Chemistry Olympiad Support Booklet
... thinking and trying to work out answers to unfamiliar questions – this is much more difficult. The recent Round 1 questions, which are contained in this booklet, are typical; they may seem ‘impossible’ at first sight, but the authors have tried to show how it is possible to work out the answers, som ...
... thinking and trying to work out answers to unfamiliar questions – this is much more difficult. The recent Round 1 questions, which are contained in this booklet, are typical; they may seem ‘impossible’ at first sight, but the authors have tried to show how it is possible to work out the answers, som ...
Chemistry Fall 2014 Review
... ____ 106. All of the following are steps in the scientific method except a. observing and recording data. b. forming a hypothesis. c. discarding data inconsistent with the hypothesis. d. making predictions based on a theory. ____ 107. Which of these statements about the scientific method is not true ...
... ____ 106. All of the following are steps in the scientific method except a. observing and recording data. b. forming a hypothesis. c. discarding data inconsistent with the hypothesis. d. making predictions based on a theory. ____ 107. Which of these statements about the scientific method is not true ...
THERMOCHEMISTRY
... · The Average Molecular Speed in the two containers becomes equal. · The temperatures of the two gases become equal. · A given quantity of heat will raise the temperature of a gas more if the sample is small. Reason: The Absolute Temperature is directly proportional to the Average Kinetic Energ ...
... · The Average Molecular Speed in the two containers becomes equal. · The temperatures of the two gases become equal. · A given quantity of heat will raise the temperature of a gas more if the sample is small. Reason: The Absolute Temperature is directly proportional to the Average Kinetic Energ ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... "too easy", and therefore may not have stimulated you to do your very best. This will not be the case in AP Chemistry. 2. AP Chemistry should allow you to achieve college credit while still enrolled in high school. This will save time and money. Some students who have passed the AP Exam elect to tak ...
... "too easy", and therefore may not have stimulated you to do your very best. This will not be the case in AP Chemistry. 2. AP Chemistry should allow you to achieve college credit while still enrolled in high school. This will save time and money. Some students who have passed the AP Exam elect to tak ...
percent composition and formulas
... left side and the correct formula(s) for the product(s) on the right side of the equation. Ethane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water C2H6 + O2 ...
... left side and the correct formula(s) for the product(s) on the right side of the equation. Ethane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water C2H6 + O2 ...
PowerPoint Notes
... 69.08 has four sig figs. 2. Zeroes at the beginning of a number are not significant. 0.0089 has two sig figs (8 and 9). 3. Zeroes at the end of a number and after the decimal point are significant. 2.50 has three sig figs. 25.00 has four sig figs. 4. Zeroes at the end of a number and before the deci ...
... 69.08 has four sig figs. 2. Zeroes at the beginning of a number are not significant. 0.0089 has two sig figs (8 and 9). 3. Zeroes at the end of a number and after the decimal point are significant. 2.50 has three sig figs. 25.00 has four sig figs. 4. Zeroes at the end of a number and before the deci ...
Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry Hybrid Orbitals Hybridization
... valence bond theory failed to correctly predict them. It is experimentally observed that bond angles in organic compounds are close to 109o, 120o, or 180o. According to Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory, electron pairs repel each other and the bonds and lone pairs around a central ...
... valence bond theory failed to correctly predict them. It is experimentally observed that bond angles in organic compounds are close to 109o, 120o, or 180o. According to Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory, electron pairs repel each other and the bonds and lone pairs around a central ...
Lesson 5 - Faculty Website Listing
... The existence of a particle in regions I & III is prohibited in classical physics as the kinetic energy in this region would be negative according to conservation of energy. However in quantum mechanics, the particle does have a non-zero probability of being located in such regions according to our ...
... The existence of a particle in regions I & III is prohibited in classical physics as the kinetic energy in this region would be negative according to conservation of energy. However in quantum mechanics, the particle does have a non-zero probability of being located in such regions according to our ...
