Ch6Sec4 Reiforce Tratis Genes Alleles
... A gene is a segment of DNA that tells the cell how to make a particular polypeptide. The location of a gene on a chromosome is called a locus. A gene has the same locus on both chromosomes in a pair of homologous chromosomes. In genetics, scientists often focus on a single gene or set of genes. Geno ...
... A gene is a segment of DNA that tells the cell how to make a particular polypeptide. The location of a gene on a chromosome is called a locus. A gene has the same locus on both chromosomes in a pair of homologous chromosomes. In genetics, scientists often focus on a single gene or set of genes. Geno ...
Immunogens and Antigens
... • Electrostatic Interactions-Attraction of a + charge to a – charge (Glu to Lys). • Hydrogen Bonds-Bridging of a COO- to the H of an OH group. • Hydrophobic Bonds-Interaction of hydrophobic –R groups of Ag and Ab. • Van der Waal’s Forces-Attraction of oscillating dipoles, weak, 7th power of distance ...
... • Electrostatic Interactions-Attraction of a + charge to a – charge (Glu to Lys). • Hydrogen Bonds-Bridging of a COO- to the H of an OH group. • Hydrophobic Bonds-Interaction of hydrophobic –R groups of Ag and Ab. • Van der Waal’s Forces-Attraction of oscillating dipoles, weak, 7th power of distance ...
the HLA complex
... alpha and beta chains, both similar to the alpha chain of class I molecules (same domains) a separate gene controls each chain: class II MHC loci consist of 2-3 genes can bind longer peptides than class I molecules ...
... alpha and beta chains, both similar to the alpha chain of class I molecules (same domains) a separate gene controls each chain: class II MHC loci consist of 2-3 genes can bind longer peptides than class I molecules ...
kdfkdfjsdk - Austin Community College
... Most important HLA are types A, B (MHC I) and DR (MHC II) MHC I present antigens to cytotoxic T cells and MHC II use antigenpresenting cells for helper T cells For this reason, it is important to have closely matched HLA between donor and recipient to avoid rejection, i.e., to avoid donor cell ...
... Most important HLA are types A, B (MHC I) and DR (MHC II) MHC I present antigens to cytotoxic T cells and MHC II use antigenpresenting cells for helper T cells For this reason, it is important to have closely matched HLA between donor and recipient to avoid rejection, i.e., to avoid donor cell ...
Quantitative Genetics of Natural Variation: some questions
... But do not expect young, high frequency alleles. Indicates alleles at the locus may be under selection. ...
... But do not expect young, high frequency alleles. Indicates alleles at the locus may be under selection. ...
HISTOCOMPATIBILITY ANTIGENS
... • Major barrier to organ/tissue transplantation is immunological • Immune system recognizes transplant as foreign and destroys it – Memory and specificity have properties of adaptive immune response – Memory is transferred by T cells (antibodies also can contribute). ...
... • Major barrier to organ/tissue transplantation is immunological • Immune system recognizes transplant as foreign and destroys it – Memory and specificity have properties of adaptive immune response – Memory is transferred by T cells (antibodies also can contribute). ...
Causes of Autoimmune Diseases
... the same species and here rejection of the graft is the role if immunosuppression is not done. 4- Xenograft: transplantation from another species and here rejection is very severe and it is unlikely for the graft to survive. ...
... the same species and here rejection of the graft is the role if immunosuppression is not done. 4- Xenograft: transplantation from another species and here rejection is very severe and it is unlikely for the graft to survive. ...
HLA typing in transfusion and transplantation
... • Complement Dependent Cytotoxicity, including AHG (anti-human globulin) ...
... • Complement Dependent Cytotoxicity, including AHG (anti-human globulin) ...
Genetics Powerpoint 2/7/17
... – Gene • Controls how an organism develops • It is a specific segment of DNA located on a chromosome ...
... – Gene • Controls how an organism develops • It is a specific segment of DNA located on a chromosome ...
