reproductive system and urinary system of the frog are closely connected and can be studied as the combined urogenital system. At the back of the abdominal cavity are two long, reddish-brown organs, the kidneys. The yellow, fingerlike lobes attached to the kidneys are fat bodies. A small, tw ...
... 30. The reproductive system and urinary system of the frog are closely connected and can be studied as the combined urogenital system. At the back of the abdominal cavity are two long, reddish-brown organs, the kidneys. The yellow, fingerlike lobes attached to the kidneys are fat bodies. A small, tw ...
LAB - Frog Dissection
... 30. The reproductive system and urinary system of the frog are closely connected and can be studied as the combined urogenital system. At the back of the abdominal cavity are two long, reddish-brown organs, the kidneys. The yellow, fingerlike lobes attached to the kidneys are fat bodies. A small, t ...
... 30. The reproductive system and urinary system of the frog are closely connected and can be studied as the combined urogenital system. At the back of the abdominal cavity are two long, reddish-brown organs, the kidneys. The yellow, fingerlike lobes attached to the kidneys are fat bodies. A small, t ...
The Respiratory System
... Your left lung is a little bit smaller than your right lung because the heart is taking up some of that space in your body. Below the lungs, there is a muscle called the __________. When you breathe in, the diaphragm ________ to help expand your ribcage and bring in air. When the diaphragm relaxes, ...
... Your left lung is a little bit smaller than your right lung because the heart is taking up some of that space in your body. Below the lungs, there is a muscle called the __________. When you breathe in, the diaphragm ________ to help expand your ribcage and bring in air. When the diaphragm relaxes, ...
Biology 455 – Entomology Lab Insect Anatomy
... During this lab, you will explore the external and internal anatomy of a cricket. This lab is intended to familiarize you with the general morphology of insects, and to introduce you to the vocabulary of insect “parts”. You will need to know and use this stuff as you identify and study various speci ...
... During this lab, you will explore the external and internal anatomy of a cricket. This lab is intended to familiarize you with the general morphology of insects, and to introduce you to the vocabulary of insect “parts”. You will need to know and use this stuff as you identify and study various speci ...
Human Body
... lungs, and body and how carbon dioxide & oxygen are exchanged in the lungs and tissues. 2c. Students know the sequential steps of digestion and the roles of teeth and mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and colon in the function of the digestive system. 2d. Students know th ...
... lungs, and body and how carbon dioxide & oxygen are exchanged in the lungs and tissues. 2c. Students know the sequential steps of digestion and the roles of teeth and mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and colon in the function of the digestive system. 2d. Students know th ...