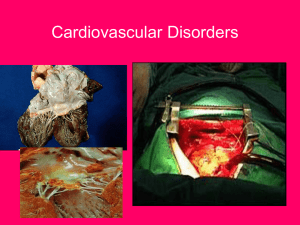
Rheumatic Fever and Heart Disease
... Diagrammatic comparison of the lesions in the four major forms of vegetative endocarditis. The rheumatic fever phase of RHD (rheumatic heart disease) is marked by a row of warty, small vegetations along the lines of closure of the valve leaflets. IE (infective endocarditis) is characterized by larg ...
... Diagrammatic comparison of the lesions in the four major forms of vegetative endocarditis. The rheumatic fever phase of RHD (rheumatic heart disease) is marked by a row of warty, small vegetations along the lines of closure of the valve leaflets. IE (infective endocarditis) is characterized by larg ...
Rheumatic Heart Disease: Genes, Inflammation and Autoimmunity
... Rheumatic heart disease is a sequel of rheumatic fever that follows an untreated group A streptococcal infection in young susceptible individuals. The disease is mediated by autoimmune reactions. Several genes related to both the innate and adaptive immune response are involved. Several HLA class II ...
... Rheumatic heart disease is a sequel of rheumatic fever that follows an untreated group A streptococcal infection in young susceptible individuals. The disease is mediated by autoimmune reactions. Several genes related to both the innate and adaptive immune response are involved. Several HLA class II ...
Biochemistry - u.arizona.edu
... Degenerative calcific (senile) aortic stenosis - age-related (80s and 90s) Congenitally bicuspid valve with degeneration - 1-2% of pop., symptomatic in adults. Postinflammatory aortic stenosis (rheumatic) - less common. Endocarditis - vegetations, masses of fibrin, inflammatory cells, and microorgan ...
... Degenerative calcific (senile) aortic stenosis - age-related (80s and 90s) Congenitally bicuspid valve with degeneration - 1-2% of pop., symptomatic in adults. Postinflammatory aortic stenosis (rheumatic) - less common. Endocarditis - vegetations, masses of fibrin, inflammatory cells, and microorgan ...
Heart valve disorder
... b. Angina pectoris: chest pain caused by inadequate O2 to the heart muscle cells. This condition may also result from stress-induced spasm of the atherosclerotic coronary arteries. c. Myocardial infarction: when the blockage of a coronary artery is more complete or prolonged. This leads to death of ...
... b. Angina pectoris: chest pain caused by inadequate O2 to the heart muscle cells. This condition may also result from stress-induced spasm of the atherosclerotic coronary arteries. c. Myocardial infarction: when the blockage of a coronary artery is more complete or prolonged. This leads to death of ...
File - Sheffield Peer Teaching Society
... • Pulmonary hyptertension • Once PVR>SVR then Eisenmenger’s ...
... • Pulmonary hyptertension • Once PVR>SVR then Eisenmenger’s ...
Tobacco Smoke
... Anitschkow cells. • Anitschkow cells : have abundant cytoplasm and central round-to-ovoid nuclei in which the chromatin is disposed in ...
... Anitschkow cells. • Anitschkow cells : have abundant cytoplasm and central round-to-ovoid nuclei in which the chromatin is disposed in ...
Pre-Lecture Quiz
... 1. The sinoatrial (SA) node, with an inherent firing rate of 60 to 100 impulses per minute, is considered the primary pacemaker of the heart. 2. Afterload refers to the degree of stretch of the ventricular cardiac muscle fibers at the end of diastole. 3. Hypertension is defined as a systolic BP that ...
... 1. The sinoatrial (SA) node, with an inherent firing rate of 60 to 100 impulses per minute, is considered the primary pacemaker of the heart. 2. Afterload refers to the degree of stretch of the ventricular cardiac muscle fibers at the end of diastole. 3. Hypertension is defined as a systolic BP that ...
