What is the target tissue of ACTH and what does it do? 1.1. Target
... Estrogen overrides the system 24 hours before ovulation when the Graafian follicle that is pushing against the ovary sends a signal that the ovum is ready for ovulation by dumping all of its remaining estrogen into the bloodstream. This very high level of estrogen stimulates GnRH release which then ...
... Estrogen overrides the system 24 hours before ovulation when the Graafian follicle that is pushing against the ovary sends a signal that the ovum is ready for ovulation by dumping all of its remaining estrogen into the bloodstream. This very high level of estrogen stimulates GnRH release which then ...
Document
... Receptor resembles growth hormone receptor Increases milk production Maintains corpus luteum Inhibits ovary ...
... Receptor resembles growth hormone receptor Increases milk production Maintains corpus luteum Inhibits ovary ...
Lecture 2
... Endocrine System • Consists of ductless endocrine glands scattered throughout body • Glands secrete hormones travel through blood to target cells – Target cells have receptors for binding with specific hormone – Regulates or directs particular function • Two hormone categories based on solubility 1) ...
... Endocrine System • Consists of ductless endocrine glands scattered throughout body • Glands secrete hormones travel through blood to target cells – Target cells have receptors for binding with specific hormone – Regulates or directs particular function • Two hormone categories based on solubility 1) ...
Endocrine System
... lymphocytes into T-cells that play an important part in fighting infections and disease. The adrenal glands release hormones which have important effects on the way in which energy is stored and food is used and on chemicals in the blood. The pancreas gland secretes digestive juices which break down ...
... lymphocytes into T-cells that play an important part in fighting infections and disease. The adrenal glands release hormones which have important effects on the way in which energy is stored and food is used and on chemicals in the blood. The pancreas gland secretes digestive juices which break down ...
iphy 3430 12-8
... Does not have target organ that secretes its own hormone. Controls growth after birth (via somatomedins) 1. Growth of bone 2. Growth of soft tissues 3. Stimulates protein synthesis (uptake of amino acids and inhibition of protein degredation) 4. Synergistic with thyroid hormone ...
... Does not have target organ that secretes its own hormone. Controls growth after birth (via somatomedins) 1. Growth of bone 2. Growth of soft tissues 3. Stimulates protein synthesis (uptake of amino acids and inhibition of protein degredation) 4. Synergistic with thyroid hormone ...
Endocrine System
... Cortisol and cortisone affect the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins by trying to maintain the body's carbohydrate reserve c. Catabolic effect on protein, cause the breakdown of amino acids with conversion to glucose, cause the deposition of glycogen in the liver, mobilization and oxidat ...
... Cortisol and cortisone affect the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins by trying to maintain the body's carbohydrate reserve c. Catabolic effect on protein, cause the breakdown of amino acids with conversion to glucose, cause the deposition of glycogen in the liver, mobilization and oxidat ...
Ch 18 Lesson 1 - Aurora City Schools
... * Cells in your body respond to messages sent by three of your major body systems- the nervous system, the immune system, and the endocrine system* Endocrine system- main function is to regulate growth and development; very important during the teen years Structure of the Endocrine System: _______ ...
... * Cells in your body respond to messages sent by three of your major body systems- the nervous system, the immune system, and the endocrine system* Endocrine system- main function is to regulate growth and development; very important during the teen years Structure of the Endocrine System: _______ ...
Increasing impact of oestrogen pollution through climate change
... To determine the potential impact of climate change, the researchers used three different scenarios based on the UK Met Office’s 2009 UK Climate Projections: average, wet and dry. These scenarios differ in average annual rainfall and river flows. The authors also accounted for differences in river t ...
... To determine the potential impact of climate change, the researchers used three different scenarios based on the UK Met Office’s 2009 UK Climate Projections: average, wet and dry. These scenarios differ in average annual rainfall and river flows. The authors also accounted for differences in river t ...
Chapter 45 Essentials
... neurohormone, simple neuroendocrine, feedback loop, negative feedback Concept Check- 1,2,3 45.2 Hormones and other chemical signals bind to target cell receptors, initiating pathways the culminate in specific cell responses Intro- bloodstream, proteins, peptides, amines, steroids Cell Surface Re ...
... neurohormone, simple neuroendocrine, feedback loop, negative feedback Concept Check- 1,2,3 45.2 Hormones and other chemical signals bind to target cell receptors, initiating pathways the culminate in specific cell responses Intro- bloodstream, proteins, peptides, amines, steroids Cell Surface Re ...
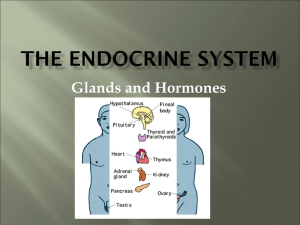
The Endocrine System
... helps control your heart beat and breathing rate. testes: Produces male reproductive hormones like testosterone. ...
