Hormones and Target Cells
... 2. Skeletal muscle cells and liver cells: With glucagon’s help, glycogen is broken down into glucose. Muscle cells retain all the glucose they derive from this process, using it to power their own activities. Liver cells, meanwhile, move much of the glucose they liberate into general circulation. ...
... 2. Skeletal muscle cells and liver cells: With glucagon’s help, glycogen is broken down into glucose. Muscle cells retain all the glucose they derive from this process, using it to power their own activities. Liver cells, meanwhile, move much of the glucose they liberate into general circulation. ...
Lymphatic System
... • Four small glands attached to the back side of the thyroid gland. • Produce hormone that maintains the balance of calcium and phosphorus in the blood ...
... • Four small glands attached to the back side of the thyroid gland. • Produce hormone that maintains the balance of calcium and phosphorus in the blood ...
File
... and proteins into glucose to have available for increased cellular respiration. Or if the body’s damaged, the energy goes to the repair site. ...
... and proteins into glucose to have available for increased cellular respiration. Or if the body’s damaged, the energy goes to the repair site. ...
Endocrine Labs
... A. Identify the major endocrine glands in the body B. List the hormones produced by the glands C. View, draw, and label microscope slides of selected glands II. Identify the following endocrine glands on the models and in a cat, if visible. List the hormones secreted by each gland A. Brain models 1. ...
... A. Identify the major endocrine glands in the body B. List the hormones produced by the glands C. View, draw, and label microscope slides of selected glands II. Identify the following endocrine glands on the models and in a cat, if visible. List the hormones secreted by each gland A. Brain models 1. ...
Endocrine Quiz Review
... -Autocrines: Act on cells that secrete them vs. Paracrines: Act on cells nearby -Endocrine glands become less effective with age Hormones: Steroid or amino acid based -Stimulate or inhibit target cell -Mechanisms: alter membrane permeability, enzyme synthesis, secretion, and mitosis -Many interact w ...
... -Autocrines: Act on cells that secrete them vs. Paracrines: Act on cells nearby -Endocrine glands become less effective with age Hormones: Steroid or amino acid based -Stimulate or inhibit target cell -Mechanisms: alter membrane permeability, enzyme synthesis, secretion, and mitosis -Many interact w ...
Endocrine System Hormones
... • The endocrine system consists of a group of organs (sometimes referred to as glands of internal secretion) whose main function is to produce and secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. Hormones serve as messengers to coordinate activities of various parts of the body. ...
... • The endocrine system consists of a group of organs (sometimes referred to as glands of internal secretion) whose main function is to produce and secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. Hormones serve as messengers to coordinate activities of various parts of the body. ...
Unit IV: Regulation Endocrine System
... – gap junctions • pores in cell membrane allow signaling chemicals to move from cell to cell – neurotransmitters • released from neurons to travel across gap to 2nd cell – paracrine (local) hormones • secreted into tissue fluids to affect nearby cells – hormones • chemical messengers that travel in ...
... – gap junctions • pores in cell membrane allow signaling chemicals to move from cell to cell – neurotransmitters • released from neurons to travel across gap to 2nd cell – paracrine (local) hormones • secreted into tissue fluids to affect nearby cells – hormones • chemical messengers that travel in ...
Endocrine Systems - Science Geek.net
... a. Initiates milk production in the mammary glands 2. Regulation by prolactin-inhibiting hormone (PIH) from hypothalamus a. High levels of estrogen during pregnancy stimulate release of PIH (1) PIH inhibits prolactin release b. Low levels of estrogen after pregnancy inhibit release of PIH (2) Absenc ...
... a. Initiates milk production in the mammary glands 2. Regulation by prolactin-inhibiting hormone (PIH) from hypothalamus a. High levels of estrogen during pregnancy stimulate release of PIH (1) PIH inhibits prolactin release b. Low levels of estrogen after pregnancy inhibit release of PIH (2) Absenc ...
Chemical Regulation Endocrine System communication
... modify or reinforce the action of the system 2 types: ...
... modify or reinforce the action of the system 2 types: ...
BioBases Exam 2
... ADH – anti-diuretic hormone: blood volume control (retains water in blood) (ii) Oxytocin – stimulates uterine contractions and lactation Thyroid: growth and metabolism Parathyroid: calcium regulation Thymus: immune system (children) Pancreas: blood sugar control Adrenal: stress, many other functions ...
... ADH – anti-diuretic hormone: blood volume control (retains water in blood) (ii) Oxytocin – stimulates uterine contractions and lactation Thyroid: growth and metabolism Parathyroid: calcium regulation Thymus: immune system (children) Pancreas: blood sugar control Adrenal: stress, many other functions ...
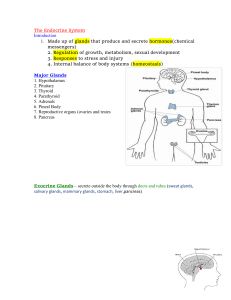
The Endocrine System
... This gland lies in the lower part of the neck and attains a maximum length of about 6cm. After puberty, the thymus begins to atrophy so that in the adult only fibrous remnants is found. Its secretion is thought to act as a brake on the development of sex organs so that as the thymus atrophies, the s ...