6.4 Reinforcement
... of a particular set of genes. Phenotype refers to the physical characteristics resulting from those genes. An alternative form of a gene is an allele. The pea plants that Mendel worked with had two alleles for each gene. For example, there was an allele for round peas and an allele for wrinkled peas ...
... of a particular set of genes. Phenotype refers to the physical characteristics resulting from those genes. An alternative form of a gene is an allele. The pea plants that Mendel worked with had two alleles for each gene. For example, there was an allele for round peas and an allele for wrinkled peas ...
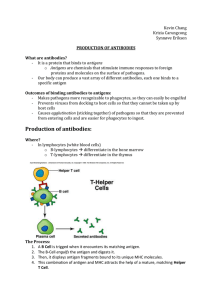
BLOCK F – Krizia,Kevin,Synnove – Production of Antibodies
... 5. Cytokines secreted by the Helper T cell help the B cell to multiply and mature into antibody producing plasma cells. 6. Antibodies then lock onto matching antigens. 7. Antibodies are made up of white blood cells, called B lymphocytes or B Cells. Each B Cell carries a different membrane-bound ant ...
... 5. Cytokines secreted by the Helper T cell help the B cell to multiply and mature into antibody producing plasma cells. 6. Antibodies then lock onto matching antigens. 7. Antibodies are made up of white blood cells, called B lymphocytes or B Cells. Each B Cell carries a different membrane-bound ant ...
Title - Iowa State University
... True breeding, cross pollinated, self bred F1s and determined and counted traits What were 3 important choices he made to structure his study? 1. True breeding - self fertilized 2. Work with discrete, categocial characters - either/or 3. Tracked for 3 generations What results did he find? Offspring ...
... True breeding, cross pollinated, self bred F1s and determined and counted traits What were 3 important choices he made to structure his study? 1. True breeding - self fertilized 2. Work with discrete, categocial characters - either/or 3. Tracked for 3 generations What results did he find? Offspring ...
Specific Immune Response Reflection
... 10. The diversity in the family of genes called the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system determines what range of epitopes can be detected by white blood cells. Some of the HLA genes have as many as 100 different possible alleles for a particular gene locus, each of which can produce a different typ ...
... 10. The diversity in the family of genes called the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system determines what range of epitopes can be detected by white blood cells. Some of the HLA genes have as many as 100 different possible alleles for a particular gene locus, each of which can produce a different typ ...
Immunology
... • Factors influencing the immune response: – genetic constitution • immune responsiveness maps to the MHC • MHC haplotye is inherited MHC alleles ...
... • Factors influencing the immune response: – genetic constitution • immune responsiveness maps to the MHC • MHC haplotye is inherited MHC alleles ...
VIDEO SUMMARIES: GENETIC VARIATION
... • Natural%selec4on%is%the%process%whereby%organisms%that%are%be:er%suited%to% the%environment%tend%to%survive%and%produce%offspring% • Purpose:%to%help%the%survival%of%the%popula4on% • Chatham%Island%(NZ)%Black%Robin% • All%from%5%one%female% • Now%250+% • No%inbreeding%effects% • Due%to%small% ...
... • Natural%selec4on%is%the%process%whereby%organisms%that%are%be:er%suited%to% the%environment%tend%to%survive%and%produce%offspring% • Purpose:%to%help%the%survival%of%the%popula4on% • Chatham%Island%(NZ)%Black%Robin% • All%from%5%one%female% • Now%250+% • No%inbreeding%effects% • Due%to%small% ...
Descriptive Epidemiology of MS
... Physical Activity and MS Physically Active Mixed Activities Sedentary Hobbies None ...
... Physical Activity and MS Physically Active Mixed Activities Sedentary Hobbies None ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI
... (a) B cell (b) Macrophage (c) Mast cell (d) Dendritic cell (2) Which one of the following has antiviral activity? (a) Interferons (b) Interleukins (c) Cytokines (d) Chemokines (3) Tissue typing can be done using (a) Immunodiffusion (b) Mixed lymphocyte reaction (c) Agglutination (d) Elispot assay (4 ...
