1) Which of the following correctly lists the levels of organization
... Transmits information from smooth muscle / glands through cranial nerves to brain ...
... Transmits information from smooth muscle / glands through cranial nerves to brain ...
The neuronal structure of the globus pallidus in the rabbit — Nissl
... which mostly penetrate into the initial portions of the dendritic trunks. The large neurons are the most numerous in the rabbit’s GP. Complex terminal endings (Fig. 2). The pallidal distal dendrites taper progressively and they may form many types of appendages on their terminal portions that are ca ...
... which mostly penetrate into the initial portions of the dendritic trunks. The large neurons are the most numerous in the rabbit’s GP. Complex terminal endings (Fig. 2). The pallidal distal dendrites taper progressively and they may form many types of appendages on their terminal portions that are ca ...
AR THR and
... absolutely critical is to identify and treat this condition very shortly after birth. If not, the child will become permanently mentally and growth retarded (cretinism - a marked impairment of the capacity for abstract thought, with preserved vegetative, personal, social functions and memory. Very o ...
... absolutely critical is to identify and treat this condition very shortly after birth. If not, the child will become permanently mentally and growth retarded (cretinism - a marked impairment of the capacity for abstract thought, with preserved vegetative, personal, social functions and memory. Very o ...
2608. BW Mod.Medicine 02/1¥1.6
... influence of TRH, which stimulates TSH as well as PRL secretion.2,13 Secondly, prolactin clearance may be decreased in hypothyroid patients.14 Thirdly, a study by Foord et al. demonstrated that cultured anterior pituitary cells from hypothyroid rats have a reduced sensitivity to the inhibitory actio ...
... influence of TRH, which stimulates TSH as well as PRL secretion.2,13 Secondly, prolactin clearance may be decreased in hypothyroid patients.14 Thirdly, a study by Foord et al. demonstrated that cultured anterior pituitary cells from hypothyroid rats have a reduced sensitivity to the inhibitory actio ...
BASAL GANGLIA
... The principal pathway through basal ganglia begin mainly in premotor and supplementary motor areas of motor cortex as well as in primary somato - sensory areas of sensory cortex, ...
... The principal pathway through basal ganglia begin mainly in premotor and supplementary motor areas of motor cortex as well as in primary somato - sensory areas of sensory cortex, ...
BASAL GANGLIA
... The principal pathway through basal ganglia begin mainly in premotor and supplementary motor areas of motor cortex as well as in primary somato - sensory areas of sensory cortex, ...
... The principal pathway through basal ganglia begin mainly in premotor and supplementary motor areas of motor cortex as well as in primary somato - sensory areas of sensory cortex, ...
18-02_pptlect
... Hormones of the adenohypophysis • Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) • Triggers the release of thyroid hormones • Thyrotropin releasing hormone promotes the release of TSH • Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) • Stimulates the release of glucocorticoids by the adrenal gland • Corticotrophin releasing ...
... Hormones of the adenohypophysis • Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) • Triggers the release of thyroid hormones • Thyrotropin releasing hormone promotes the release of TSH • Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) • Stimulates the release of glucocorticoids by the adrenal gland • Corticotrophin releasing ...
Module D hormones
... Regulation of Glucose Pancreatic hormones are required to regulate blood glucose level • glucagon released by Alpha ( ) cells • insulin released by Beta Cells ( ) • somatostatin released by Delta Cells ( ) Regulation of Glucose Alpha ( ) cells release glucagon to control blood glucose level • Wh ...
... Regulation of Glucose Pancreatic hormones are required to regulate blood glucose level • glucagon released by Alpha ( ) cells • insulin released by Beta Cells ( ) • somatostatin released by Delta Cells ( ) Regulation of Glucose Alpha ( ) cells release glucagon to control blood glucose level • Wh ...
what`s it all about…
... Frequently misunderstood, and too often overlooked and misdiagnosed, thyroid disease affects almost every aspect of our health, so understanding more about the thyroid, and the symptoms that occur when something goes wrong with this small gland, can help you protect or regain your good health. Women ...
... Frequently misunderstood, and too often overlooked and misdiagnosed, thyroid disease affects almost every aspect of our health, so understanding more about the thyroid, and the symptoms that occur when something goes wrong with this small gland, can help you protect or regain your good health. Women ...
thyroid gland
... 4. Enhance some action of the catecholamine (EP, NE) because they upregulate β receptors for this reason symptoms of hyperthyroidism include increase heart rate and increased blood pressure. 5. With growth hormone and insulin, thyroid hormone accelerates body growth (nervous and skeletal system), de ...
