January 2016 - Stony Brook University
... in COMPUTATIONAL APPLIED MATHEMATICS Spring 2016 (January) (CLOSED BOOK EXAM) This is a two part exam. In part A, solve 4 out of 5 problems for full credit. In part B, solve 4 out of 5 problems for full credit. Indicate below which problems you have attempted by circling the appropriate numbers: Par ...
... in COMPUTATIONAL APPLIED MATHEMATICS Spring 2016 (January) (CLOSED BOOK EXAM) This is a two part exam. In part A, solve 4 out of 5 problems for full credit. In part B, solve 4 out of 5 problems for full credit. Indicate below which problems you have attempted by circling the appropriate numbers: Par ...
study guide first semester chemistry
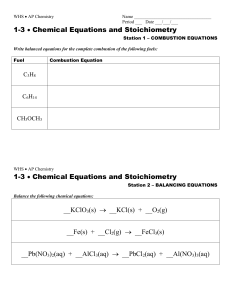
... 1. Write the balanced equation for the following: (include the state of each reactant and product) a. magnesium reacts with nitrogen to produce magnesium nitride. (3Mg(s) + N2(g) Mg3N2(s) b. silver nitrate reacts with copper to form copper(II) nitrate and silver. ...
... 1. Write the balanced equation for the following: (include the state of each reactant and product) a. magnesium reacts with nitrogen to produce magnesium nitride. (3Mg(s) + N2(g) Mg3N2(s) b. silver nitrate reacts with copper to form copper(II) nitrate and silver. ...
Recitation 3 - MIT OpenCourseWare
... first used where the wave functions become infinite dimensional wave vectors and the Hamiltonian an infinite dimensional matrix. In special cases where there are only a finite possible number of states for a system such as the 2 spin states for a single fermion, then these wave vectors can be repres ...
... first used where the wave functions become infinite dimensional wave vectors and the Hamiltonian an infinite dimensional matrix. In special cases where there are only a finite possible number of states for a system such as the 2 spin states for a single fermion, then these wave vectors can be repres ...
Chemistry Review: Unit2 - Menno Simons Christian School
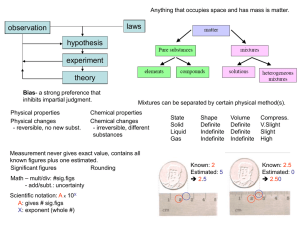
... Heat is produced or absorbed, starting material is used up, there is a change in colour, a material with new properties is formed, gas bubbles form in a liquid, a precipitate forms in a liquid and the change is difficult to reverse. 7) In the table below list whether there is a chemical or physical ...
... Heat is produced or absorbed, starting material is used up, there is a change in colour, a material with new properties is formed, gas bubbles form in a liquid, a precipitate forms in a liquid and the change is difficult to reverse. 7) In the table below list whether there is a chemical or physical ...
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE
... 54. explain the properties of gases using the kinetic-molecular theory. 55. use the gas laws to describe how gases behave. 56. explain how Dalton’s law of partial pressures relates to mixtures of gases. 57. explain why kinetics is important in understanding reactions. 58. explain what happens on a m ...
... 54. explain the properties of gases using the kinetic-molecular theory. 55. use the gas laws to describe how gases behave. 56. explain how Dalton’s law of partial pressures relates to mixtures of gases. 57. explain why kinetics is important in understanding reactions. 58. explain what happens on a m ...
Electron Correlation
... The concept of electrons avoiding each other, is called the dynamical correlation, but there is also a more subtle effect called nondynamical or static correlation energy. Nondynamical correlation energy reflects the inadequacy of a single reference in describing a given molecular state, and is due ...
... The concept of electrons avoiding each other, is called the dynamical correlation, but there is also a more subtle effect called nondynamical or static correlation energy. Nondynamical correlation energy reflects the inadequacy of a single reference in describing a given molecular state, and is due ...