Mathematical Chemistry
... enumeration schemes of chemistry where the matching is between mathematical objects (e.g., numbers) and chemical objects (e.g., structural isomers).23 However, anthropologists have suggested other origins, namely that counting arose in connection with primitive religious rituals.24 During the ritual ...
... enumeration schemes of chemistry where the matching is between mathematical objects (e.g., numbers) and chemical objects (e.g., structural isomers).23 However, anthropologists have suggested other origins, namely that counting arose in connection with primitive religious rituals.24 During the ritual ...
CYPRUS
... Course lectures are in Greek and the students must take a final exam for each course. The final grade results from a combination of homework grades, intermediate (mid-term) exams, literature projects or laboratory reports. There are no prerequisite courses, but in a series of related courses (e.g., ...
... Course lectures are in Greek and the students must take a final exam for each course. The final grade results from a combination of homework grades, intermediate (mid-term) exams, literature projects or laboratory reports. There are no prerequisite courses, but in a series of related courses (e.g., ...
syllabus details - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... energies, electronegativity and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs), halogens (F I) and period 3 elements (Na Ar). ...
... energies, electronegativity and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs), halogens (F I) and period 3 elements (Na Ar). ...
Sub Unit Plan 1 Chem Periodic Table
... II.4 Elements can be differentiated by their physical properties. Physical properties of substances, such as density, conductivity, malleability, solubility, and hardness, differ among elements. (3.1w) II.5 Elements can be differentiated by chemical properties. Chemical properties describe how an el ...
... II.4 Elements can be differentiated by their physical properties. Physical properties of substances, such as density, conductivity, malleability, solubility, and hardness, differ among elements. (3.1w) II.5 Elements can be differentiated by chemical properties. Chemical properties describe how an el ...
Medicinal Chemistry
... pharmacy - the department of medicinal chemistry consists of a diverse group of faculty members phd graduate students postdoctoral fellows and research scientists working at, the essential medicinal chemistry of curcumin journal of - department of medicinal chemistry institute for therapeutics disco ...
... pharmacy - the department of medicinal chemistry consists of a diverse group of faculty members phd graduate students postdoctoral fellows and research scientists working at, the essential medicinal chemistry of curcumin journal of - department of medicinal chemistry institute for therapeutics disco ...
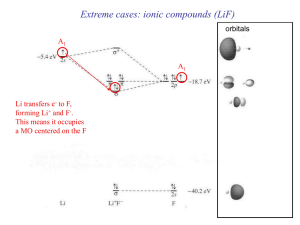
Molecular geometry
... X. VB versus MO Quantum-Mechanical Approximation Technique Perturbation theory (used in valence bond theory): A complex system (such as a molecule) is viewed as a simpler system (such as two atoms) that is slightly altered or perturbed by some additional force or interaction (such as the intera ...
... X. VB versus MO Quantum-Mechanical Approximation Technique Perturbation theory (used in valence bond theory): A complex system (such as a molecule) is viewed as a simpler system (such as two atoms) that is slightly altered or perturbed by some additional force or interaction (such as the intera ...
Teaching plan Modelling of Organs and Systems (MOS)
... From Hunter et al., Nature Review 2003. Multi-scale modelling of biological systems requires the development of mathematical and engineering tools that can describe in a realistic way the structure and function of the different components of the system and integrated them into a common reference at ...
... From Hunter et al., Nature Review 2003. Multi-scale modelling of biological systems requires the development of mathematical and engineering tools that can describe in a realistic way the structure and function of the different components of the system and integrated them into a common reference at ...
CHEM1901/3 Tutorials The problem sheets on the following pages
... the course they are told that mass is neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. This principle is the basis for determining compound formulas and performing stoichiometric calculations. When thermochemistry is introduced, students learn that energy, too, cannot be created or destroyed, al ...
... the course they are told that mass is neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. This principle is the basis for determining compound formulas and performing stoichiometric calculations. When thermochemistry is introduced, students learn that energy, too, cannot be created or destroyed, al ...