2.3 Summary Critical areas summary
... drawings and informal geometric constructions, and work with two- and three-dimensional shapes to solve problems involving area, surface area, and volume (4) draw inferences about populations based on samples Mathematics II (1) extending the number system (2) quadratic functions and modeling (3) exp ...
... drawings and informal geometric constructions, and work with two- and three-dimensional shapes to solve problems involving area, surface area, and volume (4) draw inferences about populations based on samples Mathematics II (1) extending the number system (2) quadratic functions and modeling (3) exp ...
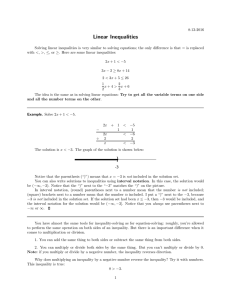
2-6 Notes 9/19/16 Solving absolute value equations
... two numbers with that absolute value. For example, both 5 and –5 have an absolute value of 5. To write this statement using algebra, you would write |x| = 5. This equation asks, “What values of x have an absolute value of 5?” The solutions are 5 and –5. Notice this equation has two solutions. Holt M ...
... two numbers with that absolute value. For example, both 5 and –5 have an absolute value of 5. To write this statement using algebra, you would write |x| = 5. This equation asks, “What values of x have an absolute value of 5?” The solutions are 5 and –5. Notice this equation has two solutions. Holt M ...
State, ACT, and Common Core Standards Alignment
... integers for unknown quantities ■ Add and subtract simple algebraic expressions ■ Solve routine first-degree equations ■ Perform straightforward word-toSymbol translations ■ Multiply two binomials* ...
... integers for unknown quantities ■ Add and subtract simple algebraic expressions ■ Solve routine first-degree equations ■ Perform straightforward word-toSymbol translations ■ Multiply two binomials* ...