... helps control your heart beat and breathing rate. testes: Produces male reproductive hormones like testosterone. ...
Women’s Health
... in postmenopausal women •Can be made from belly fat; in excess increasing risk for heart disease and breast cancer ...
... in postmenopausal women •Can be made from belly fat; in excess increasing risk for heart disease and breast cancer ...
Lecture 11. Role of endocrinic glands in regulation of body functions
... It was only after the 1960s that scientists discovered that the pineal gland is responsible for the production of melatonin, which is regulated in a circadian rhythm. Melatonin is a derivative of the amino acid tryptophan, which also has other functions in the Central Nervous System. The production ...
... It was only after the 1960s that scientists discovered that the pineal gland is responsible for the production of melatonin, which is regulated in a circadian rhythm. Melatonin is a derivative of the amino acid tryptophan, which also has other functions in the Central Nervous System. The production ...
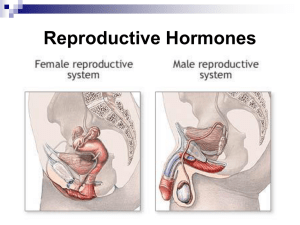
Female Reproductive System
... Anterior pituitary produces and stores: The anterior pituitary produces six major hormones, and the posterior pituitary stores two hormones originating in the hypothalamus. The pituitary's target endocrine glands are the thyroid, adrenal gland, and the gonads. Through these glands it Controls on t ...
... Anterior pituitary produces and stores: The anterior pituitary produces six major hormones, and the posterior pituitary stores two hormones originating in the hypothalamus. The pituitary's target endocrine glands are the thyroid, adrenal gland, and the gonads. Through these glands it Controls on t ...
The Endocrine System
... C. Regulates sleep, hibernation (animals), aging “sociological” or “biological clock ...
... C. Regulates sleep, hibernation (animals), aging “sociological” or “biological clock ...
Environmental Health & Toxicology
... • Should we set safety limits to protect all including most sensitive or just the average person? • By protecting all, it might cost more money… ...
... • Should we set safety limits to protect all including most sensitive or just the average person? • By protecting all, it might cost more money… ...
FEMALE HORMONES and their activity
... Testosterone is responsible for much more than defining sexual characteristics in men or influencing sex drive. Testosterone is essential for life since it helps to regulate basic metabolism. Testosterone also facilitates protein synthesis and the building of body tissues. Testosterone is produced b ...
... Testosterone is responsible for much more than defining sexual characteristics in men or influencing sex drive. Testosterone is essential for life since it helps to regulate basic metabolism. Testosterone also facilitates protein synthesis and the building of body tissues. Testosterone is produced b ...
What are some of the major hormones released by the endocrine
... Increases levels of blood glucose, accelerates protein metabolism, produces anti-imflammatory effect. ...
... Increases levels of blood glucose, accelerates protein metabolism, produces anti-imflammatory effect. ...
Desalination as a Health Hazard
... implemented in the 1970's. The toxicologic testing that was done was only animal testing for acute effects. There was little or no testing for chronic or hormone disrupting multigenerational toxic effects. None of the toxicologic testing was done on the combinations of the multiplicity of chemicals ...
... implemented in the 1970's. The toxicologic testing that was done was only animal testing for acute effects. There was little or no testing for chronic or hormone disrupting multigenerational toxic effects. None of the toxicologic testing was done on the combinations of the multiplicity of chemicals ...
Endocrine System
... source of female hormones (estrogen and progesterone). These hormones control the development of female body characteristics, such as the breasts, body shape, and body hair. The ovaries also regulate the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. ...
... source of female hormones (estrogen and progesterone). These hormones control the development of female body characteristics, such as the breasts, body shape, and body hair. The ovaries also regulate the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. ...
File
... Attached to posterior thyroid…. Produce PARATHORMONE which helps control blood calcium level, prevents hypocalcemia THYMUS…. Endocrine gland and lymphatic organ Located behind the ________, above and in front of the ______________ Begins to disappear at _________ ADRENAL GLANDS Located on to ...
... Attached to posterior thyroid…. Produce PARATHORMONE which helps control blood calcium level, prevents hypocalcemia THYMUS…. Endocrine gland and lymphatic organ Located behind the ________, above and in front of the ______________ Begins to disappear at _________ ADRENAL GLANDS Located on to ...
endocrinesystemshort
... chemical structure. A hormone interacts only with specific target cells the way a key fits into a lock. Hormones travel through the bloodstream until they find their “lock” or particular cell type. ...
... chemical structure. A hormone interacts only with specific target cells the way a key fits into a lock. Hormones travel through the bloodstream until they find their “lock” or particular cell type. ...