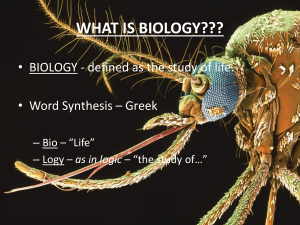
ANIMAL DIVERSITY
... • All are _____ploblastic, ______coelomate _____________stomes with bilateral symmetry • Paired setae (or chaetae) on nearly all segments – Can be very ___________________________ bundles on parapodia – Or very ___________________________ in the oligochaetes or leeches ...
... • All are _____ploblastic, ______coelomate _____________stomes with bilateral symmetry • Paired setae (or chaetae) on nearly all segments – Can be very ___________________________ bundles on parapodia – Or very ___________________________ in the oligochaetes or leeches ...
Name: Pre-Lab: Animal Diversity
... size from microscopic to over 20 meters long in some tapeworms! Examine the Planaria slide whole mount. Examine the body for a number of digestive openings (the stained planaria shows the digestive system). Observe the pharynx and mouth. The pharynx lies in a pharyngeal chamber inside the mouth. The ...
... size from microscopic to over 20 meters long in some tapeworms! Examine the Planaria slide whole mount. Examine the body for a number of digestive openings (the stained planaria shows the digestive system). Observe the pharynx and mouth. The pharynx lies in a pharyngeal chamber inside the mouth. The ...
Unit 13 ~ Learning Guide Name
... improvement over the exoskeleton is its _____________________________________. The exoskeleton must be periodically shed and regrown. This leaves the animal vulnerable for a short time while it is re-growing its exoskeleton and is also very costly in terms of energy. With the endoskeleton's ability ...
... improvement over the exoskeleton is its _____________________________________. The exoskeleton must be periodically shed and regrown. This leaves the animal vulnerable for a short time while it is re-growing its exoskeleton and is also very costly in terms of energy. With the endoskeleton's ability ...
Food Webs and Food Chains
... Food Chains • The energy flow from one trophic level to the other is know as a food chain • A food chain is simple and direct ...
... Food Chains • The energy flow from one trophic level to the other is know as a food chain • A food chain is simple and direct ...
Introduction to Animals
... • Have some type of skeletal support • Endoskeleton inside and made of cartilage &/or bone • Exoskeletons found in arthropods – Cover the outside of the body – Limit size – Must be molted making animal vulnerable to predators ...
... • Have some type of skeletal support • Endoskeleton inside and made of cartilage &/or bone • Exoskeletons found in arthropods – Cover the outside of the body – Limit size – Must be molted making animal vulnerable to predators ...
Intro to Ecology
... an ecosystem is greater than the total mass of primary consumers, and the total mass of primary consumers is greater than the total mass of secondary consumers and so on. •A biomass pyramid can be used to show this decrease in biomass at each higher feeding level. Mrs. Degl ...
... an ecosystem is greater than the total mass of primary consumers, and the total mass of primary consumers is greater than the total mass of secondary consumers and so on. •A biomass pyramid can be used to show this decrease in biomass at each higher feeding level. Mrs. Degl ...
THE HUMAN BODY
... A. An Organ System is a group of organs that all contribute to a Particular Function. B. Examples are the Circulatory, Respiratory, and Digestive Systems. C. Each organ system carries out its own specific function, but for the organism to survive the organ systems must work together- this is called ...
... A. An Organ System is a group of organs that all contribute to a Particular Function. B. Examples are the Circulatory, Respiratory, and Digestive Systems. C. Each organ system carries out its own specific function, but for the organism to survive the organ systems must work together- this is called ...
4. Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration PDF File
... Describe the difference between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration (2 marks) Which activity is most likely to use aerobic respiration for energy? ...
... Describe the difference between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration (2 marks) Which activity is most likely to use aerobic respiration for energy? ...
Morphologically description of body shape
... o Morphologically description of body shape: 1. Slender. 2. 3.5-6.5 cm in length . 3. Translucent. 4. Laterally compressed , pointed at both ends . 5. The anterior two-thirds of the body is roughly triangular in section, and the posterior third is nearly oval . ...
