Structure - Bhoj University
... changes with change in sign, the particle is said to be in odd state and is said to have negative or odd parity. Nuclear states are characterized by a definite parity which may be different for different states of the same nucleus. According to the parity law, two particles which are the mirror imag ...
... changes with change in sign, the particle is said to be in odd state and is said to have negative or odd parity. Nuclear states are characterized by a definite parity which may be different for different states of the same nucleus. According to the parity law, two particles which are the mirror imag ...
Spin-density wave in a quantum wire
... Another very interesting system that motivates our investigation is provided by onedimensional electron surface states on vicinal surface of gold (Mugarza et al. 2002) as well as by electron states of self-assembled gold chains on stepped Si(111) surface of silicon (Crain et al. 2006). In both of th ...
... Another very interesting system that motivates our investigation is provided by onedimensional electron surface states on vicinal surface of gold (Mugarza et al. 2002) as well as by electron states of self-assembled gold chains on stepped Si(111) surface of silicon (Crain et al. 2006). In both of th ...
Absorption and Emission
... electromagnetic waves and their equivalence to light waves. After Hertz’s achievement, the electromagnetic theory of James Clerk Maxwell, developed from 1861 to 1864, became the basis of examining optical absorption and dispersion phenomena. As the name indicates, electromagnetic waves have two comp ...
... electromagnetic waves and their equivalence to light waves. After Hertz’s achievement, the electromagnetic theory of James Clerk Maxwell, developed from 1861 to 1864, became the basis of examining optical absorption and dispersion phenomena. As the name indicates, electromagnetic waves have two comp ...
Slide 1
... • Small things: The Fundamental Building Blocks of Nature – What is the “stuff” in atoms • ElectroMagnetism (electric charge) – What holds electrons and protons together • Quantum Mechanics – Why atoms form the way they do – Electron in orbits – Atoms absorbing and emitting photons (light) • Differe ...
... • Small things: The Fundamental Building Blocks of Nature – What is the “stuff” in atoms • ElectroMagnetism (electric charge) – What holds electrons and protons together • Quantum Mechanics – Why atoms form the way they do – Electron in orbits – Atoms absorbing and emitting photons (light) • Differe ...
Tuesday, June 21, 2005
... Example for Linear Momentum Conservation A type of particle, a neutral kaon (K0), decays (breaks up) into a pair of particles called pions (p+ and p-) that are oppositely charged but have equal mass. Assuming the K0 is initially produced at rest, prove that the two pions must have momenta that are ...
... Example for Linear Momentum Conservation A type of particle, a neutral kaon (K0), decays (breaks up) into a pair of particles called pions (p+ and p-) that are oppositely charged but have equal mass. Assuming the K0 is initially produced at rest, prove that the two pions must have momenta that are ...
10.2 Simple Harmonic Motion and the Reference Circle
... In a circus act, a performer supports the combined weight (1080 N) of a number of colleagues. Each thighbone of this performer has a length of 0.55 m and an effective cross sectional area of 7.7×10-4 m2. Determine the amount that each thighbone compresses under the extra weight. ...
... In a circus act, a performer supports the combined weight (1080 N) of a number of colleagues. Each thighbone of this performer has a length of 0.55 m and an effective cross sectional area of 7.7×10-4 m2. Determine the amount that each thighbone compresses under the extra weight. ...
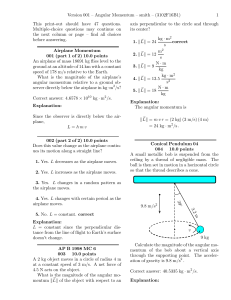
Angular Momentum Solutions
... 5. The torque due to gravity. correct Explanation: Gravity is the only force acting on the particle. The change in angular momentum is negative (going from zero to negative values) because the torque of the gravity force is negative (−k̂ direction) as you can see from the ~ ×F ...
... 5. The torque due to gravity. correct Explanation: Gravity is the only force acting on the particle. The change in angular momentum is negative (going from zero to negative values) because the torque of the gravity force is negative (−k̂ direction) as you can see from the ~ ×F ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... The experimental work which was done shows variation of conductivity for gold according to Figs (24-2-1) and (2-4-2-2). The conductivity decreases then attains a minimum value in the range of (40-50 Hz), then increases a gain. The theoretical expression (3-1-11) which is displayed graphically in Fig ...
... The experimental work which was done shows variation of conductivity for gold according to Figs (24-2-1) and (2-4-2-2). The conductivity decreases then attains a minimum value in the range of (40-50 Hz), then increases a gain. The theoretical expression (3-1-11) which is displayed graphically in Fig ...
here.
... direction of the momentum vector, ensuring that E > 0. Within the context of the KG equation, this is seemingly ok, since the particle will then remain in that stationary state for ever. However, under the influence of external perturbations, the particle could make a transition to a lower energy st ...
... direction of the momentum vector, ensuring that E > 0. Within the context of the KG equation, this is seemingly ok, since the particle will then remain in that stationary state for ever. However, under the influence of external perturbations, the particle could make a transition to a lower energy st ...









![06 Momentum WS 08 [v6.0]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017198328_1-636fbdb6d6c62db5233df770cc2cf61d-300x300.png)