... 4. Enhance some action of the catecholamine (EP, NE) because they upregulate β receptors for this reason symptoms of hyperthyroidism include increase heart rate and increased blood pressure. 5. With growth hormone and insulin, thyroid hormone accelerates body growth (nervous and skeletal system), de ...
Thyroid hormones
... T3/T4 enter circulation transported to plasma proteins (99%). Thyroid only contributes 20% of the free circulating T3 with the rest produced by peripheral conversion of T4 to T3. T4 may be deiodinated to inactive reverse T3. Regulation is based on the free component of thyroid hormone. Action not un ...
... T3/T4 enter circulation transported to plasma proteins (99%). Thyroid only contributes 20% of the free circulating T3 with the rest produced by peripheral conversion of T4 to T3. T4 may be deiodinated to inactive reverse T3. Regulation is based on the free component of thyroid hormone. Action not un ...
Epinephrine (EPI) and Norepinephrine (NE)
... Epinephrine (EPI) and Norepinephrine (NE) • What are the endocrine connections? – Direct effects listed above that occur during sympathetic activation of adrenal medulla during a stress response – Thyroid hormone is permissive on the actions of EPI/NE by increasing # of adrenergic receptors in targ ...
... Epinephrine (EPI) and Norepinephrine (NE) • What are the endocrine connections? – Direct effects listed above that occur during sympathetic activation of adrenal medulla during a stress response – Thyroid hormone is permissive on the actions of EPI/NE by increasing # of adrenergic receptors in targ ...
Reference Guide - US BioTek Laboratories
... physical and mental status in addition to circadian variations. A 24-hour urine sample offers the most sensitive means to account for the production and metabolic activity of steroid hormones against the natural variations that we see in a 24-hour period. Steroid hormones are transported by the bloo ...
... physical and mental status in addition to circadian variations. A 24-hour urine sample offers the most sensitive means to account for the production and metabolic activity of steroid hormones against the natural variations that we see in a 24-hour period. Steroid hormones are transported by the bloo ...
A Critical Review of the Role of the Proposed VMpo Nucleus in Pain
... basis of this limited sample of recordings, the lamina I input to the region of VMpo seems to be thermoreceptive and nociceptive. Dostrovsky and Craig were unable to activate cold-responsive lamina I STT cells antidromically from the ventrobasal complex in 2 monkeys in which a stimulating electrode ...
... basis of this limited sample of recordings, the lamina I input to the region of VMpo seems to be thermoreceptive and nociceptive. Dostrovsky and Craig were unable to activate cold-responsive lamina I STT cells antidromically from the ventrobasal complex in 2 monkeys in which a stimulating electrode ...
BNG/Briefing 18 - British Society for Neuroendocrinology
... induce puberty. These cells do this by secreting a small hormone, gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH), which stimulates the production and release of gonadotrophin hormones. This tiny number of GnRH-producing neurons, holds the key to puberty. If, during brain development, the GnRH neurons fail t ...
... induce puberty. These cells do this by secreting a small hormone, gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH), which stimulates the production and release of gonadotrophin hormones. This tiny number of GnRH-producing neurons, holds the key to puberty. If, during brain development, the GnRH neurons fail t ...
Olney JW. Brain lesions, obesity, and other disirbances in mice
... disorders, in both youth and old age, is gradually unfolding, and there is hope that antiexcitotoxic drugs may be therapeutically useful in clinical neurology. Interesting new findings include: L.DOPA and an ortho-hydroxylated derivative have excitotoxic activity that could possibly have pathophysio ...
... disorders, in both youth and old age, is gradually unfolding, and there is hope that antiexcitotoxic drugs may be therapeutically useful in clinical neurology. Interesting new findings include: L.DOPA and an ortho-hydroxylated derivative have excitotoxic activity that could possibly have pathophysio ...
hypothyroid - Hatzalah of Miami-Dade
... Endemic Goiter Environmental iodine deficiency Affects more than 200 million people throughout the world Most common in mountainous areas - Alps, Himalayas, and Andes Consumption of cassava meal may aggravate ...
... Endemic Goiter Environmental iodine deficiency Affects more than 200 million people throughout the world Most common in mountainous areas - Alps, Himalayas, and Andes Consumption of cassava meal may aggravate ...