... o Morphologically description of body shape: 1. Slender. 2. 3.5-6.5 cm in length . 3. Translucent. 4. Laterally compressed , pointed at both ends . 5. The anterior two-thirds of the body is roughly triangular in section, and the posterior third is nearly oval . ...
Spring Semester Exam Review
... Q9. Why do turtles lay more eggs than can survive? (hint: think about what happens to a lot of them as they travel to the ocean after they hatch) OVERPRODUCTION is necessary because natural selection requires that some organisms will be less fit and die off. If there were not more offspring than can ...
... Q9. Why do turtles lay more eggs than can survive? (hint: think about what happens to a lot of them as they travel to the ocean after they hatch) OVERPRODUCTION is necessary because natural selection requires that some organisms will be less fit and die off. If there were not more offspring than can ...
Biology - Riverside Military Academy
... How does this law relate to the cycling of carbon in an ecosystem? Chapter 3: 1. Generalize the difference between a successional stage and a climax community. 2. Infer whether species diversity increases or decreases after a fire on a grassland. Explain your response. 3. Explain why the concepts of ...
... How does this law relate to the cycling of carbon in an ecosystem? Chapter 3: 1. Generalize the difference between a successional stage and a climax community. 2. Infer whether species diversity increases or decreases after a fire on a grassland. Explain your response. 3. Explain why the concepts of ...
ANIMAL POWERPOINT CHPT 40
... Positive feedback involves a change in some variable that triggers mechanism that amplify rather than reverse the change. Regulated change is essential to normal body functions Over the short term, homeostatic mechanisms keep body temperature close to a set point, whatever it is at that particular t ...
... Positive feedback involves a change in some variable that triggers mechanism that amplify rather than reverse the change. Regulated change is essential to normal body functions Over the short term, homeostatic mechanisms keep body temperature close to a set point, whatever it is at that particular t ...
The Study of Life
... Interdependence of Organisms • Organisms interactions and combined with the non-living factors in the environment is ecology and the overall product of Biology ...
... Interdependence of Organisms • Organisms interactions and combined with the non-living factors in the environment is ecology and the overall product of Biology ...
ECOLOGY - Bishop Amat Memorial High School
... population that can be maintained for an indefinite period of time by a particular environment ...
... population that can be maintained for an indefinite period of time by a particular environment ...
Study Guide Evolution of Animals Chapter – 19
... 28. Chordates possess 4 characters at least once during their life time (in embryo or larva or adult): a) Notochord – an elastic chord, is replaced by vertebrae in most chordates called Vertebrates b) Dorsal and hollow nerve tube – develops into brain and spinal cord in vertebrates c) Pharyngeal Gil ...
... 28. Chordates possess 4 characters at least once during their life time (in embryo or larva or adult): a) Notochord – an elastic chord, is replaced by vertebrae in most chordates called Vertebrates b) Dorsal and hollow nerve tube – develops into brain and spinal cord in vertebrates c) Pharyngeal Gil ...
Answer
... animals mostly live in water. Hence, they have special adaptive features such as a streamlined body, presence of a tail for movement, gills, etc. to live in water. (ii) Class Amphibia: It includes frogs, toads, and salamanders. These animals have a dual mode of life. In the larval stage, the respira ...
... animals mostly live in water. Hence, they have special adaptive features such as a streamlined body, presence of a tail for movement, gills, etc. to live in water. (ii) Class Amphibia: It includes frogs, toads, and salamanders. These animals have a dual mode of life. In the larval stage, the respira ...
Mammals
... 1. The lower chambers of the heart are called ventricle 2. Marsupials and Monotremes composes what 5% of mammals? 3. Atridactyls are even or odd toed? 4. Gland in the region of the neck of a rat: thymus 5. Organ that links baby to material circulatory system. placenta 6. A cloaca would be found in w ...
... 1. The lower chambers of the heart are called ventricle 2. Marsupials and Monotremes composes what 5% of mammals? 3. Atridactyls are even or odd toed? 4. Gland in the region of the neck of a rat: thymus 5. Organ that links baby to material circulatory system. placenta 6. A cloaca would be found in w ...