... This gland lies in the lower part of the neck and attains a maximum length of about 6cm. After puberty, the thymus begins to atrophy so that in the adult only fibrous remnants is found. Its secretion is thought to act as a brake on the development of sex organs so that as the thymus atrophies, the s ...
Hormones - msdiehlapbiology
... • Two ways hormones affect target organs. • The secretion, target, action, and regulation of at least 3 hormones. • An illustration of both positive and negative feedback in the regulation of homeostasis by hormones. ...
... • Two ways hormones affect target organs. • The secretion, target, action, and regulation of at least 3 hormones. • An illustration of both positive and negative feedback in the regulation of homeostasis by hormones. ...
The Endocrine System
... The endocrine system is made up of glands that release hormones into the blood. Hormones are chemicals that deliver messages throughout the body. ...
... The endocrine system is made up of glands that release hormones into the blood. Hormones are chemicals that deliver messages throughout the body. ...
Endocrine System
... 5. What hormone/gland controls the fight, fright, or flight? A. the adrenal gland/epinephrine B. The pineal gland ...
... 5. What hormone/gland controls the fight, fright, or flight? A. the adrenal gland/epinephrine B. The pineal gland ...
The Endocrine System - St. Ambrose School
... • Hormones are chemical messengers that target specific cells • The specific cells that are effected by the specific hormones are called target cells • If a cell does not have receptors, or the receptors do not respond to a particular hormone, the hormone has no effect on it • The body’s response to ...
... • Hormones are chemical messengers that target specific cells • The specific cells that are effected by the specific hormones are called target cells • If a cell does not have receptors, or the receptors do not respond to a particular hormone, the hormone has no effect on it • The body’s response to ...
endocrine & nervous systems
... Which substances are found on cell surfaces and respond to nerve and hormone signals? starches and simple sugars subunits of DNA vitamins and minerals receptor molecules ...
... Which substances are found on cell surfaces and respond to nerve and hormone signals? starches and simple sugars subunits of DNA vitamins and minerals receptor molecules ...
Lecture 8 - Endocrine
... • Influences growth, metabolism, and homeostasis over prolonged periods • Secretes hormone products into interstitial spaces which are then absorbed into the blood and transported throughout the body • Hormonal control is much slower than nervous control, but the effects of the endocrine system are ...
... • Influences growth, metabolism, and homeostasis over prolonged periods • Secretes hormone products into interstitial spaces which are then absorbed into the blood and transported throughout the body • Hormonal control is much slower than nervous control, but the effects of the endocrine system are ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... The posterior lobe of the pituitary gland also stores and secretes two of the hormones that are synthesized in the hypothalamus. The anterior lobe produces ad secretes its own hormones, most of which govern the release of hormones form other endocrine glands. Six hormones total are produced. 1. ...
... The posterior lobe of the pituitary gland also stores and secretes two of the hormones that are synthesized in the hypothalamus. The anterior lobe produces ad secretes its own hormones, most of which govern the release of hormones form other endocrine glands. Six hormones total are produced. 1. ...
Endocrine System
... controlling the level of minerals in the blood/bones. Pituitary Gland- “master gland,” controls the other glands in your body Puberty- stage of life when a person begins to mature sexually/when a child’s body changes into an adult’s. Testes- main sex glands in males Testosterone-main male hormone Th ...
... controlling the level of minerals in the blood/bones. Pituitary Gland- “master gland,” controls the other glands in your body Puberty- stage of life when a person begins to mature sexually/when a child’s body changes into an adult’s. Testes- main sex glands in males Testosterone-main male hormone Th ...
The Endocrine System
... Other Endocrine Glands Pineal Gland – located between the cerebral hemispheres, secretes melatonin, important for maintaining Circadian rhythms (light and dark activity) Thymus Gland – large in young children, gradually shrinks with age, secretes thymosins, important to immune function Reproductive ...
... Other Endocrine Glands Pineal Gland – located between the cerebral hemispheres, secretes melatonin, important for maintaining Circadian rhythms (light and dark activity) Thymus Gland – large in young children, gradually shrinks with age, secretes thymosins, important to immune function Reproductive ...
Endocrine System and Puberty
... uterus and the vagina Mucous helps with infection control Child birth cannot occur until it dilates to 10 cm. Vagina/Birth Canal Muscular tube about 6 inches in length After baby passes through cervix baby passes through this ...
... uterus and the vagina Mucous helps with infection control Child birth cannot occur until it dilates to 10 cm. Vagina/Birth Canal Muscular tube about 6 inches in length After baby passes through cervix baby passes through this ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR FINAL EXAM:
... Suspensory ligaments (breast) _________________________________________________________________________ (For Written Exam): Tortora, 13th ed. Chapter 18: The Endocrine System 1. ***Know the hormones produced by the endocrine system; their source, function, regulation and disorders associated with hy ...
... Suspensory ligaments (breast) _________________________________________________________________________ (For Written Exam): Tortora, 13th ed. Chapter 18: The Endocrine System 1. ***Know the hormones produced by the endocrine system; their source, function, regulation and disorders associated with hy ...
Mammary gland

A mammary gland is an organ in female mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the word ""mammary."" In humans, the mammary glands are situated in the breasts. In ruminants such as cows, goats, and deer, the mammary glands are contained in the udders. The mammary glands of mammals other than primates, such as dogs and cats, are sometimes called dugs.