Chemistry EOC Review Name
... 120. Name three factors that increase the rate of solvation 121. What is meant by solubility? 122. What is the rule for determining if substances will soluble in each other? 123. Explain how saturated, unsaturated, and supersaturated solutions are different from each other. 124. Generally, an increa ...
... 120. Name three factors that increase the rate of solvation 121. What is meant by solubility? 122. What is the rule for determining if substances will soluble in each other? 123. Explain how saturated, unsaturated, and supersaturated solutions are different from each other. 124. Generally, an increa ...
makeup2
... 58. A solution of a non-electrolyte, x, contains 84 grams of x per kilogram of water and freezes at -1.46°C. What is the molecular weight of x? (Kf = 1.86) (A) 84 x 1.86 x 1.46 = 222 g/mol (B) 84 x (1.86 / 1.46) = 107 g/mol (C) 84 x (1.46 / 1.86) = 66 g/mol (D) 1.46 x (1.86 / 84) = 0.032 g/mol 59. ...
... 58. A solution of a non-electrolyte, x, contains 84 grams of x per kilogram of water and freezes at -1.46°C. What is the molecular weight of x? (Kf = 1.86) (A) 84 x 1.86 x 1.46 = 222 g/mol (B) 84 x (1.86 / 1.46) = 107 g/mol (C) 84 x (1.46 / 1.86) = 66 g/mol (D) 1.46 x (1.86 / 84) = 0.032 g/mol 59. ...
Bond
... including its role in nature, depends primarily on its molecular structure, or shape. Molecular shape contributes toward determining a compound’s boiling point, freezing point, viscosity, solubility, types of reactions it can participate in, and a host of other physical and chemical properties. The ...
... including its role in nature, depends primarily on its molecular structure, or shape. Molecular shape contributes toward determining a compound’s boiling point, freezing point, viscosity, solubility, types of reactions it can participate in, and a host of other physical and chemical properties. The ...
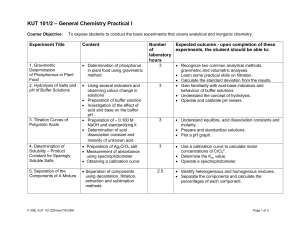
KUT 101/2 – General Chemistry Practical I
... • Preparation of Na2S2O3 solution and standardizing it • Determination of the oxidizing capacity of an unknown liquid bleach • Preparation of Cu(NO)3 and performing basic laboratory procedures • Reduction of copper with zinc • Preparation of ∼ 0.100 M NaOH and standardizing it. • Analysis of an unkn ...
... • Preparation of Na2S2O3 solution and standardizing it • Determination of the oxidizing capacity of an unknown liquid bleach • Preparation of Cu(NO)3 and performing basic laboratory procedures • Reduction of copper with zinc • Preparation of ∼ 0.100 M NaOH and standardizing it. • Analysis of an unkn ...
Chapter 1 - TamAPChemistryHart
... 15. A solid white substance A is heated strongly in the absence of air. It decomposes to form a new white substance B and a gas C. The gas has exactly the same properties as the product obtained when carbon is burned in an excess of oxygen. Based on these observations, can we determine whether solid ...
... 15. A solid white substance A is heated strongly in the absence of air. It decomposes to form a new white substance B and a gas C. The gas has exactly the same properties as the product obtained when carbon is burned in an excess of oxygen. Based on these observations, can we determine whether solid ...
Review - Final Exam
... 22. What are the valence electrons? What happens to the valence electrons across a row of representative elements and down a group? What information is gained from the valence electrons? Why do chemical families have similar properties? 23. Draw Lewis (Electron Dot) symbols for the elements across t ...
... 22. What are the valence electrons? What happens to the valence electrons across a row of representative elements and down a group? What information is gained from the valence electrons? Why do chemical families have similar properties? 23. Draw Lewis (Electron Dot) symbols for the elements across t ...
The Quantum Mechanical Harmonic Oscillator
... motion as a function of time - at least that’s what all of the physicists for several generations after Newton would have thought. In a wrenching change of attitude that took place during the first third of the twentieth century, physicists learned a new way of thinking: the way of quantum mechanics ...
... motion as a function of time - at least that’s what all of the physicists for several generations after Newton would have thought. In a wrenching change of attitude that took place during the first third of the twentieth century, physicists learned a new way of thinking: the way of quantum mechanics ...
E:\My Documents\sch3u\SCH3Ureview.wpd
... 8) A compound is found to have the following percentage composition by mass: 30.57 % Carbon, 3.83 % Hydrogen, 45.22 % Chlorine, 20.38 % Oxygen. a) Determine the empirical formula for this compound. b) Based on a molar mass of 157.0 g, what is the molecular formula of this compound. c) Give at least ...
... 8) A compound is found to have the following percentage composition by mass: 30.57 % Carbon, 3.83 % Hydrogen, 45.22 % Chlorine, 20.38 % Oxygen. a) Determine the empirical formula for this compound. b) Based on a molar mass of 157.0 g, what is the molecular formula of this compound. c) Give at least ...
Practice Bypass Answers
... h) At room temperature (72 oF) propane is a gas and water is a liquid. This means that 72 oF must be higher than the boiling point for propane, but lower than the boiling point for water. Explain why propane has a lower boiling point than water. Provide an analysis of the interparticle forces betwee ...
... h) At room temperature (72 oF) propane is a gas and water is a liquid. This means that 72 oF must be higher than the boiling point for propane, but lower than the boiling point for water. Explain why propane has a lower boiling point than water. Provide an analysis of the interparticle forces betwee ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... find other web sites that help prepare you for the coming year. We recommend that you complete as many online quizzes as possible, take detailed notes, and practice the items indicated in the packet. Completed work must be submitted by AUGUST 25th, Mail the assignments to the school address or drop ...
... find other web sites that help prepare you for the coming year. We recommend that you complete as many online quizzes as possible, take detailed notes, and practice the items indicated in the packet. Completed work must be submitted by AUGUST 25th, Mail the assignments to the school address or drop ...
Introductory Chemistry I
... 4. The maximum number of electrons that can occupy the 3d orbitals is a. 5 b. 6 c. 10 d. 14 e. 18 5. Let’s say that you are examining the outermost electrons in a ground-state germanium atom. Which of the following sets of values for the four quantum numbers (n, l, ml, and ms) could you use to descr ...
... 4. The maximum number of electrons that can occupy the 3d orbitals is a. 5 b. 6 c. 10 d. 14 e. 18 5. Let’s say that you are examining the outermost electrons in a ground-state germanium atom. Which of the following sets of values for the four quantum numbers (n, l, ml, and ms) could you use to descr ...
Chemistry I Exam
... D. The student rested for one hour half way through the trip. E. The graph is a curve rather than a straight line because the speed of the bicycle decreased as the time of day increased. ...
... D. The student rested for one hour half way through the trip. E. The graph is a curve rather than a straight line because the speed of the bicycle decreased as the time of day increased. ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... For those students who have already taken a high school chemistry course, much of the material in the summer packet will be familiar to you. For those students who will be taking AP Chemistry as your first high school chemistry course, the problems will help you build a foundation in chemistry and i ...
... For those students who have already taken a high school chemistry course, much of the material in the summer packet will be familiar to you. For those students who will be taking AP Chemistry as your first high school chemistry course, the problems will help you build a foundation in chemistry and i ...
how to deal accurately with both the core and valence electrons
... Goal: Describe properties of matter from theoretical methods firmly rooted in fundamental equations ...
... Goal: Describe properties of matter from theoretical methods firmly rooted in fundamental equations ...