L2- INEFFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS
... Endocarditis, irrespective of the underlying cardiac condition, is a serious, life-threatening disease that was always fatal in the preantibiotic era. Advances in antimicrobial therapy Early recognition and management of complications of IE Improved surgical technology have reduced the morbidity and ...
... Endocarditis, irrespective of the underlying cardiac condition, is a serious, life-threatening disease that was always fatal in the preantibiotic era. Advances in antimicrobial therapy Early recognition and management of complications of IE Improved surgical technology have reduced the morbidity and ...
Complete heart block in Acute Rheumatic fever
... during the acute phase of rheumatic fever. Almost 40% to 60% of patients exhibit a delay in AV conduction, which is manifested by a prolonged PR interval.2,4 Besides first-degree AV block, other disturbances encountered in acute rheumatic fever include second-degree AV block, junctional tachycardia ...
... during the acute phase of rheumatic fever. Almost 40% to 60% of patients exhibit a delay in AV conduction, which is manifested by a prolonged PR interval.2,4 Besides first-degree AV block, other disturbances encountered in acute rheumatic fever include second-degree AV block, junctional tachycardia ...
Things you need to know
... What is rheumatic fever? • Rheumatic fever is a sickness caused by a germ called Streptococcus, also known as ‘strep’. • The strep germ is a common cause of sore throats and skin sores in children aged 5-14 years. • In some children and adults ‘strep’ throat can cause sickness in other parts of ...
... What is rheumatic fever? • Rheumatic fever is a sickness caused by a germ called Streptococcus, also known as ‘strep’. • The strep germ is a common cause of sore throats and skin sores in children aged 5-14 years. • In some children and adults ‘strep’ throat can cause sickness in other parts of ...
Cardiovascular Disorders/homeostatic Imbalances
... • http://www.healthcentral.com/cholesterol/u nderstanding-cholesterol-13-115.html • http://www.medindia.net/animation/heart_a ttack.asp ...
... • http://www.healthcentral.com/cholesterol/u nderstanding-cholesterol-13-115.html • http://www.medindia.net/animation/heart_a ttack.asp ...
Explain and enumerate the different classifications
... care for the following disorder Inflammatory Hear ...
... care for the following disorder Inflammatory Hear ...
6. Rheumatic heart disease in pregnancy
... rheumatic fever? Acute rheumatic fever (ARF) is an illness caused by a reaction to a bacterial infection with group A streptococcus. It causes an acute, generalised inflammatory response and an illness that targets specific parts of the body, including the heart, joints, brain and skin. Individuals ...
... rheumatic fever? Acute rheumatic fever (ARF) is an illness caused by a reaction to a bacterial infection with group A streptococcus. It causes an acute, generalised inflammatory response and an illness that targets specific parts of the body, including the heart, joints, brain and skin. Individuals ...
Week 10 Activity INUR3306
... system. Rheumatic fever follows pharyngeal infection with rheumatogenic group A streptococci. Damaged valves and endocardium contribute to the development of infective endocarditis. Specifically, the damaged part of a heart valve forms a local blood clot, a condition known as non-bacterial thromboti ...
... system. Rheumatic fever follows pharyngeal infection with rheumatogenic group A streptococci. Damaged valves and endocardium contribute to the development of infective endocarditis. Specifically, the damaged part of a heart valve forms a local blood clot, a condition known as non-bacterial thromboti ...
1920s Diseases
... • Measles, a childhood disease characterized by high fever, sore throat, and skin rash, was widespread in the 1920s. Lasts up to 4 weeks, permanently scars body, and less than a 50% chance of viable pregnancy. ...
... • Measles, a childhood disease characterized by high fever, sore throat, and skin rash, was widespread in the 1920s. Lasts up to 4 weeks, permanently scars body, and less than a 50% chance of viable pregnancy. ...
worksheet for infectious and communicable diseases
... WORKSHEET ANSWERS FOR INFECTIOUS AND COMMUNICABLE DISEASES Fill-in the letter(s) corresponding to the disease which manifests the stated characteristics: A. Varicella ...
