Hyperandrogenism in menopause: a case report and literature review
... use of the medication, and the patient could not afford an out-of-pocket cost of ~ $1000/month for the intramuscular depot injection of leuprolide. Over the next two years, the patient had a progression of her symptoms, including continued scalp hair loss requiring a wig, increased body and facial h ...
... use of the medication, and the patient could not afford an out-of-pocket cost of ~ $1000/month for the intramuscular depot injection of leuprolide. Over the next two years, the patient had a progression of her symptoms, including continued scalp hair loss requiring a wig, increased body and facial h ...
The Pituitary Gland
... Posterior lobe – stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus. 1. antidiuretic hormone (ADH) – released into blood and targets kidney cells, stimulating the nephrons to absorb or release water. This regulates the water balance inside the body. 2. oxytocin – produced only by females, thi ...
... Posterior lobe – stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus. 1. antidiuretic hormone (ADH) – released into blood and targets kidney cells, stimulating the nephrons to absorb or release water. This regulates the water balance inside the body. 2. oxytocin – produced only by females, thi ...
Cushing`s Disease in Horses The condition known as Cushing`s
... Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH), which is the hormone released by the pituitary gland to increase the levels of cortisol in the body. ACTH levels are naturally higher in the fall, and may fall slightly outside of the reference range during that time of year, resulting in false positives. Addition ...
... Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH), which is the hormone released by the pituitary gland to increase the levels of cortisol in the body. ACTH levels are naturally higher in the fall, and may fall slightly outside of the reference range during that time of year, resulting in false positives. Addition ...
د.هالة عبدالغني الراوي 2017 المرحلة الخامسة Hirsutism Definition:growth
... The most common is the Ferriman & Gallwey grading system, which scores 11 areas of the body on a scale of 1 to 4 according to the degree of terminal hair growth. The scores then added together. ...
... The most common is the Ferriman & Gallwey grading system, which scores 11 areas of the body on a scale of 1 to 4 according to the degree of terminal hair growth. The scores then added together. ...
Document
... Hyperosmolar nonketotic coma (HONK), also called hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic coma (HHNC), is a metabolic derangement that occurs principally in patients with type 2 diabetes. This condition is characterized by hyperglycemia, hyperosmolarity, and an absence of significant ketosis. Adrenal i ...
... Hyperosmolar nonketotic coma (HONK), also called hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic coma (HHNC), is a metabolic derangement that occurs principally in patients with type 2 diabetes. This condition is characterized by hyperglycemia, hyperosmolarity, and an absence of significant ketosis. Adrenal i ...
Chapter 3 Section 3
... • Pituitary Gland – responsible for the secretion of many different hormones that affect various aspects of behavior such as the growth hormone. • Thyroid Gland – produces thyroxin which affects the body’s metabolism – it’s rate of converting food to energy. • Adrenal Gland – the outer layer of the ...
... • Pituitary Gland – responsible for the secretion of many different hormones that affect various aspects of behavior such as the growth hormone. • Thyroid Gland – produces thyroxin which affects the body’s metabolism – it’s rate of converting food to energy. • Adrenal Gland – the outer layer of the ...
Hyperadrenocorticism This is a disease primarily of older dogs. In
... Hyperadrenocorticism This is a disease primarily of older dogs. In this condition the body produces excessive amounts of its own internal steroid – cortisol. In most cases a gland in the brain, (pituitary gland), over-stimulates the adrenal glands, (located close to the kidneys), to produce this exc ...
... Hyperadrenocorticism This is a disease primarily of older dogs. In this condition the body produces excessive amounts of its own internal steroid – cortisol. In most cases a gland in the brain, (pituitary gland), over-stimulates the adrenal glands, (located close to the kidneys), to produce this exc ...
File - Ms. G`s Classroom
... Stimulates the adrenal cortex (outer part) to secrete a group of steroid hormones called glucocorticoids. In females, stimulates the maturation of a follicle and egg inside the ovary. In males, stimulates sperm production. Stimulate ovulation in females and the formation of the corpus luteum from th ...
