Artifical Neural Networks (ANN) - In data pattern recognition for
... inspected. In addition to required knowledge and expertise in the relevant field, inspections also require a significant amount of time. It may be possible ...
... inspected. In addition to required knowledge and expertise in the relevant field, inspections also require a significant amount of time. It may be possible ...
methods in knowledge gathering - Department of Computer Science
... function perform exactly the same, according to any performance measures, when averaged over all possible cost functions.” [Wolpert and Macready 96] ...
... function perform exactly the same, according to any performance measures, when averaged over all possible cost functions.” [Wolpert and Macready 96] ...
CIS 830 (Advanced Topics in AI) Lecture 2 of 45 - KDD
... Algorithm specification – overview • Translate rules to set initial network structure • Add units not specified by translation • Add links not specified by translation • perturb the network by adding near zero random numbers to all link weights and biases ...
... Algorithm specification – overview • Translate rules to set initial network structure • Add units not specified by translation • Add links not specified by translation • perturb the network by adding near zero random numbers to all link weights and biases ...
Neural Networks 2 - Monash University
... The is a good method for obtaining an initial understanding of a set of data about which the analyst does not have any opinion (e.g. no need to estimate number of clusters) The map can be used as an initial unbiased starting point for further analysis. Once the clusters are selected from the the ...
... The is a good method for obtaining an initial understanding of a set of data about which the analyst does not have any opinion (e.g. no need to estimate number of clusters) The map can be used as an initial unbiased starting point for further analysis. Once the clusters are selected from the the ...
Slide ()
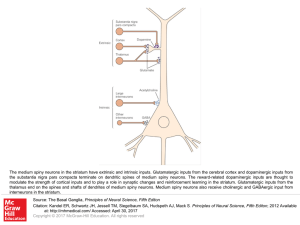
... The medium spiny neurons in the striatum have extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex and dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta terminate on dendritic spines of medium spiny neurons. The reward-related dopaminergic inputs are thought to mod ...
... The medium spiny neurons in the striatum have extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex and dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta terminate on dendritic spines of medium spiny neurons. The reward-related dopaminergic inputs are thought to mod ...
Theories of Forgetting
... There is strong evidence for both proactive and retroactive interference. It is probable that much forgetting can be attributed to both types of interference. Research is limited in several ways: • Few studies of processes used to minimise interference. • The theory largely ignores the role of inhib ...
... There is strong evidence for both proactive and retroactive interference. It is probable that much forgetting can be attributed to both types of interference. Research is limited in several ways: • Few studies of processes used to minimise interference. • The theory largely ignores the role of inhib ...
Document
... if b is a final board state that is won, then V(b) = 100 if b is a final board state that is lost, then V(b) = -100 if b is a final board state that is drawn, then V(b) = 0 if b is not a final state in the game, then V(b) = V(b'), where b' is the best final board state that can be achieved starting ...
... if b is a final board state that is won, then V(b) = 100 if b is a final board state that is lost, then V(b) = -100 if b is a final board state that is drawn, then V(b) = 0 if b is not a final state in the game, then V(b) = V(b'), where b' is the best final board state that can be achieved starting ...
UNDERSTANDING OF DEEP NEURAL NETWORKS
... ● Instead of clipping pixels with small norm we can clip pixels with small contributions. ● Pixel contribution is directly proportional to amount of activation it increases or ...
... ● Instead of clipping pixels with small norm we can clip pixels with small contributions. ● Pixel contribution is directly proportional to amount of activation it increases or ...
Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
... preference are widely dispersed over thedendritic tree and do not converge on single dendrites • Neurons with a highly tuned output signal receive input signals that are heterogeneous The results support a neuronal integration model involving summation of distributed inputs, rather than models that ...
... preference are widely dispersed over thedendritic tree and do not converge on single dendrites • Neurons with a highly tuned output signal receive input signals that are heterogeneous The results support a neuronal integration model involving summation of distributed inputs, rather than models that ...
AI_Connectionism_Excel
... - Categories at the middle level are most consistent across cultures, easiest to process, and members are more clearly grouped (What else do you notice?) ...
... - Categories at the middle level are most consistent across cultures, easiest to process, and members are more clearly grouped (What else do you notice?) ...
The role of AI and learning
... • We can see AI from 4 different perspectives: 1. Systems that think like humans 2. Systems that act like humans 3. Systems that think rationally 4. Systems that act rationally ...
