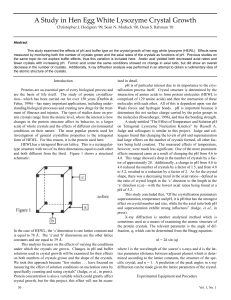
Comparison of the electronic structures of four crystalline phases of
... the delithiated form of LiFePO4 in connection with Li ion battery cathodes.1 The mineral names “heterosite” and “olivine” have been used to describe this orthorhombic form of iron phosphate which has the space group symmetry P nma (No. 62 in the International Tables for Crystallography2 ). Although ...
... the delithiated form of LiFePO4 in connection with Li ion battery cathodes.1 The mineral names “heterosite” and “olivine” have been used to describe this orthorhombic form of iron phosphate which has the space group symmetry P nma (No. 62 in the International Tables for Crystallography2 ). Although ...
What is a mineral? - The Science Queen
... Crystalline means that atoms are arranged in a pattern that is repeated over and ...
... Crystalline means that atoms are arranged in a pattern that is repeated over and ...
Chapter 5:
... is 6.12×10-27, whereas at 1000 K this increases to 1.37×10-8 At room temperature there are very few Schottky defects, even at 1000K there are only about 1 or 2 defects per hundred million sites. Depending on the value of DH, a Schottky or Frenkel defect may be present. The lower DH dominates, but in ...
... is 6.12×10-27, whereas at 1000 K this increases to 1.37×10-8 At room temperature there are very few Schottky defects, even at 1000K there are only about 1 or 2 defects per hundred million sites. Depending on the value of DH, a Schottky or Frenkel defect may be present. The lower DH dominates, but in ...
Ab initio Electronic Structure Calculations and
... ferromagnetism with Tc = 41.5 K, while Ni3Ga is an exchange-enhanced paramagnetic metal. The unique properties of these intermetallic compounds are due, in part, to the nature of their atomic/crystal and electronic structures. The electronic structure of Ni 3 Al and Ni 3 Ga have been extensively stu ...
... ferromagnetism with Tc = 41.5 K, while Ni3Ga is an exchange-enhanced paramagnetic metal. The unique properties of these intermetallic compounds are due, in part, to the nature of their atomic/crystal and electronic structures. The electronic structure of Ni 3 Al and Ni 3 Ga have been extensively stu ...
Superconductivity Is Pair Work - Max-Planck
... The properties of the Cooper pairs are radically different from those of the electrons. Pursuant to the rules of quantum mechanics, electrons possess a half-integer spin. They thus belong to the group of particles known as fermions. These are quite acquisitive, each requiring a quantum state for it ...
... The properties of the Cooper pairs are radically different from those of the electrons. Pursuant to the rules of quantum mechanics, electrons possess a half-integer spin. They thus belong to the group of particles known as fermions. These are quite acquisitive, each requiring a quantum state for it ...
Ch 2 Review User Friendly
... 28) How does the rate of cooling magma affect mineral crystal size? … the faster magma cools the _____________er the crystal. 29) What is a solution? ………………………………………………………………….. 30) What is a vein? …………………………………………………………………………. 31) What is a chimney? ………………………………………………………………………. 32) How are minerals ...
... 28) How does the rate of cooling magma affect mineral crystal size? … the faster magma cools the _____________er the crystal. 29) What is a solution? ………………………………………………………………….. 30) What is a vein? …………………………………………………………………………. 31) What is a chimney? ………………………………………………………………………. 32) How are minerals ...
Building Materials by Packing Spheres
... natural building blocks for composite materials with micrometer-scale features, but these particles have one inherent limitation: they are nearly always spheres. Because a colloidal particle is much larger than its constituent atoms, its shape is determined by surface tension, not by its interior co ...
... natural building blocks for composite materials with micrometer-scale features, but these particles have one inherent limitation: they are nearly always spheres. Because a colloidal particle is much larger than its constituent atoms, its shape is determined by surface tension, not by its interior co ...
Modular Chemistry: Secondary Building Units as a
... group of N vertices is a special case of decoration which we refer to as augmentation.24) An increasing number of assembled frameworks have as components polytopic groupings of linkers such as 1,3,5-benzenetribenzoate (BTB), which in themselves may act to decorate a vertex in an assembly. Polytopic ...
... group of N vertices is a special case of decoration which we refer to as augmentation.24) An increasing number of assembled frameworks have as components polytopic groupings of linkers such as 1,3,5-benzenetribenzoate (BTB), which in themselves may act to decorate a vertex in an assembly. Polytopic ...
Section 1 Review
... 2. Identify What are the three most common nonsilicate crystal structures? 3. Apply Concepts Give one exanlple of a mineral. Describe at least three character ...
... 2. Identify What are the three most common nonsilicate crystal structures? 3. Apply Concepts Give one exanlple of a mineral. Describe at least three character ...
Nanostructures and Computation—S.G. Johnson
... negative refraction. Because these are complicated structures, there are many open problems in their theoretical understanding, from what phenomena are possible to how to predict their behavior without resorting to brute-force computation. In this modeling, we have made strides in developing semi-an ...
... negative refraction. Because these are complicated structures, there are many open problems in their theoretical understanding, from what phenomena are possible to how to predict their behavior without resorting to brute-force computation. In this modeling, we have made strides in developing semi-an ...
What Is A Mineral?
... compounds of two or more chemical elements. The compositions of some minerals vary because of ionic substitution, whereby one ion in a crystal structure can be replaced by another ion having a like electrical charge and a like ionic radius. ...
... compounds of two or more chemical elements. The compositions of some minerals vary because of ionic substitution, whereby one ion in a crystal structure can be replaced by another ion having a like electrical charge and a like ionic radius. ...
mineralcards17 - PAMS-Doyle
... inorganic solid, definite chemical composition, crystalline structure ...
... inorganic solid, definite chemical composition, crystalline structure ...
Structural Features of Hexakis-DMSO Nickel(II) Complex Cations
... bis(tetraphenylborate)] was prepared, and characterized by a single-crystal X-ray method. The compound crystallizes in the triclinic space group P1 and Z = 1 with cell parameters a = 12.4224(17)Å, b = 12.5588(18)Å, c = 12.9099(18)Å, a = 61.745(2)˚, b = 89.999(2)˚, g = 63.942(2)˚, V = 1537.8(4)Å3. Si ...
... bis(tetraphenylborate)] was prepared, and characterized by a single-crystal X-ray method. The compound crystallizes in the triclinic space group P1 and Z = 1 with cell parameters a = 12.4224(17)Å, b = 12.5588(18)Å, c = 12.9099(18)Å, a = 61.745(2)˚, b = 89.999(2)˚, g = 63.942(2)˚, V = 1537.8(4)Å3. Si ...
Crystal structure

In mineralogy and crystallography, a crystal structure is a unique arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid. It describes a highly ordered structure, occurring due to the intrinsic nature of its constituents to form symmetric patterns.The crystal lattice can be thought of as an array of 'small boxes' infinitely repeating in all three spatial directions. Such a unit cell is the smallest unit of volume that contains all of the structural and symmetry information to build-up the macroscopic structure of the lattice by translation.Patterns are located upon the points of a lattice, which is an array of points repeating periodically in three dimensions. The lengths of the edges of a unit cell and the angles between them are called the lattice parameters. The symmetry properties of the crystal are embodied in its space group.A crystal's structure and symmetry play a role in determining many of its physical properties, such as cleavage, electronic band structure, and optical transparency.





![Poly[(tri-`butyl-phosphine)gold(I)]ammonhim](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016955699_1-3ddf66273799341f4663a1d22989efb5-300x300.png)