... Stimulates the adrenal cortex (outer part) to secrete a group of steroid hormones called glucocorticoids. In females, stimulates the maturation of a follicle and egg inside the ovary. In males, stimulates sperm production. Stimulate ovulation in females and the formation of the corpus luteum from th ...
Word Search
... 1. Gland in the brain that is the control center for all regulatory activities of the body. 2. Condition in which levels of thyroid hormones in the blood are very low. 3. Helps regulate when you sleep at night and when you wake in the morning. 4. Master gland, makes hormones that control several oth ...
... 1. Gland in the brain that is the control center for all regulatory activities of the body. 2. Condition in which levels of thyroid hormones in the blood are very low. 3. Helps regulate when you sleep at night and when you wake in the morning. 4. Master gland, makes hormones that control several oth ...
Testosterone
... development, lowering of the voice, and overall growth. It also affects libido, memory, and lean body mass, and it may contribute to mood issues and irritability. Contrary to popular belief, testosterone is not exclusively a male hormone. Women make a tiny bit in their ovaries and adrenal glands, an ...
... development, lowering of the voice, and overall growth. It also affects libido, memory, and lean body mass, and it may contribute to mood issues and irritability. Contrary to popular belief, testosterone is not exclusively a male hormone. Women make a tiny bit in their ovaries and adrenal glands, an ...
No Slide Title
... * causes liver to convert glycogen into glucose and releases the glucose into the bloodstream b. Insulin – causes most of the body’s cells to take in glucose * When insulin is low or absent, glucose is not taken up by most body cells and the body begins to use fat as an energy source 3. Disorder: Di ...
... * causes liver to convert glycogen into glucose and releases the glucose into the bloodstream b. Insulin – causes most of the body’s cells to take in glucose * When insulin is low or absent, glucose is not taken up by most body cells and the body begins to use fat as an energy source 3. Disorder: Di ...
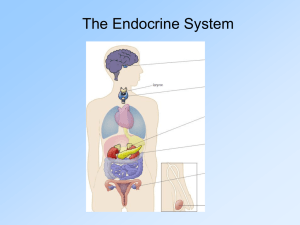
Endocrine System
... important functions such as energy metabolism, reproduction, and stress response. The pituitary gland is often referred to as the "master gland" because it regulates the hormones used by the thyroid, adrenal cortex, ovaries, testes, and the breasts (in women). The pituitary is located in the brain b ...
... important functions such as energy metabolism, reproduction, and stress response. The pituitary gland is often referred to as the "master gland" because it regulates the hormones used by the thyroid, adrenal cortex, ovaries, testes, and the breasts (in women). The pituitary is located in the brain b ...
Ready for Review - Paramedic EMS Zone
... Hyperosmolar nonketotic coma (HONK), also called hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic nonketotic coma (HHNC), is a metabolic derangement that occurs principally in patients with type 2 diabetes. This condition is characterised by hyperglycaemia, hyperosmolarity, and an absence of significant ketosis. Adrenal ...
... Hyperosmolar nonketotic coma (HONK), also called hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic nonketotic coma (HHNC), is a metabolic derangement that occurs principally in patients with type 2 diabetes. This condition is characterised by hyperglycaemia, hyperosmolarity, and an absence of significant ketosis. Adrenal ...
bio 342 human physiology
... (reproduction & growth) Suppress inflammatory & immune responses Potentiates response to EPI (vascular smooth muscle) ...
... (reproduction & growth) Suppress inflammatory & immune responses Potentiates response to EPI (vascular smooth muscle) ...
Polycystic ovary syndrome
... 1. Subfertility: achieving pregnancy is more difficult. 2. Scanty or no periods, irregular, usually lighter, bleeding. 3. Weight gain. 4. Excess hair on face (may be on arms and legs). Other features: ● Acne. ● Increased miscarriage rate. What are the problems with PCOS? The central problem is persi ...
... 1. Subfertility: achieving pregnancy is more difficult. 2. Scanty or no periods, irregular, usually lighter, bleeding. 3. Weight gain. 4. Excess hair on face (may be on arms and legs). Other features: ● Acne. ● Increased miscarriage rate. What are the problems with PCOS? The central problem is persi ...
