Molecular Structures of the Products of a Diphosphonate Ester
... experimental conditions, 2, 3 and 4 exhibit emission peaks at 423, 420 and 428 nm, respectively, which are very similar to that of 1. These emissions can be tentatively ascribed to an intraligand transition. Based on these similarities, one can deduce that the electron transition modes in 2, 3 and 4 ...
... experimental conditions, 2, 3 and 4 exhibit emission peaks at 423, 420 and 428 nm, respectively, which are very similar to that of 1. These emissions can be tentatively ascribed to an intraligand transition. Based on these similarities, one can deduce that the electron transition modes in 2, 3 and 4 ...
Four Characteristics of Minerals
... Volume – amount of space that is taken up by an object If liquids or gases can be changed into a solid form; it can be a mineral. ...
... Volume – amount of space that is taken up by an object If liquids or gases can be changed into a solid form; it can be a mineral. ...
Ch 1 Earth Materials
... influence on mineral characteristics • Define and distinguish between minerals and rocks • List key properties used to identify minerals • Identify most common mineral families and accessory mineral families • Explain what holds rocks together ...
... influence on mineral characteristics • Define and distinguish between minerals and rocks • List key properties used to identify minerals • Identify most common mineral families and accessory mineral families • Explain what holds rocks together ...
Chapter 8 – Symmetry in Crystal Physics – p. 1
... Must be fulfilled for all transformation matrices aij corresponding to symmetry operations of the point group of the crystal (crystal class) (remark: in general, it is not necessary to test all symmetry operations, but only the set of generating operations of the point group). Neumann’s principle ma ...
... Must be fulfilled for all transformation matrices aij corresponding to symmetry operations of the point group of the crystal (crystal class) (remark: in general, it is not necessary to test all symmetry operations, but only the set of generating operations of the point group). Neumann’s principle ma ...
of a mineral? - Bakersfield College
... Why are gold, pyrite, and diamond considered minerals? The 5-part mineral definition: ...
... Why are gold, pyrite, and diamond considered minerals? The 5-part mineral definition: ...
INTRODUCTION 1 The oral route is the most desirable for drug
... The process of crystallization depends on achieving three conditions in succession; a state of super saturation (super cooling in the case of crystallization from a melt), formation of nuclei and growth of crystals or amorphous particles20, 21. Crystal habit is influenced by the degree of super satu ...
... The process of crystallization depends on achieving three conditions in succession; a state of super saturation (super cooling in the case of crystallization from a melt), formation of nuclei and growth of crystals or amorphous particles20, 21. Crystal habit is influenced by the degree of super satu ...
Go Here For PPT
... CRYSTAL - A mineral grain displaying the characteristics of its atomic structure. - almost 4000 different kinds of minerals - differences result from the different elements used and the ways they are bonded ...
... CRYSTAL - A mineral grain displaying the characteristics of its atomic structure. - almost 4000 different kinds of minerals - differences result from the different elements used and the ways they are bonded ...
CLAY MINERALS
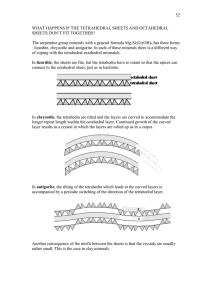
... rings are related by mirror planes parallel to (010) and diads parallel to the b axis. Two sets of individual tetrahedra are distinguishable in this layer, and are labelled T1 and T2. The T1 tetrahedra are all related to one another by symmetry, as are the T2 tetrahedra. In the third dimension these ...
... rings are related by mirror planes parallel to (010) and diads parallel to the b axis. Two sets of individual tetrahedra are distinguishable in this layer, and are labelled T1 and T2. The T1 tetrahedra are all related to one another by symmetry, as are the T2 tetrahedra. In the third dimension these ...
Effect of Hippuric Acid on the Growth, Structural and Optical
... Abstract: Non-linear optical potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP) and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP) single crystals with 1 mol% of hippuric acid dopant were grown from aqueous solution by employing slow evaporation technique. With appropriate dopants, the KDP and ADP crystals exhibit several d ...
... Abstract: Non-linear optical potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP) and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP) single crystals with 1 mol% of hippuric acid dopant were grown from aqueous solution by employing slow evaporation technique. With appropriate dopants, the KDP and ADP crystals exhibit several d ...
The crystal structure of L
... isotropic peaks as a result of local structural differences for the two independent molecules. Along the b-axis, the molecules are arranged in two distinct ‘‘sinusoidal’’ chains (Fig. 5); one chain involves molecules of type A only and the other chain involves molecules of type B only. In each chain, ...
... isotropic peaks as a result of local structural differences for the two independent molecules. Along the b-axis, the molecules are arranged in two distinct ‘‘sinusoidal’’ chains (Fig. 5); one chain involves molecules of type A only and the other chain involves molecules of type B only. In each chain, ...
