Contribution of microbiology to the management of sepsis
... Time line of “immunology” 1774 – Benjamin Jesty: use of material from cowpox lesions for vaccination against smallpox 1776 – George Washington: inoculation of whole army against smallpox using material from infected patients 1778- Edward Jenner: “An inquiry into the causes and effects of the variol ...
... Time line of “immunology” 1774 – Benjamin Jesty: use of material from cowpox lesions for vaccination against smallpox 1776 – George Washington: inoculation of whole army against smallpox using material from infected patients 1778- Edward Jenner: “An inquiry into the causes and effects of the variol ...
division of immunology and serology
... related to low viral set point i.e., a surrogate marker for slow disease progression. The patients with recent HIV infection were identified by using the following criteria; a. p24 antigenemic and HIV antibody negative b. Documented negative HIV test result within previous six months of the first po ...
... related to low viral set point i.e., a surrogate marker for slow disease progression. The patients with recent HIV infection were identified by using the following criteria; a. p24 antigenemic and HIV antibody negative b. Documented negative HIV test result within previous six months of the first po ...
Introduction to the Geography of Health
... epidemic few people are infected and can act as a source of the pathogen so the disease spreads slowly. ...
... epidemic few people are infected and can act as a source of the pathogen so the disease spreads slowly. ...
Immune Globulin (Human)
... fractionation from human plasma. The immune globulin is isolated from solubilized Cohn fraction II. The fraction II solution is adjusted to a final concentration of 0.3% tri-n-butyl phosphate (TNBP) and 0.2% sodium cholate. After the addition of solvent (TNBP) and detergent (sodium cholate), the sol ...
... fractionation from human plasma. The immune globulin is isolated from solubilized Cohn fraction II. The fraction II solution is adjusted to a final concentration of 0.3% tri-n-butyl phosphate (TNBP) and 0.2% sodium cholate. After the addition of solvent (TNBP) and detergent (sodium cholate), the sol ...
BinaxNOW S. pneumoniae
... Conventional microbiology methods have limitations UAT is an important tool for the diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease highly sensitive results Reliability not affected by prior antibiotics Test is performed on easily obtained specimens ...
... Conventional microbiology methods have limitations UAT is an important tool for the diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease highly sensitive results Reliability not affected by prior antibiotics Test is performed on easily obtained specimens ...
MANAGEMENT OF NEEDLESTICK INJURIES AND EXPOSURES
... 2. When source patient is known to be HIV positive, determine (if possible) what anti-retroviral therapy they are currently receiving (or have taken in the past) and which consultant has responsibility for their care. 3. HIV PEP can be discontinued if the source patient’s HIV antibody test is negati ...
... 2. When source patient is known to be HIV positive, determine (if possible) what anti-retroviral therapy they are currently receiving (or have taken in the past) and which consultant has responsibility for their care. 3. HIV PEP can be discontinued if the source patient’s HIV antibody test is negati ...
Read the Entire Press Release Here
... Parion plans to initiate Phase 2 studies of P-1037 for the treatment of cystic fibrosis in the second half of 2014 Durham, NC (April 30, 2014) – Parion Sciences, a company dedicated to the development of novel treatments for pulmonary and ocular diseases, announced today that it has reached an agree ...
... Parion plans to initiate Phase 2 studies of P-1037 for the treatment of cystic fibrosis in the second half of 2014 Durham, NC (April 30, 2014) – Parion Sciences, a company dedicated to the development of novel treatments for pulmonary and ocular diseases, announced today that it has reached an agree ...
8 Prevention of Hepatitis A, B and C and Other
... Immunization of people living with HIV and people at risk for HIV infection.) The schedule for HBV vaccine in HIV-infected adult patients (1, 2) is as follows. • HBV vaccination should start with the conventional dose (20 µg at months 0, 1 and a third time between months 6 and 12) for patients with ...
... Immunization of people living with HIV and people at risk for HIV infection.) The schedule for HBV vaccine in HIV-infected adult patients (1, 2) is as follows. • HBV vaccination should start with the conventional dose (20 µg at months 0, 1 and a third time between months 6 and 12) for patients with ...
