mass mass calc
... Solution #1 shows the pattern most often used by students in this course because it tends to be the one that is the most flexible when new problems are presented later on. Choose one of the three methods that suits you best or make up your own. Regardless of how you choose to solve these problems, b ...
... Solution #1 shows the pattern most often used by students in this course because it tends to be the one that is the most flexible when new problems are presented later on. Choose one of the three methods that suits you best or make up your own. Regardless of how you choose to solve these problems, b ...
Part II - American Chemical Society
... a. The Mg2+ ion is smaller and has a higher charge than the Mg+ ion, so the lattice energy that arises when Mg2+ ions form compounds is much greater than what would be observed if Mg+ ions formed compounds. The increase in lattice energy more than offsets the larger ionization energy of the Mg2+ ion ...
... a. The Mg2+ ion is smaller and has a higher charge than the Mg+ ion, so the lattice energy that arises when Mg2+ ions form compounds is much greater than what would be observed if Mg+ ions formed compounds. The increase in lattice energy more than offsets the larger ionization energy of the Mg2+ ion ...
Chemical Compounds
... 4. The oxidation state of hydrogen is generally +1 except when it is bonded to metals such as sodium (NaH) in which case it's oxidation number is -1. 5. Fluorine has an oxidation number of -1 in its compounds … always. Group 1 elements have an oxidation number of +1 in their compounds … always. Grou ...
... 4. The oxidation state of hydrogen is generally +1 except when it is bonded to metals such as sodium (NaH) in which case it's oxidation number is -1. 5. Fluorine has an oxidation number of -1 in its compounds … always. Group 1 elements have an oxidation number of +1 in their compounds … always. Grou ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... -The starting substances, called reactants (left side of the equation) - The substances produced in the reaction, called products (appear on the right side of the equation) - The number in front of the chemical formulas are Stoichiometry coefficients. © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... -The starting substances, called reactants (left side of the equation) - The substances produced in the reaction, called products (appear on the right side of the equation) - The number in front of the chemical formulas are Stoichiometry coefficients. © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Student Solutions Manual Errata
... spheres in the diagram) as being separate from, but strongly attracted to, one another. Covalent bonding occurs when two atoms are mutually attracted to a pair (or pairs) of electrons. Because the atoms share the electrons, we can think of the atoms (or the spheres in the diagram) as being joined to ...
... spheres in the diagram) as being separate from, but strongly attracted to, one another. Covalent bonding occurs when two atoms are mutually attracted to a pair (or pairs) of electrons. Because the atoms share the electrons, we can think of the atoms (or the spheres in the diagram) as being joined to ...
Kinetics Simulations of the Neutralizing Capacity of Silicate Minerals
... drainage based on rate information from the literature and little or no site-specific information other than mineralogy. Second, we wanted to investigate through a series of calculations of rates of silicate mineral dissolution relative to rates of abiotic pyrite oxidation by dissolved O2 the extent ...
... drainage based on rate information from the literature and little or no site-specific information other than mineralogy. Second, we wanted to investigate through a series of calculations of rates of silicate mineral dissolution relative to rates of abiotic pyrite oxidation by dissolved O2 the extent ...
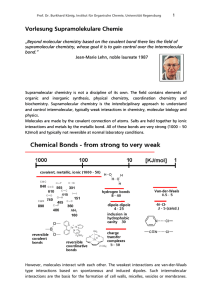
Vorlesung Supramolekulare Chemie
... Supramolecular chemistry is not a discipline of its own. The field contains elements of organic and inorganic synthesis, physical chemistry, coordination chemistry and biochemistry. Supramolecular chemistry is the interdisciplinary approach to understand and control intermolecular, typically weak in ...
... Supramolecular chemistry is not a discipline of its own. The field contains elements of organic and inorganic synthesis, physical chemistry, coordination chemistry and biochemistry. Supramolecular chemistry is the interdisciplinary approach to understand and control intermolecular, typically weak in ...
Reaction rate theory: What it was, where is it today, and where is it
... understanding the critical factors which determine rates away from equilibrium. The nonequilibrium quantum theory is even less well developed than the classical, and suffers from the fact that even today, we do not know how to solve the real time quantum dynamics for systems with “many” degrees of f ...
... understanding the critical factors which determine rates away from equilibrium. The nonequilibrium quantum theory is even less well developed than the classical, and suffers from the fact that even today, we do not know how to solve the real time quantum dynamics for systems with “many” degrees of f ...