... WORKSHEET ANSWERS FOR INFECTIOUS AND COMMUNICABLE DISEASES Fill-in the letter(s) corresponding to the disease which manifests the stated characteristics: A. Varicella ...
Strep Throat Information
... Scarlet fever: A very fine raised rash (feels like sandpaper) is present. The rash blanches with pressure. The rash appears most often on the neck, chest, in folds of the armpit, elbow, groin, and in the inner thigh. Later on, there may be peeling of the skin on the fingertips and toes. Perianal cel ...
... Scarlet fever: A very fine raised rash (feels like sandpaper) is present. The rash blanches with pressure. The rash appears most often on the neck, chest, in folds of the armpit, elbow, groin, and in the inner thigh. Later on, there may be peeling of the skin on the fingertips and toes. Perianal cel ...
File
... that could be seen in the heart of this patient? (50) • 5.2 List 2 other causes for endocardial vegetation? (20) • 5.3 Name 3 extra cardiac manifestations of rheumatic fever? (30) ...
... that could be seen in the heart of this patient? (50) • 5.2 List 2 other causes for endocardial vegetation? (20) • 5.3 Name 3 extra cardiac manifestations of rheumatic fever? (30) ...
Heart Inflammatory Questions Can we go over endocarditis and
... cause fluid accumulation, chronic causes fibrous thickening which inhibits cardiac filling during diastole; risk factors – infection, myocardial injury, hypersensitivity, renal failure Signs/symptoms – precordial pain, pericardial friction rub as the myocardium rubbing against the inflamed pericardi ...
... cause fluid accumulation, chronic causes fibrous thickening which inhibits cardiac filling during diastole; risk factors – infection, myocardial injury, hypersensitivity, renal failure Signs/symptoms – precordial pain, pericardial friction rub as the myocardium rubbing against the inflamed pericardi ...
Rheumatic fever

Rheumatic fever, also known as acute rheumatic fever (ARF), is an inflammatory disease that can involve the heart, joints, skin, and brain. The disease typically develops two to four weeks after a throat infection. Signs and symptoms include fever, multiple painful joints, involuntary muscle movements, and a characteristic but uncommon non itchy rash known as erythema marginatum. The heart is involved in about half of cases. Permanent damage to the heart valves, known as rheumatic heart disease (RHD), usually only occurs after multiple attacks but may occasionally occur after a single case of ARF. The damaged valves may result in heart failure. The abnormal valves also increase the risk of the person developing atrial fibrillation and infection of the valves.Acute rheumatic fever may occur following an infection of the throat by the bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes. If it is untreated ARF occurs in up to three percent of people. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve the production of antibodies against a person's own tissues. Some people due to their genetics are more likely to get the disease when exposed to the bacteria than others. Other risk factors include malnutrition and poverty. Diagnosis of ARF is often based on the presence of signs and symptoms in combination with evidence of a recent streptococcal infection.Treating people who have strep throat with antibiotics, such as penicillin, decreases their risk of getting ARF. This often involves testing people with sore throats for the infection, which may not be available in the developing world. Other preventative measures include improved sanitation. In those with ARF and RHD prolonged periods of antibiotics are sometimes recommended. Gradual return to normal activities may occur following an attack. Once RHD develops, treatment is more difficult. Occasionally valve replacement surgery or repair is required. Otherwise complications are treated as per normal.Acute rheumatic fever occurs in about 325,000 children each year and about 18 million people currently have rheumatic heart disease. Those who get ARF are most often between the ages of 5 and 14, with 20% of first-time attacks occurring in adults. The disease is most common in the developing world and among indigenous peoples in the developed world. In 2013 it resulted in 275,000 deaths down from 374,000 deaths in 1990. Most deaths occur in the developing world where as many as 12.5% of people affected may die each year. Descriptions of the condition are believed to date back to at least the 5th century BCE in the writings of Hippocrates. The disease is so named because its symptoms are similar to those of some rheumatic disorders.