The effects of low-dose testosterone treatment on lipid metabolism
... reverse inhibitory effects of oestrogen on bone formation (Raisz et al., 1996). This therefore suggests a potential therapeutic role for androgen therapy in osteoporosis prevention. Little is known about the long-term safety of androgen treatment in women. It is, however, of great importance in view ...
... reverse inhibitory effects of oestrogen on bone formation (Raisz et al., 1996). This therefore suggests a potential therapeutic role for androgen therapy in osteoporosis prevention. Little is known about the long-term safety of androgen treatment in women. It is, however, of great importance in view ...
Human Life Cycle 1
... The development and growth of follicles depends on the synthesis of specific hormone receptors and adequate levels of the relevant hormones; the adenohypophysial gonadotrophins luteinising hormone (LH) and folliclestimulating hormone (FSH). Thecal cells LH receptors granulosa cells FSH and oestr ...
... The development and growth of follicles depends on the synthesis of specific hormone receptors and adequate levels of the relevant hormones; the adenohypophysial gonadotrophins luteinising hormone (LH) and folliclestimulating hormone (FSH). Thecal cells LH receptors granulosa cells FSH and oestr ...
O`Kane
... B. is released from the hypothalamus. C. helps enhance (increase) appetite. D. gets released from adipocytes when lipids are absorbed. 9. Endocrine secretions are released into the _______________ whereas exocrine secretions are released into the ________________. A. external environment; external e ...
... B. is released from the hypothalamus. C. helps enhance (increase) appetite. D. gets released from adipocytes when lipids are absorbed. 9. Endocrine secretions are released into the _______________ whereas exocrine secretions are released into the ________________. A. external environment; external e ...
Endocrine Student Notes
... When sugars cannot be utilized, more _______ are mobilized resulting in more ____________ in the blood. When the ketones accumulate faster than they can be used, the blood pH drops, resulting in _________________ and ketones begin to spill into the urine. This severe condition can lead to coma or de ...
... When sugars cannot be utilized, more _______ are mobilized resulting in more ____________ in the blood. When the ketones accumulate faster than they can be used, the blood pH drops, resulting in _________________ and ketones begin to spill into the urine. This severe condition can lead to coma or de ...
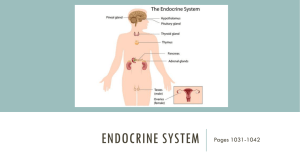
Endocrine System
... Growth hormone or GH - GH stimulates growth in childhood and is important for maintaining a healthy body composition. In adults it is also important for maintaining muscle mass and bone mass. It can affect fat distribution in the body. Adrenocorticotropin or ACTH - ACTH stimulates production of co ...
... Growth hormone or GH - GH stimulates growth in childhood and is important for maintaining a healthy body composition. In adults it is also important for maintaining muscle mass and bone mass. It can affect fat distribution in the body. Adrenocorticotropin or ACTH - ACTH stimulates production of co ...
HERE
... which blocks further development of the female system **Maternal estrogen does not cross the blood-placental barrier** **Testosterone can cross the blood-placental barrier** ...
... which blocks further development of the female system **Maternal estrogen does not cross the blood-placental barrier** **Testosterone can cross the blood-placental barrier** ...
Chemical Signals in Animals or The Endocrine System
... •body is producing insulin but the body attacks its own beta cells and destroys them. ...
... •body is producing insulin but the body attacks its own beta cells and destroys them. ...
Subcutaneous Hormone Pellets
... for the following conditions associated with a deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone: Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired) - testicular failure due to cryptorchidism, bilateral torsion, orchitis, vanishing testes syndrome or orchidectomy; Hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism or sec ...
... for the following conditions associated with a deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone: Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired) - testicular failure due to cryptorchidism, bilateral torsion, orchitis, vanishing testes syndrome or orchidectomy; Hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism or sec ...
Endocrine System Vocabulary Acromegaly Adrenal Glands
... contain 2 major types of hormone producing cells 1) alpha cells (glucagons synthesizing) & 2) beta cells (insulin producing). They also produce other peptides in small amounts, including somatostatin (secreted by the delta cells) that inhibit insulin & glucagons release. 18.Menopause: during late mi ...
... contain 2 major types of hormone producing cells 1) alpha cells (glucagons synthesizing) & 2) beta cells (insulin producing). They also produce other peptides in small amounts, including somatostatin (secreted by the delta cells) that inhibit insulin & glucagons release. 18.Menopause: during late mi ...
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS)
... Genotyping was carried out by PCR-RFLP for rs5919393 (C/T) and rs5919411 (A/G) and by direct sequencing of PCR products generated for rs12014709 (G/T). All the PCR reactions was carried out in 20uL reaction containing 10ul of 2X PCR master mix (Ampliqon, Dutch), 20 picomoles of forward and reverse p ...
... Genotyping was carried out by PCR-RFLP for rs5919393 (C/T) and rs5919411 (A/G) and by direct sequencing of PCR products generated for rs12014709 (G/T). All the PCR reactions was carried out in 20uL reaction containing 10ul of 2X PCR master mix (Ampliqon, Dutch), 20 picomoles of forward and reverse p ...
