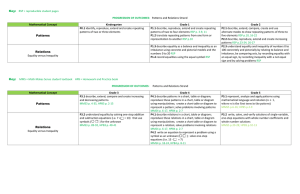
Patterns and Relations
... P4.1 describe patterns in a chart, table or diagram; reproduce these patterns in a chart, table or diagram using manipulatives; create a chart table or diagram to represent a pattern; solve problems involving patterns MMS4 p. 6-17, HPB4 p. 2-7 P4.1 describe relations in a chart, table or diagram; re ...
... P4.1 describe patterns in a chart, table or diagram; reproduce these patterns in a chart, table or diagram using manipulatives; create a chart table or diagram to represent a pattern; solve problems involving patterns MMS4 p. 6-17, HPB4 p. 2-7 P4.1 describe relations in a chart, table or diagram; re ...
Section 3. Proofs 3.1. Introduction. 3.1.1. Assumptions.
... To prove this kind of statement, we need prove that for every x ∈ D , P ( x ) is true. In order to prove this kind of statement, there are two methods: Method 1: Method of Exhaustion. The method of exhaustion is used when the domain is finite. Exhaustion cannot be used when the domain is infinite. T ...
... To prove this kind of statement, we need prove that for every x ∈ D , P ( x ) is true. In order to prove this kind of statement, there are two methods: Method 1: Method of Exhaustion. The method of exhaustion is used when the domain is finite. Exhaustion cannot be used when the domain is infinite. T ...