Endocrine System Notes - Wiki-Health
... Located right beneath the hypothalamus About the size of a pea but considered to be the most important part in the endocrine system Known as the “master gland” because it makes hormones that control several other endocrine glands (Makes 8 types of hormones) Production and secretion of pituitary hor ...
... Located right beneath the hypothalamus About the size of a pea but considered to be the most important part in the endocrine system Known as the “master gland” because it makes hormones that control several other endocrine glands (Makes 8 types of hormones) Production and secretion of pituitary hor ...
Hormones from Endocrine Glands
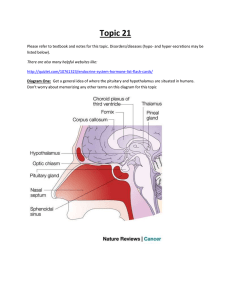
... Please refer to textbook and notes for this topic. Disorders/diseases (hypo- and hyper-secretions may be listed below). There are also many helpful websites like: http://quizlet.com/10761323/endocrine-system-hormone-list-flash-cards/ Diagram One: Get a general idea of where the pituitary and hypotha ...
... Please refer to textbook and notes for this topic. Disorders/diseases (hypo- and hyper-secretions may be listed below). There are also many helpful websites like: http://quizlet.com/10761323/endocrine-system-hormone-list-flash-cards/ Diagram One: Get a general idea of where the pituitary and hypotha ...
Ch 18 Notes: Endocrine System 2014
... Mineralcorticoids = increase sodium and water reabsorption. Disorder: increased aldosterone (aldosteronism) = muscular paralysis and hypertension Glucocorticoids (eg. cortisol) = serve as anti-inflammatory substances Disorders: Hyposecretion = Addison's disease Hypersecretion = Cushing's syndrome Go ...
... Mineralcorticoids = increase sodium and water reabsorption. Disorder: increased aldosterone (aldosteronism) = muscular paralysis and hypertension Glucocorticoids (eg. cortisol) = serve as anti-inflammatory substances Disorders: Hyposecretion = Addison's disease Hypersecretion = Cushing's syndrome Go ...
Super Female
... • Most have some mental retardation (degree varies widely) • Physical features include low muscle tone, flat facial features, with a small nose, upward slant to the eyes, small skin folds on the inner corner of the eyes, small, abnormally shaped ears, single deep crease across the center of the palm ...
... • Most have some mental retardation (degree varies widely) • Physical features include low muscle tone, flat facial features, with a small nose, upward slant to the eyes, small skin folds on the inner corner of the eyes, small, abnormally shaped ears, single deep crease across the center of the palm ...
The Endocrine System - BIOLOGY and HONORS PHYSIOLOGY Mr
... butterfly, the Thyroid Gland is actually 2 glands in one… Secretes the hormone thyroxine to regulate metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in the bloodstream. Iodine is an integral element in this hormone. Secretes calcitonin to regulate Calcium (Ca+) and phosphate ion levels in blood ...
... butterfly, the Thyroid Gland is actually 2 glands in one… Secretes the hormone thyroxine to regulate metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in the bloodstream. Iodine is an integral element in this hormone. Secretes calcitonin to regulate Calcium (Ca+) and phosphate ion levels in blood ...
male pattern baldness - Royal Jelly Formulation from Irene Stein
... the crown of the head. Over time, the crown ...
... the crown of the head. Over time, the crown ...
The Endocrine System
... Adrenal cortex disorders ____________________________ disease Results from _____________________ of all adrenal cortex hormones _________________ skin tone, muscles are ___________, burnout, susceptibility to infection ___________________________________ May result from an ACTH-releasing ...
... Adrenal cortex disorders ____________________________ disease Results from _____________________ of all adrenal cortex hormones _________________ skin tone, muscles are ___________, burnout, susceptibility to infection ___________________________________ May result from an ACTH-releasing ...
Základní vyšetření v endokrinologii
... A method for assessing prolactin recovery based on precipitation of macroprolactin by polyethylene glycol (PEG) has been proposed as a simple test for detection of macroprolactinaemia ...
... A method for assessing prolactin recovery based on precipitation of macroprolactin by polyethylene glycol (PEG) has been proposed as a simple test for detection of macroprolactinaemia ...
Quick Reference Guide - MRSA Topical Eradication
... Two 24 hour urine collection samples for catecholamines (N.B. regional laboratories may use alternative baseline screening tests) to help exclude phaeochromocytoma#. Ideally avoid interfering medication including paracetamol, many antihypertensives, catecholamine containing drugs & some antidepressa ...
... Two 24 hour urine collection samples for catecholamines (N.B. regional laboratories may use alternative baseline screening tests) to help exclude phaeochromocytoma#. Ideally avoid interfering medication including paracetamol, many antihypertensives, catecholamine containing drugs & some antidepressa ...
Pituitary Gland - Rochester Community Schools
... kinase to active form and inhibits an enzyme required for glucagon synthesis. ...
... kinase to active form and inhibits an enzyme required for glucagon synthesis. ...
Essentials of Pathophysiology CHAPTER 31 ORGANIZATION AND CONTROL OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... in receptor numbers by means of a process called _________________ ; this increases the sensitivity of the body to existing hormone levels. ...
... in receptor numbers by means of a process called _________________ ; this increases the sensitivity of the body to existing hormone levels. ...
Chapter 45 Student Guided Notes
... destroys the beta cells of the pancreas (so you can’t make insulin!). ○ Type I diabetes usually appears in childhood and destroys the person’s ability to produce insulin. ...
... destroys the beta cells of the pancreas (so you can’t make insulin!). ○ Type I diabetes usually appears in childhood and destroys the person’s ability to produce insulin. ...