AP Chemistry - Notes
... b. conservation of atoms (mass) - atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions, they are recombined to form different substances - mass is neither created nor destroyed chemical reactions (as opposed to nuclear reactions) - chemical reactions must therefore be balanced - have same k ...
... b. conservation of atoms (mass) - atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions, they are recombined to form different substances - mass is neither created nor destroyed chemical reactions (as opposed to nuclear reactions) - chemical reactions must therefore be balanced - have same k ...
A Nonlinear Programming Algorithm for Solving Semidefinite
... Q2 What optimization method is best suited for (2)? In particular, can the optimization method exploit sparsity in the problem data? Q2 Since (2) is a nonconvex programming problem, can we even expect to find a global solution in practice? To answer Q1, we appeal to a theorem that posits the existen ...
... Q2 What optimization method is best suited for (2)? In particular, can the optimization method exploit sparsity in the problem data? Q2 Since (2) is a nonconvex programming problem, can we even expect to find a global solution in practice? To answer Q1, we appeal to a theorem that posits the existen ...
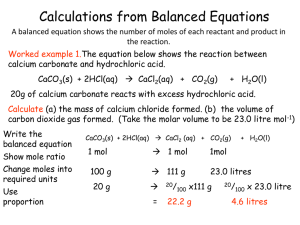
Stoichiometry and the Mole
... with the plan to network the printers together. How many laser printers did the administration have to buy? It is rather simple to show that 26 laser printers are needed for all the employees. However, what if a chemist was calculating quantities for a chemical reaction? Interestingly enough, simila ...
... with the plan to network the printers together. How many laser printers did the administration have to buy? It is rather simple to show that 26 laser printers are needed for all the employees. However, what if a chemist was calculating quantities for a chemical reaction? Interestingly enough, simila ...
university of zagreb - Hrvatsko fizikalno društvo
... explanation of natural phenomena and processes which take place in our environment, as well as at most distant points of the Universe. Physics contributes to the development of other natural sciences, biomedicine and technology very much. Recently the physics methods are successfully applied in othe ...
... explanation of natural phenomena and processes which take place in our environment, as well as at most distant points of the Universe. Physics contributes to the development of other natural sciences, biomedicine and technology very much. Recently the physics methods are successfully applied in othe ...
Feature selection and extraction
... ■ Decision tree reaches its lowest error (4.7 %) whenever PL and PW are among the ...
... ■ Decision tree reaches its lowest error (4.7 %) whenever PL and PW are among the ...
The d- and f- Block Element Block Elements The d- and f
... decrease in radius with increasing atomic number. This is because the new electron enters a d orbital each time the nuclear charge increases by unity. It may be recalled that the shielding effect of a d electron is not that effective, hence the net electrostatic attraction between the nuclear charge ...
... decrease in radius with increasing atomic number. This is because the new electron enters a d orbital each time the nuclear charge increases by unity. It may be recalled that the shielding effect of a d electron is not that effective, hence the net electrostatic attraction between the nuclear charge ...
Personal Tutoring Help on Questions and Problems
... * can be prepared by the thermal decomposition of ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3). The other product is H2O. (a) Write a balanced equation for this reaction. (b) How many grams of N2O are formed if 0.46 mole of NH4NO3 is used in the reaction? 3.77 The fertilizer ammonium sulfate [(NH4)2SO4] is prepared by ...
... * can be prepared by the thermal decomposition of ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3). The other product is H2O. (a) Write a balanced equation for this reaction. (b) How many grams of N2O are formed if 0.46 mole of NH4NO3 is used in the reaction? 3.77 The fertilizer ammonium sulfate [(NH4)2SO4] is prepared by ...
Mole and Energy - Deans Community High School
... Index for the various types of calculations in higher chemistry ...
... Index for the various types of calculations in higher chemistry ...
OCR A Level Chemistry A H432 Specification
... Teaching of practical skills is integrated with the theoretical topics and they’re assessed both through written papers and, for A level only, the Practical Endorsement. Chemistry B (Salters) – a context-led approach. Learners study chemistry in a range of different contexts, conveying the excitemen ...
... Teaching of practical skills is integrated with the theoretical topics and they’re assessed both through written papers and, for A level only, the Practical Endorsement. Chemistry B (Salters) – a context-led approach. Learners study chemistry in a range of different contexts, conveying the excitemen ...