3:30 - 4:15 pm
... I am declining to be vaccinated. I understand that due to my occupational exposure to blood or other potentially infectious materials I may be at risk of acquiring hepatitis B virus infection. I have been given the opportunity to be vaccinated with hepatitis B vaccine, at no charge to myself. Howe ...
... I am declining to be vaccinated. I understand that due to my occupational exposure to blood or other potentially infectious materials I may be at risk of acquiring hepatitis B virus infection. I have been given the opportunity to be vaccinated with hepatitis B vaccine, at no charge to myself. Howe ...
Meningococcal infection - Meningitis Research Foundation
... for Ambulance Personnel Meningococcal disease is the leading infectious cause of death in children and can kill a healthy person of any age within hours of their first symptoms. There are two main clinical presentations: meningitis and septicaemia. These can occur on their own, but often occur toget ...
... for Ambulance Personnel Meningococcal disease is the leading infectious cause of death in children and can kill a healthy person of any age within hours of their first symptoms. There are two main clinical presentations: meningitis and septicaemia. These can occur on their own, but often occur toget ...
SUBJECT: Infection Control Policy: Fingernail Enhancements
... Unsafe and improper injection, infusion and multi-dose vial practices in the healthcare setting result in transmission of bloodborne viruses and other microbial pathogens to patients during routine health care procedures. To prevent microbial contamination of products administered to patients, stand ...
... Unsafe and improper injection, infusion and multi-dose vial practices in the healthcare setting result in transmission of bloodborne viruses and other microbial pathogens to patients during routine health care procedures. To prevent microbial contamination of products administered to patients, stand ...
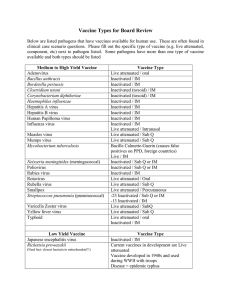
Vaccine Table for Board Review
... Live / IM Inactivated / Sub Q or IM Inactivated / Sub Q or IM Inactivated / IM Live attenuated / Oral Live attenuated / Sub Q Live attenuated / Percutaneous -23 Inactivated / Sub Q or IM -13 Inactivated / IM Live attenuated / SubQ Live attenuated / Sub Q Live attenuated / oral Inactivated / IM Vacci ...
... Live / IM Inactivated / Sub Q or IM Inactivated / Sub Q or IM Inactivated / IM Live attenuated / Oral Live attenuated / Sub Q Live attenuated / Percutaneous -23 Inactivated / Sub Q or IM -13 Inactivated / IM Live attenuated / SubQ Live attenuated / Sub Q Live attenuated / oral Inactivated / IM Vacci ...
Canine Babesiosis
... * Abdominal Ultrasound: Moderate Splenomegaly * Reticulocyte Count: 46,529 * Blood Smear Evaluation: Consistent with pancytopenia ...
... * Abdominal Ultrasound: Moderate Splenomegaly * Reticulocyte Count: 46,529 * Blood Smear Evaluation: Consistent with pancytopenia ...
1. Staphylococcal scalded
... mouth, nostrils, and periocular area. This is accompanied by systemic symptoms, such as a fever of about 38°C, irritability, and poor appetite. Wrinkles and fissures around the mouth, eye discharge and crust formation result in characteristic facial features. Erythema occurs on the neck, axillary fo ...
... mouth, nostrils, and periocular area. This is accompanied by systemic symptoms, such as a fever of about 38°C, irritability, and poor appetite. Wrinkles and fissures around the mouth, eye discharge and crust formation result in characteristic facial features. Erythema occurs on the neck, axillary fo ...
Immunoglobulin Reactivity to Pneumococcal Serotypes
... These seven serotypes are responsible for 83% of invasive pneumococcal disease in children <4 years old in the US and cause the majority of invasive disease in Europe All healthy infants and toddler should receive four doses of Prevenar ® vaccine ...
... These seven serotypes are responsible for 83% of invasive pneumococcal disease in children <4 years old in the US and cause the majority of invasive disease in Europe All healthy infants and toddler should receive four doses of Prevenar ® vaccine ...
