1. What is a Chemical Reaction?
... • A chemical reaction is the process by which atoms of one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances(s) with new chemical and physical properties. • A chemical reaction is another name for a chemical change. • When substances chemically react, observations can be made that provi ...
... • A chemical reaction is the process by which atoms of one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances(s) with new chemical and physical properties. • A chemical reaction is another name for a chemical change. • When substances chemically react, observations can be made that provi ...
Ch. 3 Sections 3.9-3.10 Notes
... Use the balanced equation to set up the appropriate mole ratios. Use the appropriate mole ratios to calculate the number of moles of the desired reactant or product. Convert from moles back to grams if required by the problem. Example: One of the most spectacular reactions of aluminum, the thermite ...
... Use the balanced equation to set up the appropriate mole ratios. Use the appropriate mole ratios to calculate the number of moles of the desired reactant or product. Convert from moles back to grams if required by the problem. Example: One of the most spectacular reactions of aluminum, the thermite ...
ch-4-earth-chemistry
... Example: A neutral sodium atom has a charge of zero (equal # of protons and neutrons) and only 1 valence electron. Once it loses that valence electron, it will have 8 valence electrons and be stable and most likely, not gain or lose anymore electrons. What would be the charge on a sodium atom that l ...
... Example: A neutral sodium atom has a charge of zero (equal # of protons and neutrons) and only 1 valence electron. Once it loses that valence electron, it will have 8 valence electrons and be stable and most likely, not gain or lose anymore electrons. What would be the charge on a sodium atom that l ...
(pdf)
... vary slowly at these energies, and since uncertainties introduced by the isotropic assumption are no larger than those of the various collision processes. Heat loss mechanisms, such as collisional excitation and subsequent radiation, are neglected. As suggested in Nagy and Cravens (1981, 1988), the ...
... vary slowly at these energies, and since uncertainties introduced by the isotropic assumption are no larger than those of the various collision processes. Heat loss mechanisms, such as collisional excitation and subsequent radiation, are neglected. As suggested in Nagy and Cravens (1981, 1988), the ...
CH100: Fundamentals for Chemistry
... component substances by physical means only by a chemical process The breakdown of a pure substance results in formation of new substances (i.e. chemical change) For a pure substance there is nothing to separate (its only 1 substance to begin with) ...
... component substances by physical means only by a chemical process The breakdown of a pure substance results in formation of new substances (i.e. chemical change) For a pure substance there is nothing to separate (its only 1 substance to begin with) ...
Matter - tompkinsmath
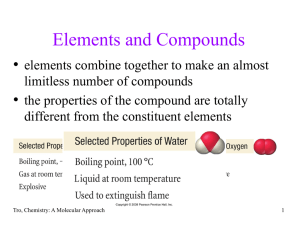
... a) Elements – substances composed of only one kind of atom which cannot be broken down using heat or electricity. Ex. Na, Br, O2, S8 b) Compounds – substances composed of 2 or more kinds of atoms and can be decomposed using heat or electricity. Ex. H2O, NaCl, C12H22O11 Mixtures – mixtures of pure su ...
... a) Elements – substances composed of only one kind of atom which cannot be broken down using heat or electricity. Ex. Na, Br, O2, S8 b) Compounds – substances composed of 2 or more kinds of atoms and can be decomposed using heat or electricity. Ex. H2O, NaCl, C12H22O11 Mixtures – mixtures of pure su ...
ZOONO TECHNICAL OVERVIEW
... obtained on PE and PP. Film formation on PTFE and other fluorinated substrates have not been reported. ...
... obtained on PE and PP. Film formation on PTFE and other fluorinated substrates have not been reported. ...
Book Proposal Form
... approval. For this, please fill out all questions of sections 1 and 2. Along with this Book Proposal Form, please provide the following material (if you have not already done so): - Your CV, including a detailed list of your previous ...
... approval. For this, please fill out all questions of sections 1 and 2. Along with this Book Proposal Form, please provide the following material (if you have not already done so): - Your CV, including a detailed list of your previous ...
C:\exams\June\June_06\chemistry\final\Chemistry 3202 June 2006
... Tl+ reacts spontaneously with Be but not with Co. What is the order of ions in terms of ...