Chemistry 30 Notes - Heat of Formation February 2nd
... If you have trouble converting mass into moles, better dig out your old Chemistry 20 notes or textbook and review. Chemistry 30 will require you to remember this basic chemistry skill! Step 2: Determine kJ for 0.390 mol We know from the question that 297 kJ of energy is released for 1 mole of SO2 — ...
... If you have trouble converting mass into moles, better dig out your old Chemistry 20 notes or textbook and review. Chemistry 30 will require you to remember this basic chemistry skill! Step 2: Determine kJ for 0.390 mol We know from the question that 297 kJ of energy is released for 1 mole of SO2 — ...
energy levels of a hydrogen atom in crossed electric and
... where {3 1 and {3 2 are the angles between the vector H and the vectors w1 and W 2 • Thus, the level shift is given by the sum of expressions (7), (14), (15) and the spin term, accurate to terms cubic in the fields. 4. We consider several special cases, limiting the discussion to first-order perturb ...
... where {3 1 and {3 2 are the angles between the vector H and the vectors w1 and W 2 • Thus, the level shift is given by the sum of expressions (7), (14), (15) and the spin term, accurate to terms cubic in the fields. 4. We consider several special cases, limiting the discussion to first-order perturb ...
South Pasadena · AP Chemistry
... Give examples of empirical formulas and molecular formulas. Identify a formula as empirical or molecular. Calculate the empirical formula from mass percentages or mass data. Determine the molecular formula of a compound given its empirical formula and molar mass. ...
... Give examples of empirical formulas and molecular formulas. Identify a formula as empirical or molecular. Calculate the empirical formula from mass percentages or mass data. Determine the molecular formula of a compound given its empirical formula and molar mass. ...
Ch. 3 9-Station Review
... Copper metal is Cu( ). A solution of cupric chloride is CuCl2( ). Melted iron is Fe( ). Salt water is NaCl( ). Helium is He( ). Dry ice is CO2( ). Steam is H2O( ). ...
... Copper metal is Cu( ). A solution of cupric chloride is CuCl2( ). Melted iron is Fe( ). Salt water is NaCl( ). Helium is He( ). Dry ice is CO2( ). Steam is H2O( ). ...
Answer on Question #63998 - Chemistry
... 1) The first ionisation energy is the energy required to remove the most loosely held electron from one mole of gaseous atoms to produce 1 mole of gaseous ions each with a charge of 1+ For example: K + energy = K+ + e‒ Ionisation energy is a measure of the energy needed to pull a particular electron ...
... 1) The first ionisation energy is the energy required to remove the most loosely held electron from one mole of gaseous atoms to produce 1 mole of gaseous ions each with a charge of 1+ For example: K + energy = K+ + e‒ Ionisation energy is a measure of the energy needed to pull a particular electron ...
chemia simr01 en - Leszek Niedzicki
... SO42-, PO43-, CN-, NH4+… and of course all larger molecules as well. ...
... SO42-, PO43-, CN-, NH4+… and of course all larger molecules as well. ...
Workshop #4 Answers
... Use the balanced equation below to solve the following problems: 2 KMnO4 + 16 HCl → 5 Cl2 + 2 KCl + 2 MnCl2 + 8 H2O (a) ...
... Use the balanced equation below to solve the following problems: 2 KMnO4 + 16 HCl → 5 Cl2 + 2 KCl + 2 MnCl2 + 8 H2O (a) ...
effective nuclear charge
... both Zn atoms and Zn2+ ions are diamagnetic, showing that the two 4s electrons are lost before the 3d Zn atoms [Ar]4s23d10 Zn2+ ions [Ar]4s03d10 ...
... both Zn atoms and Zn2+ ions are diamagnetic, showing that the two 4s electrons are lost before the 3d Zn atoms [Ar]4s23d10 Zn2+ ions [Ar]4s03d10 ...
Chapter 3
... The Bohr was limited. Erwin Schodinger in 1926 developed a mathematical treatment into which both the wave and particle nature of matter could be incorporated. This is known as quantum mechanics. ...
... The Bohr was limited. Erwin Schodinger in 1926 developed a mathematical treatment into which both the wave and particle nature of matter could be incorporated. This is known as quantum mechanics. ...