Chapter 13 Notes
... hormone from the islet cells and injected it into the dogs The dogs recovered, indicating that this hormone was responsible for controlling blood sugar levels Banting was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1923, but Best was not included ...
... hormone from the islet cells and injected it into the dogs The dogs recovered, indicating that this hormone was responsible for controlling blood sugar levels Banting was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1923, but Best was not included ...
21 Endocrine Flashcards, INDEX back
... skin, hyperglycemia, immune suppression. Females get masculinization features (facial hair, thicker jaw and skull) Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. In a female fetus causes the clitoris to enlarge and the labia major fuse into a scrotal sac. Genetic problem, missing the enzyme to convert cholesterol ...
... skin, hyperglycemia, immune suppression. Females get masculinization features (facial hair, thicker jaw and skull) Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. In a female fetus causes the clitoris to enlarge and the labia major fuse into a scrotal sac. Genetic problem, missing the enzyme to convert cholesterol ...
Chapter 39 - Midway ISD
... Base of the skull, secretes 9 hormones that directly regulate many body functions and endocrine glands. See pg. 1004 for hormones. ...
... Base of the skull, secretes 9 hormones that directly regulate many body functions and endocrine glands. See pg. 1004 for hormones. ...
Endocrine Systemnew
... • Type 2- Either the body doesn’t produce enough insulin, or the cells ignore it. – If you consume too much sugar over a long period of time, your body has to release large amounts of insulin. This can result in your cells building up a tolerance for insulin, which means they won’t be affected by it ...
... • Type 2- Either the body doesn’t produce enough insulin, or the cells ignore it. – If you consume too much sugar over a long period of time, your body has to release large amounts of insulin. This can result in your cells building up a tolerance for insulin, which means they won’t be affected by it ...
The Endocrine System Medical Team Directions: You will be part of
... Directions: You will be part of an Endocrine System Medical Team (ESMT) whose job is to thoroughly investigate this body system. Your mission is to learn about this specific system, working with others to complete your mission. Your team will travel along the Internet highway and gather information ...
... Directions: You will be part of an Endocrine System Medical Team (ESMT) whose job is to thoroughly investigate this body system. Your mission is to learn about this specific system, working with others to complete your mission. Your team will travel along the Internet highway and gather information ...
Endocrine System - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... The medical assistant in a local medical office is about to administer an injection of cortisol. The patient asks “Once you inject that steriod in my arm, why won’t it affect my arm and other body parts?” Which of the following would best answer this patient’s question? a. Hormones do not affect any ...
... The medical assistant in a local medical office is about to administer an injection of cortisol. The patient asks “Once you inject that steriod in my arm, why won’t it affect my arm and other body parts?” Which of the following would best answer this patient’s question? a. Hormones do not affect any ...
ENDOCRINE GLANDS
... These actions get us ready for fight or flight Reproductive Glands gonads- body’s reproductive glands ovaries- produces eggs estrogen- development of ova and physical characteristics such as reproductive system, widening hips, and breast development. progesterone- Prepares the uterus for the arrivin ...
... These actions get us ready for fight or flight Reproductive Glands gonads- body’s reproductive glands ovaries- produces eggs estrogen- development of ova and physical characteristics such as reproductive system, widening hips, and breast development. progesterone- Prepares the uterus for the arrivin ...
1.5 Individual human development during youth: Physical
... development of female sex characteristics, breast development and the regulation of the menstrual cycle. ...
... development of female sex characteristics, breast development and the regulation of the menstrual cycle. ...
HYPERCORTISOLISM CUSHING SYNDROME
... Plasma ACTH level High dose dexamethasone suppression test Metyrapone test CRH stimulation test 3. Localization (Where) Adrenal CT, Pituitary MRI ...
... Plasma ACTH level High dose dexamethasone suppression test Metyrapone test CRH stimulation test 3. Localization (Where) Adrenal CT, Pituitary MRI ...
Chapter 10
... So let’s say there’s too much glucose in your blood. Your pancreatic islets cells send insulin into the blood which tells your cells to start absorbing all the glucose, thereby decreasing the concentration of glucose in your blood. The hormone in this situation is insulin, and you can deduce how it ...
... So let’s say there’s too much glucose in your blood. Your pancreatic islets cells send insulin into the blood which tells your cells to start absorbing all the glucose, thereby decreasing the concentration of glucose in your blood. The hormone in this situation is insulin, and you can deduce how it ...
Endocrine system
... acids from fat cells, increase heart rate, stroke volume, and dilate the bronchioles in lungs, alter blood flow away from skin and digestive organs. Epinephrine has stronger effect on heart and metabolic rates, norepinephrine modulates blood pressure more. Adrenal cortex: (stress hormones stimulated ...
... acids from fat cells, increase heart rate, stroke volume, and dilate the bronchioles in lungs, alter blood flow away from skin and digestive organs. Epinephrine has stronger effect on heart and metabolic rates, norepinephrine modulates blood pressure more. Adrenal cortex: (stress hormones stimulated ...