... (a) B cell (b) Macrophage (c) Mast cell (d) Dendritic cell (2) Which one of the following has antiviral activity? (a) Interferons (b) Interleukins (c) Cytokines (d) Chemokines (3) Tissue typing can be done using (a) Immunodiffusion (b) Mixed lymphocyte reaction (c) Agglutination (d) Elispot assay (4 ...
Autoimmune Disease
... It has been hypothesized that susceptibility to an autoimmune disease is determined by differences in the ability of allelic variants of MHC molecules to present autoantigenic peptides Alternatively, self peptides may drive the positive selection of developing thymocytes that are specific for partic ...
... It has been hypothesized that susceptibility to an autoimmune disease is determined by differences in the ability of allelic variants of MHC molecules to present autoantigenic peptides Alternatively, self peptides may drive the positive selection of developing thymocytes that are specific for partic ...
1 Incomplete Dominance: A type of intermediate inheritance
... Principle of Segregation • Proposed theory by Mendel from his experiments with simple plant cross-breeding. • During Meiosis of sex cells: – Inherited chromosomes with genes (characters) and specific alleles (traits) from parents are separated into gametes (sperm or egg cells). – Each gamete produc ...
... Principle of Segregation • Proposed theory by Mendel from his experiments with simple plant cross-breeding. • During Meiosis of sex cells: – Inherited chromosomes with genes (characters) and specific alleles (traits) from parents are separated into gametes (sperm or egg cells). – Each gamete produc ...
Role of Gluten Peptides
... Gluten peptides are not easily digest by gastric, pancreatic or brush border enzymes – High concentration of proline and glutamine amino acids ...
... Gluten peptides are not easily digest by gastric, pancreatic or brush border enzymes – High concentration of proline and glutamine amino acids ...
Human leukocyte antigen
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system is the locus of genes that encode for proteins on the surface of cells that are responsible for regulation of the immune system in humans. This group of genes resides on chromosome 6 (exception: the gene for β2-microglobulin which is located on chromosome 15), and encodes cell-surface antigen-presenting proteins and has many other functions. The HLA genes are the human versions of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) genes that are found in most vertebrates (and thus are the most studied of the MHC genes). The proteins encoded by certain genes are also known as antigens, as a result of their historic discovery as factors in organ transplants. The major HLAs are essential elements for immune function. Different classes have different functions:HLAs corresponding to MHC class I (A, B, and C) present peptides from inside the cell. For example, if the cell is infected by a virus, the HLA system brings fragments of the virus to the surface of the cell so that the cell can be destroyed by the immune system. These peptides are produced from digested proteins that are broken down in the proteasomes. In general, these particular peptides are small polymers, about 9 amino acids in length. Foreign antigens presented by MHC class I attract killer T-cells (also called CD8 positive- or cytotoxic T-cells) that destroy cells.HLAs corresponding to MHC class II (DP, DM, DOA, DOB, DQ, and DR) present antigens from outside of the cell to T-lymphocytes. These particular antigens stimulate the multiplication of T-helper cells, which in turn stimulate antibody-producing B-cells to produce antibodies to that specific antigen. Self-antigens are suppressed by regulatory T cells.HLAs corresponding to MHC class III encode components of the complement system.HLAs have other roles. They are important in disease defense. They are the major cause of organ transplant rejections. They may protect against or fail to protect (if down-regulated by an infection) against cancers. Mutations in HLA may be linked to autoimmune disease (examples: type I diabetes, coeliac disease). HLA may also be related to people's perception of the odor of other people, and may be involved in mate selection, as at least one study found a lower-than-expected rate of HLA similarity between spouses in an isolated community.Aside from the genes encoding the 6 major antigen-presenting proteins, there are a large number of other genes, many involved in immune function, located on the HLA complex. Diversity of HLAs in the human population is one aspect of disease defense, and, as a result, the chance of two unrelated individuals with identical HLA molecules on all loci is very low. HLA genes have historically been identified as a result of the ability to successfully transplant organs between HLA-similar individuals.