book chapter on saddle point searches
... a search for the optimal transition mechanism. We discuss a recently proposed method that can be used in such cases, the Dimer method. ...
... a search for the optimal transition mechanism. We discuss a recently proposed method that can be used in such cases, the Dimer method. ...
Structure and Properties of Matter
... out are elements. Antoine Laurent Lavoisier (1743-94), a French chemist was first to explain an element. He defined an element as basic form of matter that cannot be broken down into simpler substances even by chemical means. Elements serve as the building blocks for various types of other substance ...
... out are elements. Antoine Laurent Lavoisier (1743-94), a French chemist was first to explain an element. He defined an element as basic form of matter that cannot be broken down into simpler substances even by chemical means. Elements serve as the building blocks for various types of other substance ...
Document
... Designing an appropiate method in order to support or reject the proposed hypothesis and answer the given research question brought various problems with it. One of the biggest problems was the lack of chemicals. I did not have the all chemicals to synthesise all complexes in the spectrochemical ser ...
... Designing an appropiate method in order to support or reject the proposed hypothesis and answer the given research question brought various problems with it. One of the biggest problems was the lack of chemicals. I did not have the all chemicals to synthesise all complexes in the spectrochemical ser ...
Significant Figures Calculations Worksheet
... 349 cm + 1.10 cm + 100 cm = 500 cm (rounded from 450.1 cm because 100 cm is precise only to the nearest hundred cm) ...
... 349 cm + 1.10 cm + 100 cm = 500 cm (rounded from 450.1 cm because 100 cm is precise only to the nearest hundred cm) ...
Chemistry
... Gaseous state: Kinetic molecular model of a gas: postulates and derivation of the kinetic gas equation; collision frequency; collision diameter; mean free path and viscosity of gases, including their temperature and pressure dependence, relation between mean free path and coefficient of viscosity, c ...
... Gaseous state: Kinetic molecular model of a gas: postulates and derivation of the kinetic gas equation; collision frequency; collision diameter; mean free path and viscosity of gases, including their temperature and pressure dependence, relation between mean free path and coefficient of viscosity, c ...
Chemical Equations and Stoichiometry
... Revolution. Hydrogen would be a more environmentally-friendly fuel. Based on what you know about chemistry, would hydrogen burn to produce .... ...
... Revolution. Hydrogen would be a more environmentally-friendly fuel. Based on what you know about chemistry, would hydrogen burn to produce .... ...
aq - Wikispaces
... The table on the left gives the eight most commonly used prefixes in the metric system. It also includes five rows that do not have prefixes. The middle row is for the unit: metre, litre, gram, newton, or any other legal metric unit. ...
... The table on the left gives the eight most commonly used prefixes in the metric system. It also includes five rows that do not have prefixes. The middle row is for the unit: metre, litre, gram, newton, or any other legal metric unit. ...
CHEMISTRY
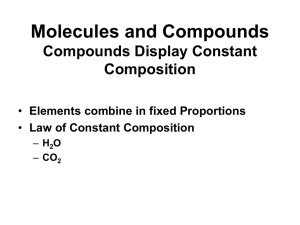
... A mixture of substances is considered homogeneous if the mixture has the same physical and chemical properties throughout it. A homogeneous mixture is also called a solution. An element is a substance that contains only one kind of atom. A compound is a substance with two or more kinds of atoms comb ...
... A mixture of substances is considered homogeneous if the mixture has the same physical and chemical properties throughout it. A homogeneous mixture is also called a solution. An element is a substance that contains only one kind of atom. A compound is a substance with two or more kinds of atoms comb ...
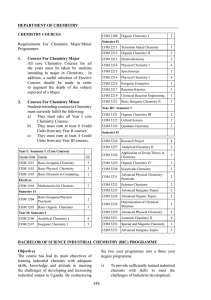
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY Requirements For Chemistry Major
... Courses For Chemistry Major All core Chemistry Courses for all the years must be taken by students intending to major in Chemistry. In addition, a useful selection of Elective Courses should be made in order to augment the depth of the subject expected of a Major. ...
... Courses For Chemistry Major All core Chemistry Courses for all the years must be taken by students intending to major in Chemistry. In addition, a useful selection of Elective Courses should be made in order to augment the depth of the subject expected of a Major. ...
X - EGR 115!
... Numerical methods are techniques used to find quantitative solutions to mathematical problems. Many numerical methods are iterative solutions – this means that the technique is applied over and over, gradually getting closer (i.e. converging) on the final answer. Iterative solutions are complete whe ...
... Numerical methods are techniques used to find quantitative solutions to mathematical problems. Many numerical methods are iterative solutions – this means that the technique is applied over and over, gradually getting closer (i.e. converging) on the final answer. Iterative solutions are complete whe ...
UNIVERSITY OF DELHI FACULTY OF SCIENCE SYLLABUS OF COURSES TO BE OFFERED
... efficiency and excellence in the Higher Education System of country. The important measures taken to enhance academic standards and quality in higher education include innovation and improvements in curriculum, teaching-learning process, examination and evaluation systems, besides governance and oth ...
... efficiency and excellence in the Higher Education System of country. The important measures taken to enhance academic standards and quality in higher education include innovation and improvements in curriculum, teaching-learning process, examination and evaluation systems, besides governance and oth ...
8 theoretical problems 2 practical problems
... 2.3 Recent quantum chemical calculations have shown that the overall reaction activation energies for the two proposals are: ...
... 2.3 Recent quantum chemical calculations have shown that the overall reaction activation energies for the two proposals are: ...
physical setting chemistry
... Base your answers to questions 71 through 74 on the passage below. Acid rain lowers the pH in ponds and lakes and over time can cause the death of some aquatic life. Acid rain is caused in large part by the burning of fossil fuels in power plants and by gasoline-powered vehicles. The acids commonly ...
... Base your answers to questions 71 through 74 on the passage below. Acid rain lowers the pH in ponds and lakes and over time can cause the death of some aquatic life. Acid rain is caused in large part by the burning of fossil fuels in power plants and by gasoline-powered vehicles. The acids commonly ...
Summary - Clydebank High School
... 1. In an ............................................... reaction heat energy is released to the surroundings. In an ............................................... reaction heat energy is absorbed from the surroundings. 2. In an exothermic reaction the reactants have ........................... sto ...
... 1. In an ............................................... reaction heat energy is released to the surroundings. In an ............................................... reaction heat energy is absorbed from the surroundings. 2. In an exothermic reaction the reactants have ........................... sto ...
CHAPTER 10
... are the polar CCl bonds. The molecules shown in (b) and (d) are nonpolar. Due to the high symmetry of the molecules and the equal magnitude of the bond moments, the bond moments in each molecule cancel one another. The resultant dipole moment will be zero. For the molecules shown in (a) and (c), th ...
... are the polar CCl bonds. The molecules shown in (b) and (d) are nonpolar. Due to the high symmetry of the molecules and the equal magnitude of the bond moments, the bond moments in each molecule cancel one another. The resultant dipole moment will be zero. For the molecules shown in (a) and (c), th ...