Chapter 13: The Endocrine System
... Constrict blood vessels to the digestive tract Adrenal Cortex Outer region of the adrenal gland Secretes 3 steroids o Glucocorticoids o Mineralocorticoids o Sex hormones Glucocorticoids Converts amino acids into glucose and help maintain blood glucose levels between meals Also cause protei ...
... Constrict blood vessels to the digestive tract Adrenal Cortex Outer region of the adrenal gland Secretes 3 steroids o Glucocorticoids o Mineralocorticoids o Sex hormones Glucocorticoids Converts amino acids into glucose and help maintain blood glucose levels between meals Also cause protei ...
29-6 Endocrine
... • The hypothalamus is a gland found in the brain – a structure of both the nervous and endocrine systems – produces releasing hormones, sent to pituitary gland • The pituitary gland is found below the hypothalamus in the brain. – controls growth and water levels in blood – produces releasing hormone ...
... • The hypothalamus is a gland found in the brain – a structure of both the nervous and endocrine systems – produces releasing hormones, sent to pituitary gland • The pituitary gland is found below the hypothalamus in the brain. – controls growth and water levels in blood – produces releasing hormone ...
Thyroid-Adrenal Fatigue Syndrome!
... If your battery is dead, then no matter how much you step on the gas pedal, you just won’t move. Conversely, if your gas pedal is stuck then you wont be able to get fuel to the engine which then needs to be ignited by a spark from the battery—simple combustion engine mechanics! As a car needs fuel, ...
... If your battery is dead, then no matter how much you step on the gas pedal, you just won’t move. Conversely, if your gas pedal is stuck then you wont be able to get fuel to the engine which then needs to be ignited by a spark from the battery—simple combustion engine mechanics! As a car needs fuel, ...
chapter 50 endocrine systems
... In adults, GH serves metabolic functions in regulating glucose and fatty acid levels in blood ...
... In adults, GH serves metabolic functions in regulating glucose and fatty acid levels in blood ...
Fasting Plasma Glucose Levels and Endogenous
... and free testosterone levels, there was a signifiant positive trend, with increasing mean hormone levels with increasing quartile of fasting plasma glucose level. A negative trend was apparent for SHBG, with mean levels decreasing with increasing quartile of fasting plasma glucose level. No trends w ...
... and free testosterone levels, there was a signifiant positive trend, with increasing mean hormone levels with increasing quartile of fasting plasma glucose level. A negative trend was apparent for SHBG, with mean levels decreasing with increasing quartile of fasting plasma glucose level. No trends w ...
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley&O'Loughlin
... Distinctive “butterfly” shape due to its left and right lobes, which are connected at the anterior midline by a narrow isthmus. Both lobes of the thyroid gland are highly vascularized, giving it an intense reddish coloration. Regulation of thyroid hormone secretion depends upon a complex thyroid gla ...
... Distinctive “butterfly” shape due to its left and right lobes, which are connected at the anterior midline by a narrow isthmus. Both lobes of the thyroid gland are highly vascularized, giving it an intense reddish coloration. Regulation of thyroid hormone secretion depends upon a complex thyroid gla ...
• Two hormones are produced: (vasopressin) Thyroid Gland The
... o Hyperthyroidism - overactive thyroid gland, high metabolic rate o - An autoimmune disease of the thyroid gland characterized by excessive production of thyroid hormone, , protrusion of the eyeballs ( Hvpothvroid o Hashimoto disease - autoimmune disease that attack the thyroid cells, resulting in h ...
... o Hyperthyroidism - overactive thyroid gland, high metabolic rate o - An autoimmune disease of the thyroid gland characterized by excessive production of thyroid hormone, , protrusion of the eyeballs ( Hvpothvroid o Hashimoto disease - autoimmune disease that attack the thyroid cells, resulting in h ...
DIRECTIONS: Each of the questions or incomplete statements
... DIRECTIONS: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select the ONE that is BEST in each case. 1. An otherwise normal female with a sudden loss of FSH, but not LH, secretion by the pituitary early in the follicular phase of the menstr ...
... DIRECTIONS: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select the ONE that is BEST in each case. 1. An otherwise normal female with a sudden loss of FSH, but not LH, secretion by the pituitary early in the follicular phase of the menstr ...
Female Sex Hormones
... By the end of the lesson you should be able to: 1. Say 2 effects of female sex hormones, and say where the hormones are made. 2. Describe and explain the roles of Oestrogen, FSH and LH ...
... By the end of the lesson you should be able to: 1. Say 2 effects of female sex hormones, and say where the hormones are made. 2. Describe and explain the roles of Oestrogen, FSH and LH ...
Thyroid, pituitary.and adrenal glands.etc
... • All hormones exert their effect at low blood concentrations • Receptors on or within target tissues are needed for all hormones to exert an effect • Most hormones (except for thyroid and adrenal medullary hormones) are not stored to any great extent and must be produced as needed • Hormones in the ...
... • All hormones exert their effect at low blood concentrations • Receptors on or within target tissues are needed for all hormones to exert an effect • Most hormones (except for thyroid and adrenal medullary hormones) are not stored to any great extent and must be produced as needed • Hormones in the ...
Alterations in the levels of plasma amino acids in polycystic
... for Reproductive Medicine (ESHRE/ASRM) revised consensus according to which at least two of the three following criteria are needed for the diagnosis: (i) anovulation or oligoovulation, (ii) clinical and/ or biochemical signs of hyperandrogenism, and (iii) ...
... for Reproductive Medicine (ESHRE/ASRM) revised consensus according to which at least two of the three following criteria are needed for the diagnosis: (i) anovulation or oligoovulation, (ii) clinical and/ or biochemical signs of hyperandrogenism, and (iii) ...