end of section a
... shallow region, the wavelength and the period of the wave are and T respectively. X is a point on the water surface in the shallow region and is 2 away from the wave at time t = 0. ...
... shallow region, the wavelength and the period of the wave are and T respectively. X is a point on the water surface in the shallow region and is 2 away from the wave at time t = 0. ...
30155-doc - Project Gutenberg
... points on a rigid body, we can construct the line joining them according to the rules of geometry ; then, starting from A, we can mark off the distance S time after time until we reach B. The number of these operations required is the numerical measure of the distance AB. This is the basis of all me ...
... points on a rigid body, we can construct the line joining them according to the rules of geometry ; then, starting from A, we can mark off the distance S time after time until we reach B. The number of these operations required is the numerical measure of the distance AB. This is the basis of all me ...
Lecture 32 - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... currents can produce electromagnetic waves • The fundamental mechanism responsible for this radiation is the acceleration of a charged particle • Whenever a charged particle accelerates, it must radiate energy ...
... currents can produce electromagnetic waves • The fundamental mechanism responsible for this radiation is the acceleration of a charged particle • Whenever a charged particle accelerates, it must radiate energy ...
physics - Regents
... source is always greater than the amount of electrical energy produced. Explain why there is a difference between the amount of energy provided by the source and the amount of electrical energy produced. [1] Base your answers to questions 63 through 65 on the graph below, which represents the relati ...
... source is always greater than the amount of electrical energy produced. Explain why there is a difference between the amount of energy provided by the source and the amount of electrical energy produced. [1] Base your answers to questions 63 through 65 on the graph below, which represents the relati ...
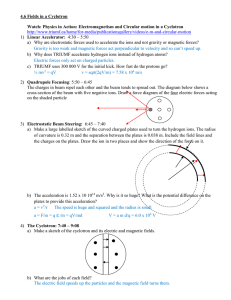
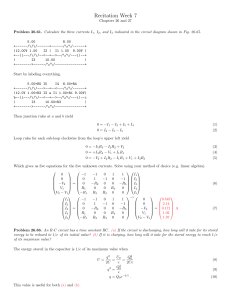
Recitation Week 7
... Problem 26.86. An R-C circuit has a time constant RC. (a) If the circuit is discharging, how long will it take for its stored energy to be reduced to 1/e of its initial value? (b) If it is charging, how long will it take for the stored energy to reach 1/e of its maximum value? The energy stored in t ...
... Problem 26.86. An R-C circuit has a time constant RC. (a) If the circuit is discharging, how long will it take for its stored energy to be reduced to 1/e of its initial value? (b) If it is charging, how long will it take for the stored energy to reach 1/e of its maximum value? The energy stored in t ...
PPT
... This is OK, since the wave equation is linear, so that the real part of Ψ and its imaginary part are each separately solutions. ...
... This is OK, since the wave equation is linear, so that the real part of Ψ and its imaginary part are each separately solutions. ...
Homework set 1, due September 4, 11:40 am
... 5. (20 points) Consider a linearly polarized plane electromagnetic wave traveling in the +x-direction in free space having as its plane of vibration the xy plane. Given that its frequency is 10 MHz and its amplitude is E0= 0.08 V/m (a) Find the period and wavelength of the wave. (b) Write an express ...
... 5. (20 points) Consider a linearly polarized plane electromagnetic wave traveling in the +x-direction in free space having as its plane of vibration the xy plane. Given that its frequency is 10 MHz and its amplitude is E0= 0.08 V/m (a) Find the period and wavelength of the wave. (b) Write an express ...
Does a Relativistic Theory Always Have a Non
... theory. It is the so-called “magnetic limit” (see below) which involves transformations of the potentials under boosts that appear in the Galilean covariant version of both classical and quantum mechanics. Both limits correspond to static theories, in which, analogously to the Newtonian gravitationa ...
... theory. It is the so-called “magnetic limit” (see below) which involves transformations of the potentials under boosts that appear in the Galilean covariant version of both classical and quantum mechanics. Both limits correspond to static theories, in which, analogously to the Newtonian gravitationa ...
Time in physics

Time in physics is defined by its measurement: time is what a clock reads. In classical, non-relativistic physics it is a scalar quantity and, like length, mass, and charge, is usually described as a fundamental quantity. Time can be combined mathematically with other physical quantities to derive other concepts such as motion, kinetic energy and time-dependent fields. Timekeeping is a complex of technological and scientific issues, and part of the foundation of recordkeeping.