Menopause and Your Hormones
... and harmony within, control sleep-wake cycles, energy level, weight and metabolism, emotions, stress response, and impact almost all body functions. Several key hormones are produced by the adrenal glands. From cholesterol, as noted in the diagram previously, we get pregnenolone. Pregnenolone is the ...
... and harmony within, control sleep-wake cycles, energy level, weight and metabolism, emotions, stress response, and impact almost all body functions. Several key hormones are produced by the adrenal glands. From cholesterol, as noted in the diagram previously, we get pregnenolone. Pregnenolone is the ...
Thyroid in dogs - Trinity Veterinary Hospital
... Total T4 (Thyroxine): T4 circulates in the blood in two forms; one form of the hormone is bound, or attached to proteins in the blood, while the other form circulates freely within the blood stream. Total T4 measures both forms of the hormone in a blood sample. If the total T4 concentration is well ...
... Total T4 (Thyroxine): T4 circulates in the blood in two forms; one form of the hormone is bound, or attached to proteins in the blood, while the other form circulates freely within the blood stream. Total T4 measures both forms of the hormone in a blood sample. If the total T4 concentration is well ...
thyroid system dysfunction (tsd) - Pope Paul VI Institute for the Study
... (RT3), there is the development of multiple symptoms related to thyroid dysfunction. This Reverse T3 Dominance is the cause of the hypometabolism which is associated with Thyroid System Dysfunction (TSD) and is associated with decreased body temperature. In the case of any hormone activity, there ne ...
... (RT3), there is the development of multiple symptoms related to thyroid dysfunction. This Reverse T3 Dominance is the cause of the hypometabolism which is associated with Thyroid System Dysfunction (TSD) and is associated with decreased body temperature. In the case of any hormone activity, there ne ...
The Endocrine System
... almost immediately, whereas some endocrine effects persist for several days or even weeks. On the other hand, under long-term stimulation, neurons soon adapt and their response declines. The endocrine system shows more persistent responses. For example, thyroid hormone secretion rises in cold weathe ...
... almost immediately, whereas some endocrine effects persist for several days or even weeks. On the other hand, under long-term stimulation, neurons soon adapt and their response declines. The endocrine system shows more persistent responses. For example, thyroid hormone secretion rises in cold weathe ...
GABA neurocircuits controlling the Hypothalamic- Pituitary
... Previous studies have demonstrated that classical benzodiazepines decrease hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenocortical cortex (HPA) axis activity. Paradoxically, high doses of benzodiazepines also stimulate basal circulating corticosterone levels in some conditions. Because benzodiazepine agonists display ...
... Previous studies have demonstrated that classical benzodiazepines decrease hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenocortical cortex (HPA) axis activity. Paradoxically, high doses of benzodiazepines also stimulate basal circulating corticosterone levels in some conditions. Because benzodiazepine agonists display ...
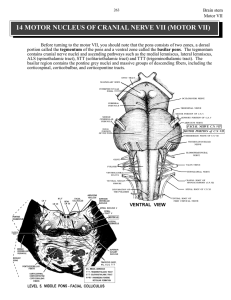
14 MOTOR NUCLEUS OF CRANIAL NERVE VII (MOTOR VII)
... transverse and longitudinal fiber bundles between which are large collections of pontine neurons called the PONTINE GREY (or GRAY). The longitudinal bundles are (1) corticobulbar, (2) corticospinal and, most important for this point, (3) CORTICOPONTINE FIBERS. ...
... transverse and longitudinal fiber bundles between which are large collections of pontine neurons called the PONTINE GREY (or GRAY). The longitudinal bundles are (1) corticobulbar, (2) corticospinal and, most important for this point, (3) CORTICOPONTINE FIBERS. ...
HS_About_Hypothyroidism__Dr_Jarvis
... According to Dr. Jorge Fleschas, Dr. Grove's tonic (bromide based) was used to fatten up children. ...
... According to Dr. Jorge Fleschas, Dr. Grove's tonic (bromide based) was used to fatten up children. ...
Hormone
... to release their hormones • Hypothalamic hormones stimulate the release of most anterior pituitary hormones • Anterior pituitary hormones stimulate targets to secrete still more hormones • Hypothalamic-pituitary-target endocrine organ feedback loop: hormones from the final target organs inhibit the ...
... to release their hormones • Hypothalamic hormones stimulate the release of most anterior pituitary hormones • Anterior pituitary hormones stimulate targets to secrete still more hormones • Hypothalamic-pituitary-target endocrine organ feedback loop: hormones from the final target organs inhibit the ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.