File
... __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ________________________________ ...
... __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ________________________________ ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Name 1. Gland in the brain that is the control
... 2. Condition in which levels of thyroid hormones in the blood are very low: _________________________ __ 3. Helps regulate when you sleep at night and when you wake in the morning ___________________________ 4. Master gland, makes hormones that control several other endocrine glands ________________ ...
... 2. Condition in which levels of thyroid hormones in the blood are very low: _________________________ __ 3. Helps regulate when you sleep at night and when you wake in the morning ___________________________ 4. Master gland, makes hormones that control several other endocrine glands ________________ ...
Endocrine System
... Secrete hormones into the circulatory system that will cause a change in the body in a different location Regulated by feedback mechanisms Stimulus-Response Hormones are only released until the appropriate changes are made (homeostasis is restored) ...
... Secrete hormones into the circulatory system that will cause a change in the body in a different location Regulated by feedback mechanisms Stimulus-Response Hormones are only released until the appropriate changes are made (homeostasis is restored) ...
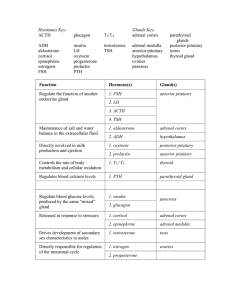
Hormones Key: Glands Key: ACTH glucagon T3/T4 adrenal cortex
... Regulate the function of another endocrine gland ...
... Regulate the function of another endocrine gland ...
The Endocrine system
... • Produces many hormones that affect other glands – thyroid stimulating hormone – Somatotropin- growth hormone – Lutenizing (LH)- causes ovulation – ICSH- causes testes to secrete testosterone – Melanocyte stimulating- distribution of melanin in skin – ADH- antidiuretic hormone ...
... • Produces many hormones that affect other glands – thyroid stimulating hormone – Somatotropin- growth hormone – Lutenizing (LH)- causes ovulation – ICSH- causes testes to secrete testosterone – Melanocyte stimulating- distribution of melanin in skin – ADH- antidiuretic hormone ...
The Endocrine system
... • Produces many hormones that affect other glands – thyroid stimulating hormone – Somatotropin- growth hormone – Lutenizing (LH)- causes ovulation – ICSH- causes testes to secrete testosterone – Melanocyte stimulating- distribution of melanin in skin – ADH- antidiuretic hormone ...
... • Produces many hormones that affect other glands – thyroid stimulating hormone – Somatotropin- growth hormone – Lutenizing (LH)- causes ovulation – ICSH- causes testes to secrete testosterone – Melanocyte stimulating- distribution of melanin in skin – ADH- antidiuretic hormone ...
human endocrine hormones
... Directions: Listed below are the major hormones produced by the human body. ACTH adrenaline aldosterone calcitonin cortisol ...
... Directions: Listed below are the major hormones produced by the human body. ACTH adrenaline aldosterone calcitonin cortisol ...
The Adrenal Cortex - Washington State University
... • Cushing’s Syndrome: excessive corticosteroid – hypertension, hyperglycemia, hypokalemia, alkalosis, characteristic pattern of fat loss from lower body and fat deposition around neck and face. This syndrome is very commonly iatrogenic. • Addison’s Syndrome: hypotension, poor survival in fasting, in ...
... • Cushing’s Syndrome: excessive corticosteroid – hypertension, hyperglycemia, hypokalemia, alkalosis, characteristic pattern of fat loss from lower body and fat deposition around neck and face. This syndrome is very commonly iatrogenic. • Addison’s Syndrome: hypotension, poor survival in fasting, in ...
Adrenogenital Syndrome
... Elevated serum testosterone whereas serum cortisol and aldosterone low Elevated 17-hydoxyprogesterone-by the 3rd day Elevated urinary pregnanetriol-major urinary metabolite of 17OHP ...
... Elevated serum testosterone whereas serum cortisol and aldosterone low Elevated 17-hydoxyprogesterone-by the 3rd day Elevated urinary pregnanetriol-major urinary metabolite of 17OHP ...