... Tl+ reacts spontaneously with Be but not with Co. What is the order of ions in terms of ...
June 2000 Practice Diploma
... Use the following information to answer the next two questions. In order to “hide” gold during the Second World War, Nobel Prize winner Neils Bohr “dissolved” the gold, stored it in a solution, and recovered it at the end of the war. One way to “dissolve” gold is to react it with Aqua-Regia, a mixt ...
... Use the following information to answer the next two questions. In order to “hide” gold during the Second World War, Nobel Prize winner Neils Bohr “dissolved” the gold, stored it in a solution, and recovered it at the end of the war. One way to “dissolve” gold is to react it with Aqua-Regia, a mixt ...
A Review of High School Chemistry
... Dalton came along in the early 1800s and proposed that these elemental materials were made up of very small, indivisible particles he called ATOMS. Dalton was to provide the framework for a theory, which although not perfect, launched the modern age of chemistry and physics. Here are some ideas of D ...
... Dalton came along in the early 1800s and proposed that these elemental materials were made up of very small, indivisible particles he called ATOMS. Dalton was to provide the framework for a theory, which although not perfect, launched the modern age of chemistry and physics. Here are some ideas of D ...
Final Exam SG Part 1 (Unit 5).
... a. What molecule (black or white) is the limiting reactant? b. What is the ratio of black and white molecules to produce the products? c. How many moles are produced from the moles of the reactants? d. If you double the amount of white molecules (so now you have 8 pairs) but keep the same amount of ...
... a. What molecule (black or white) is the limiting reactant? b. What is the ratio of black and white molecules to produce the products? c. How many moles are produced from the moles of the reactants? d. If you double the amount of white molecules (so now you have 8 pairs) but keep the same amount of ...
Solution FRQs Practice
... particles in solution. Since the salt dissociates into 2 particles for every NaCl that dissolves, it will ___________ (increase/decrease) the boiling point more that an equal concentration of sugar (a molecular cpd) that does not dissociate or ionize. At _______ (high/low) temperatures and _________ ...
... particles in solution. Since the salt dissociates into 2 particles for every NaCl that dissolves, it will ___________ (increase/decrease) the boiling point more that an equal concentration of sugar (a molecular cpd) that does not dissociate or ionize. At _______ (high/low) temperatures and _________ ...
Chapter
... each line describes the number of electrons shared by the bonded atoms single line = 2 shared electrons, a single covalent bond double line = 4 shared electrons, a double covalent bond triple line = 6 shared electrons, a triple covalent bond ...
... each line describes the number of electrons shared by the bonded atoms single line = 2 shared electrons, a single covalent bond double line = 4 shared electrons, a double covalent bond triple line = 6 shared electrons, a triple covalent bond ...
The prebiotic molecules observed in the interstellar gas
... many of the interstellar grains have very specific structures, and are in fact large molecules. Determining just what those unknown structures are is a formidable challenge, because the refined spectroscopic techniques used to determine the structures of the known molecules are likely to fail at mol ...
... many of the interstellar grains have very specific structures, and are in fact large molecules. Determining just what those unknown structures are is a formidable challenge, because the refined spectroscopic techniques used to determine the structures of the known molecules are likely to fail at mol ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... referred as the atomic number. Hence, different atoms have different atomic numbers. The well-known periodic table summarizes this and other concepts about atoms. Thus, different atoms have distinct physical characteristics. In the sense of this book, the distinction of an atom is limited to the ato ...
... referred as the atomic number. Hence, different atoms have different atomic numbers. The well-known periodic table summarizes this and other concepts about atoms. Thus, different atoms have distinct physical characteristics. In the sense of this book, the distinction of an atom is limited to the ato ...
AP CHEMISTRY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT
... The Law of Conservation of Mass: mass is neither lost nor gained during an ordinary chemical reaction. In other words, the products of a reaction must have the same number of type of atoms as the reactants. Law of Definite Proportion: a given compound always contains exactly proportions of elements ...
... The Law of Conservation of Mass: mass is neither lost nor gained during an ordinary chemical reaction. In other words, the products of a reaction must have the same number of type of atoms as the reactants. Law of Definite Proportion: a given compound always contains exactly proportions of elements ...