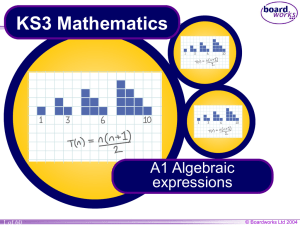
A6 Quadratic equations
... If Jenny’s average speed on the way to work was 8 miles per hour her average speed on the way home would be –12 miles per hour, a negative number. We can therefore ignore the second solution. When practical problems lead to quadratic equations it is very often the case that only one of the solution ...
... If Jenny’s average speed on the way to work was 8 miles per hour her average speed on the way home would be –12 miles per hour, a negative number. We can therefore ignore the second solution. When practical problems lead to quadratic equations it is very often the case that only one of the solution ...
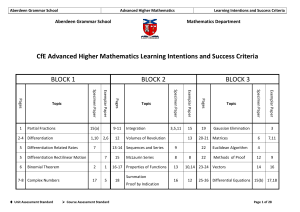
Unit 1
... It is sometimes said that statements of the form 'x + 2 = 5' are conditional equations, and that statements of the form ‘x+y= y+x’ are identities. We shall not use this technical sort of jargon. There is one more question of meaning which we would like to discuss before ending this linguistic intros ...
... It is sometimes said that statements of the form 'x + 2 = 5' are conditional equations, and that statements of the form ‘x+y= y+x’ are identities. We shall not use this technical sort of jargon. There is one more question of meaning which we would like to discuss before ending this linguistic intros ...
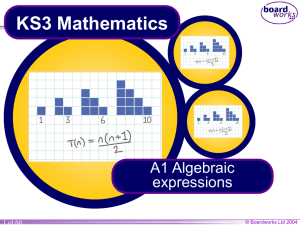
A6 Quadratic equations
... If Jenny’s average speed on the way to work was 8 miles per hour her average speed on the way home would be –12 miles per hour, a negative number. We can therefore ignore the second solution. When practical problems lead to quadratic equations it is very often the case that only one of the solution ...
... If Jenny’s average speed on the way to work was 8 miles per hour her average speed on the way home would be –12 miles per hour, a negative number. We can therefore ignore the second solution. When practical problems lead to quadratic equations it is very often the case that only one of the solution ...