Document
... • A mineral is a solid, naturally occurring substance that has a specific chemical composition and a highly ordered internal (crystalline) structure. ...
... • A mineral is a solid, naturally occurring substance that has a specific chemical composition and a highly ordered internal (crystalline) structure. ...
Structural properties - Département de Physique
... Website : www.equipes.lps.u-psud.fr/m2structure/ Lectures and tutorials : 46h (28h lectures, 18h tutorials) Practicals : 14h (= 2 days per student) In this lecture, we aim at providing a conceptual basis to understand modern experimental techniques used to investigate the structural, electronic and ...
... Website : www.equipes.lps.u-psud.fr/m2structure/ Lectures and tutorials : 46h (28h lectures, 18h tutorials) Practicals : 14h (= 2 days per student) In this lecture, we aim at providing a conceptual basis to understand modern experimental techniques used to investigate the structural, electronic and ...
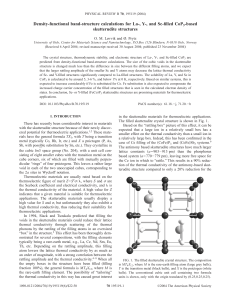
Density-functional band-structure calculations for La-, Y
... the isotropic distribution of the filling atoms. The model with x = 12.5% has been constructed using a 2 ⫻ 2 ⫻ 2 primitive (rhombohedral) cell in order to preserve cubic symmetry. The other models use the conventional cubic cell. The relaxation procedure allowed the unit cell to change size and shap ...
... the isotropic distribution of the filling atoms. The model with x = 12.5% has been constructed using a 2 ⫻ 2 ⫻ 2 primitive (rhombohedral) cell in order to preserve cubic symmetry. The other models use the conventional cubic cell. The relaxation procedure allowed the unit cell to change size and shap ...
PPS - School of Physics
... Dusty plasma is consisted of neutral gas, ions, electrons, and micron-size particles that have a negative charge. Under certain conditions, dust immersed in plasma form stable structures similar to the liquid or the solid. There are two known empirical rules for fluid-solid first-order phase transit ...
... Dusty plasma is consisted of neutral gas, ions, electrons, and micron-size particles that have a negative charge. Under certain conditions, dust immersed in plasma form stable structures similar to the liquid or the solid. There are two known empirical rules for fluid-solid first-order phase transit ...
research highlight in Nature Mat. (July 2011)
... quantum dots that were capped with the two isomeric forms of the tripeptide glutadione. Although cell uptake was independent of ligand chirality, quantum dots capped with the d-isomer were less likely to induce autophagy than the l-isomer. Although cell viability could not yet be enhanced to unity, ...
... quantum dots that were capped with the two isomeric forms of the tripeptide glutadione. Although cell uptake was independent of ligand chirality, quantum dots capped with the d-isomer were less likely to induce autophagy than the l-isomer. Although cell viability could not yet be enhanced to unity, ...
Minerals I - Winthrop Chemistry, Physics, and Geology
... There are only 6 symmetry classes; each mineral belongs to only ONE symmetry class, and thus all crystals exhibit that symmetry only! ...
... There are only 6 symmetry classes; each mineral belongs to only ONE symmetry class, and thus all crystals exhibit that symmetry only! ...
ppt - National Single Crystal X
... • The Green least squares line should run from the lower left to the upper right corner for the correct absolute structure. • Vertical bars on data points indicate the su on the Bijvoet Difference. Example ...
... • The Green least squares line should run from the lower left to the upper right corner for the correct absolute structure. • Vertical bars on data points indicate the su on the Bijvoet Difference. Example ...
Structural basis for the fast phase change of DVD-RAM
... Structural basis for the fast phase change of DVD-RAM The research group of Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI), Riken Harima Institute, Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. and Tsukuba University et al. has discovered the key structure of DVD-RAM, which highly contributes to ...
... Structural basis for the fast phase change of DVD-RAM The research group of Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI), Riken Harima Institute, Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. and Tsukuba University et al. has discovered the key structure of DVD-RAM, which highly contributes to ...
Crystal structure

In mineralogy and crystallography, a crystal structure is a unique arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid. It describes a highly ordered structure, occurring due to the intrinsic nature of its constituents to form symmetric patterns.The crystal lattice can be thought of as an array of 'small boxes' infinitely repeating in all three spatial directions. Such a unit cell is the smallest unit of volume that contains all of the structural and symmetry information to build-up the macroscopic structure of the lattice by translation.Patterns are located upon the points of a lattice, which is an array of points repeating periodically in three dimensions. The lengths of the edges of a unit cell and the angles between them are called the lattice parameters. The symmetry properties of the crystal are embodied in its space group.A crystal's structure and symmetry play a role in determining many of its physical properties, such as cleavage, electronic band structure, and optical transparency.