Vaccines
... – Methods of acquisition include natural maternal antibodies, antitoxins, and immune globulins – Protection transferred from another person or animal ...
... – Methods of acquisition include natural maternal antibodies, antitoxins, and immune globulins – Protection transferred from another person or animal ...
Pharyngitis-handout
... is usually severe and dysphagia and low-grade fever are common. The infection is usually limited to one side. Gonococcal Pharyngitis: Incidence has increased in recent years. Most infections are asymptomatic but gonorrhoeal infection may be responsible for an occasional case of mild pharyngitis. Inf ...
... is usually severe and dysphagia and low-grade fever are common. The infection is usually limited to one side. Gonococcal Pharyngitis: Incidence has increased in recent years. Most infections are asymptomatic but gonorrhoeal infection may be responsible for an occasional case of mild pharyngitis. Inf ...
Prevention of infectious diseases in school children
... • Endorsement - Project supported by Ministries of Health and Education and Johnson&Johnson ...
... • Endorsement - Project supported by Ministries of Health and Education and Johnson&Johnson ...
Antibody Kills 91% of HIV Strains
... Vienna, where prevention science is expected to take center stage. More than 33 million people were living with HIV at the end of 2008, and about 2.7 million contracted the virus that year, according to United Nations estimates. Vaccines, which are believed to work by activating the body's ability t ...
... Vienna, where prevention science is expected to take center stage. More than 33 million people were living with HIV at the end of 2008, and about 2.7 million contracted the virus that year, according to United Nations estimates. Vaccines, which are believed to work by activating the body's ability t ...
Prevention of infectious diseases in school children
... • Endorsement - Project supported by Ministries of Health and Education and Johnson&Johnson ...
... • Endorsement - Project supported by Ministries of Health and Education and Johnson&Johnson ...
related (Pogosta) virus in different parts of Finland
... in 88% of the patients w20x. In children joint symptoms are rare but rash is usually visible w20x. In this study 33% of positive IgG antibody tests for Pogosta virus were samples from patients younger than 20 yr. Thus, we found Pogosta disease to be common in children, which was quite striking becau ...
... in 88% of the patients w20x. In children joint symptoms are rare but rash is usually visible w20x. In this study 33% of positive IgG antibody tests for Pogosta virus were samples from patients younger than 20 yr. Thus, we found Pogosta disease to be common in children, which was quite striking becau ...
Information about Meningococcal Disease and Vaccination and
... disease. Getting meningococcal vaccine is much safer than getting the disease. Some people who get meningococcal vaccine have mild side effects, such as redness or pain where the shot was given. These symptoms usually last for 1-2 days. A small percentage of people who receive the vaccine develop a ...
... disease. Getting meningococcal vaccine is much safer than getting the disease. Some people who get meningococcal vaccine have mild side effects, such as redness or pain where the shot was given. These symptoms usually last for 1-2 days. A small percentage of people who receive the vaccine develop a ...
Aster Leafhopper - The Learning Store
... leaves become bronzed and break off easily. Carrot roots become covered with root hairs and develop a bitter taste, making them unmarketable. Infection also leaves the roots vulnerable to soft rots. When young plants are infected, they often die from secondary infections or pest outbreaks. Aster yel ...
... leaves become bronzed and break off easily. Carrot roots become covered with root hairs and develop a bitter taste, making them unmarketable. Infection also leaves the roots vulnerable to soft rots. When young plants are infected, they often die from secondary infections or pest outbreaks. Aster yel ...
Clustering and commonalities among autoimmune diseases
... mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) and anti-phospholipid syndrome (a-PLS). Each individually has unique pathognomonic features together with a relatively disease-specific autoimmune serological signature of predominant reactivity to one or another nuclear or cytoplasmic autoantigen. Among these d ...
... mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) and anti-phospholipid syndrome (a-PLS). Each individually has unique pathognomonic features together with a relatively disease-specific autoimmune serological signature of predominant reactivity to one or another nuclear or cytoplasmic autoantigen. Among these d ...