Chapter1 Fundamental law of geometrical optics 第一章 几何光学的
... Velocity v=3*10 10 cm/sec in empty space ...
... Velocity v=3*10 10 cm/sec in empty space ...
AP Physics B Waves and Optics Sample MC
... best example of this wave. (B) are perpendicular to the wave motion and sound is the best example of this wave. (C) are parallel to the wave motion and light is the best example of this wave. (D) are parallel to the wave motion and sound is the best example of this wave. (E) None of these. ...
... best example of this wave. (B) are perpendicular to the wave motion and sound is the best example of this wave. (C) are parallel to the wave motion and light is the best example of this wave. (D) are parallel to the wave motion and sound is the best example of this wave. (E) None of these. ...
Material and design choices for a small movement +
... optical platform. These requirements in general are: Stability; the precision optical platform needs to stay exactly where it is put until an effort is made to move it. Repeatability; the precision optical platform needs to be able to be moved and then moved back to the same location within the rang ...
... optical platform. These requirements in general are: Stability; the precision optical platform needs to stay exactly where it is put until an effort is made to move it. Repeatability; the precision optical platform needs to be able to be moved and then moved back to the same location within the rang ...
Document
... can be employed to solve essentially all linear problems. This principle states that, for linear systems, the effects of a of stimuli equals the of the individual stimuli. This property of linearity will be mathematically defined shortly; for now we will discuss the physical significance of ...
... can be employed to solve essentially all linear problems. This principle states that, for linear systems, the effects of a of stimuli equals the of the individual stimuli. This property of linearity will be mathematically defined shortly; for now we will discuss the physical significance of ...
Physics Final Review Packet
... Answer the following questions as they pertain to mirrors: a) Describe the physical properties of the image seen in a plane mirror. Virtual, same size, same distance b) Describe the physical properties of a virtual image. Upright, can’t show up on screen c) An object produces a virtual image in a co ...
... Answer the following questions as they pertain to mirrors: a) Describe the physical properties of the image seen in a plane mirror. Virtual, same size, same distance b) Describe the physical properties of a virtual image. Upright, can’t show up on screen c) An object produces a virtual image in a co ...
Final Exam - Department of Physics and Astronomy : University of
... Yellow light (λ = 600 nm) is used to view an object under a microscope. The object lens diameter is 10.00 mm. (a) What is the limiting angle of resolution (i.e. angle of diffraction)? (b) Suppose it is possible to use visible light of any wavelength. What color should you choose to give the smallest ...
... Yellow light (λ = 600 nm) is used to view an object under a microscope. The object lens diameter is 10.00 mm. (a) What is the limiting angle of resolution (i.e. angle of diffraction)? (b) Suppose it is possible to use visible light of any wavelength. What color should you choose to give the smallest ...
Q - IndiaStudyChannel
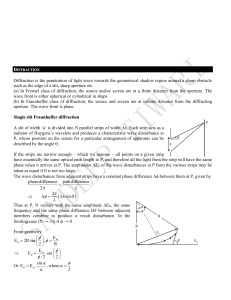
... wave front is either spherical or cylindrical in shape (b) In Fraunhoffer class of diffraction, the source and screen are at infinite distance from the diffracting aperture. The wave front is plane. Single slit Fraunhoffer diffraction P ...
... wave front is either spherical or cylindrical in shape (b) In Fraunhoffer class of diffraction, the source and screen are at infinite distance from the diffracting aperture. The wave front is plane. Single slit Fraunhoffer diffraction P ...
Light Sources
... passing through the aperture. (The smaller the aperture, the more it spreads out.) • If we want to image the aperture on an image plane (resist), we can collect the light using a lens and focus it on the image plane. • But the finite diameter of the lens means some information is lost (higher spatia ...
... passing through the aperture. (The smaller the aperture, the more it spreads out.) • If we want to image the aperture on an image plane (resist), we can collect the light using a lens and focus it on the image plane. • But the finite diameter of the lens means some information is lost (higher spatia ...
Lab 2: Abbe Theory of Imaging
... The set-up is now ready for the examination of slides. The image will be observed on an index card in another modified target assembly. The location of the observation plane will be about 450mm after the last lens and will give an image about twice the size as the object slide when the card at the b ...
... The set-up is now ready for the examination of slides. The image will be observed on an index card in another modified target assembly. The location of the observation plane will be about 450mm after the last lens and will give an image about twice the size as the object slide when the card at the b ...
6.1 Electromagnetic Waves
... a harmonic wave in either time or distance • waves are characterized by their period, frequency, wavelength and wave number • Planck's Law gives the energy of electromagnetic quanta • ν and λ are related by the speed of light, which in turn is determined by the refractive index • electromagnetic rad ...
... a harmonic wave in either time or distance • waves are characterized by their period, frequency, wavelength and wave number • Planck's Law gives the energy of electromagnetic quanta • ν and λ are related by the speed of light, which in turn is determined by the refractive index • electromagnetic rad ...
A new optical configuration in speckle interferometry for contouring
... the grating frequency formed due to two the random phase of the speckle field. apertures, After processing, the specklegram Žprocessed double exposed plate. is whole-field filtered w11x. Three halos are formed at the Fourier transform plane including the zeroth order; filtering through one of the fi ...
... the grating frequency formed due to two the random phase of the speckle field. apertures, After processing, the specklegram Žprocessed double exposed plate. is whole-field filtered w11x. Three halos are formed at the Fourier transform plane including the zeroth order; filtering through one of the fi ...
Maxwell equation - Technion moodle
... In a homogeneous medium, all components of the fields E, D, H, B are continuous functions of position. At the boundary between two dielectric media, in the absence of free electric charges and currents, the tangential components of the electric E and magnetic H fields, and the normal components of t ...
... In a homogeneous medium, all components of the fields E, D, H, B are continuous functions of position. At the boundary between two dielectric media, in the absence of free electric charges and currents, the tangential components of the electric E and magnetic H fields, and the normal components of t ...