... • We can see AI from 4 different perspectives: 1. Systems that think like humans 2. Systems that act like humans 3. Systems that think rationally 4. Systems that act rationally ...
The Evolutionary Emergence of Socially Intelligent Agents
... we do not understand such intelligence well enough to program it into a machine. Therefore, we must either increase our understanding until we can, or create a system which outperforms the specifications we can give it. The first possibility includes the traditional top-down methodology, which is cl ...
... we do not understand such intelligence well enough to program it into a machine. Therefore, we must either increase our understanding until we can, or create a system which outperforms the specifications we can give it. The first possibility includes the traditional top-down methodology, which is cl ...
Unimodal or Bimodal Distribution of Synaptic Weights?
... Most Hebbian learning rules or BCM rules used to describe receptive field development exhibit a spontaneous separation of synaptic weights into two groups, i.e., strong and weak synapses, so that the distribution of synaptic weights is bimodal. This implies that even rather ‘weak’, non-significant c ...
... Most Hebbian learning rules or BCM rules used to describe receptive field development exhibit a spontaneous separation of synaptic weights into two groups, i.e., strong and weak synapses, so that the distribution of synaptic weights is bimodal. This implies that even rather ‘weak’, non-significant c ...
Machine Learning
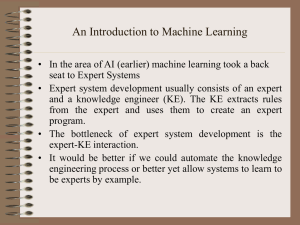
... • In the area of AI (earlier) machine learning took a back seat to Expert Systems • Expert system development usually consists of an expert and a knowledge engineer (KE). The KE extracts rules from the expert and uses them to create an expert program. • The bottleneck of expert system development is ...
... • In the area of AI (earlier) machine learning took a back seat to Expert Systems • Expert system development usually consists of an expert and a knowledge engineer (KE). The KE extracts rules from the expert and uses them to create an expert program. • The bottleneck of expert system development is ...
Lec 18 - Forgetting
... "memory trace" is formed in the brain and over time this trace tends to disintegrate, unless it is occasionally used. Definitions and Controversy Forgetting can have very different causes than simply removal of stored content. Forgetting can mean access problems, availability problems, or can have o ...
... "memory trace" is formed in the brain and over time this trace tends to disintegrate, unless it is occasionally used. Definitions and Controversy Forgetting can have very different causes than simply removal of stored content. Forgetting can mean access problems, availability problems, or can have o ...
Simulation of Back Propagation Neural Network for Iris Flower
... Target outputs (3×120): There are three outputs for each feature vector. There are 120 such vectors for training and will be the targets for the input vectors. Test inputs (4×30): Once the network has been trained, it has to be tested on data that it has not seen before. 30 vectors are used for test ...
... Target outputs (3×120): There are three outputs for each feature vector. There are 120 such vectors for training and will be the targets for the input vectors. Test inputs (4×30): Once the network has been trained, it has to be tested on data that it has not seen before. 30 vectors are used for test ...
Catastrophic interference
Catastrophic Interference, also known as catastrophic forgetting, is the tendency of a artificial neural network to completely and abruptly forget previously learned information upon learning new information. Neural networks are an important part of the network approach and connectionist approach to cognitive science. These networks use computer simulations to try and model human behaviours, such as memory and learning. Catastrophic interference is an important issue to consider when creating connectionist models of memory. It was originally brought to the attention of the scientific community by research from McCloskey and Cohen (1989), and Ractcliff (1990). It is a radical manifestation of the ‘sensitivity-stability’ dilemma or the ‘stability-plasticity’ dilemma. Specifically, these problems refer to the issue of being able to make an artificial neural network that is sensitive to, but not disrupted by, new information. Lookup tables and connectionist networks lie on the opposite sides of the stability plasticity spectrum. The former remains completely stable in the presence of new information but lacks the ability to generalize, i.e. infer general principles, from new inputs. On the other hand, connectionst networks like the standard backpropagation network are very sensitive to new information and can generalize on new inputs. Backpropagation models can be considered good models of human memory insofar as they mirror the human ability to generalize but these networks often exhibit less stability than human memory. Notably, these backpropagation networks are susceptible to catastrophic interference. This is considered an issue when attempting to model human memory because, unlike these networks, humans typically do not show catastrophic forgetting. Thus, the issue of catastrophic interference must be eradicated from these backpropagation models in order to enhance the plausibility as models of human memory.