Antibodies - blobs.org
... The body has a number of ways of fighting off invaders like bacteria and viruses. Sometimes it uses chemicals that kill them off randomly. However, a really clever system has been designed to target them very specifically. Antibodies are the body’s clever labels for marking out these invaders. ...
... The body has a number of ways of fighting off invaders like bacteria and viruses. Sometimes it uses chemicals that kill them off randomly. However, a really clever system has been designed to target them very specifically. Antibodies are the body’s clever labels for marking out these invaders. ...
Oral Delivery of the Factor VIII Gene: Immunotherapy for Hemophilia A
... In a murine knockout model, feeding of chitosan-FVIII DNA nanoparticles in gelatin mediated a prolonged restoration of hemostasis. Functional FVIII protein was detected in plasma, reaching a peak level of 2–4% normal FVIII at day 22. A bleeding challenge after one month resulted in survival of 13 of ...
... In a murine knockout model, feeding of chitosan-FVIII DNA nanoparticles in gelatin mediated a prolonged restoration of hemostasis. Functional FVIII protein was detected in plasma, reaching a peak level of 2–4% normal FVIII at day 22. A bleeding challenge after one month resulted in survival of 13 of ...
Immune System
... • Plasma cells: antibody-producing effector B-cells • Secondary immune response: immune response if the individual is exposed to the same antigen at some later time~ Immunological memory ...
... • Plasma cells: antibody-producing effector B-cells • Secondary immune response: immune response if the individual is exposed to the same antigen at some later time~ Immunological memory ...
WBC`s-(L3
... B-lymphocytes recognize foreign organism by its surface receptors Interact with antigen>>> proliferation of B-lymphocytes to plasma cells Plasma cells secrete the specific antibody to destroy the antigen Some of this plasma cells will be kept in ...
... B-lymphocytes recognize foreign organism by its surface receptors Interact with antigen>>> proliferation of B-lymphocytes to plasma cells Plasma cells secrete the specific antibody to destroy the antigen Some of this plasma cells will be kept in ...
Antigens and Antibodies
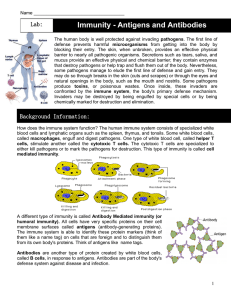
... How does the immune system function? The human immune system consists of specialized white blood cells and lymphatic organs such as the spleen, thymus, and tonsils. Some white blood cells, called macrophages, engulf and digest pathogens. One type of white blood cell, called helper T cells, stimulate ...
... How does the immune system function? The human immune system consists of specialized white blood cells and lymphatic organs such as the spleen, thymus, and tonsils. Some white blood cells, called macrophages, engulf and digest pathogens. One type of white blood cell, called helper T cells, stimulate ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM - Coast Colleges Home Page
... Antigen-specific (relies on recognition of foreign antigens) Systemic (body-wide) Memory (stronger future immune response) 2 types of Immune Response: - Humoral (Antibody-Mediated) - Cellular (Cell-Mediated) ...
... Antigen-specific (relies on recognition of foreign antigens) Systemic (body-wide) Memory (stronger future immune response) 2 types of Immune Response: - Humoral (Antibody-Mediated) - Cellular (Cell-Mediated) ...
test ch 12 body defenses
... 4. The process whereby leukocytes pass through the wall of a capillary is called ___________. 5. Lymphocytes that develop immunocompetence in the _________ are T cells. 6. The inflammatory response is considered the body’s ___________ line of defense. 7. The most numerous type of phagocyte is the___ ...
... 4. The process whereby leukocytes pass through the wall of a capillary is called ___________. 5. Lymphocytes that develop immunocompetence in the _________ are T cells. 6. The inflammatory response is considered the body’s ___________ line of defense. 7. The most numerous type of phagocyte is the___ ...
Non Specific Immune Responses (Chapter 16) First Line of Defense:
... C2 and C4 (splits into fragments a and b)ÆC4b and C1b activate C3 B. Alternative Activation: (does not involve antigen) Proteins B, D, F factors in blood bind to pathogen and activate C3 C. Lectin pathway: Macrophage that ingestions pathogens release chemical to stimulate liver to produce lectin (pr ...
... C2 and C4 (splits into fragments a and b)ÆC4b and C1b activate C3 B. Alternative Activation: (does not involve antigen) Proteins B, D, F factors in blood bind to pathogen and activate C3 C. Lectin pathway: Macrophage that ingestions pathogens release chemical to stimulate liver to produce lectin (pr ...
Cell Unit Test Study Guide
... 3. What organelle forms a barrier between the cell and its environment? a. Cell membrane 4. What organelle acts as the cell’s delivery system? a. Endoplasmic reticulum 5. What organelle can you find ribosomes on? a. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 6. What organelle packages and distributes proteins? a. ...
... 3. What organelle forms a barrier between the cell and its environment? a. Cell membrane 4. What organelle acts as the cell’s delivery system? a. Endoplasmic reticulum 5. What organelle can you find ribosomes on? a. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 6. What organelle packages and distributes proteins? a. ...
3.6 Immune System
... 1. What are the two types of immune response in the second line of defense? 2. What are the characteristics of the innate immune response? 3. What type of blood cells are involved in the innate immune response? 4. What is the difference between a pathogen and a phagocyte? 5. When you are sick, w ...
... 1. What are the two types of immune response in the second line of defense? 2. What are the characteristics of the innate immune response? 3. What type of blood cells are involved in the innate immune response? 4. What is the difference between a pathogen and a phagocyte? 5. When you are sick, w ...
Diseases of the Immune System Robbins Basic Pathology Chapter 4
... Somatic rearrangement of antigen receptor genes during lymphocyte maturation (Figure not in text) ...
... Somatic rearrangement of antigen receptor genes during lymphocyte maturation (Figure not in text) ...
January 6, 2014 - Immunology Overview
... Activation, Differentiation Markers CD25: Interleukin-2 Receptor CD28: Co-stimulatory receptor on T cells CD34: Stem cell marker ...
... Activation, Differentiation Markers CD25: Interleukin-2 Receptor CD28: Co-stimulatory receptor on T cells CD34: Stem cell marker ...
immune system 2010
... 2. Helper T cells recognise the antigens as foreign. a) They stimulate B cells (plasma cells) to produce antibodies. b) They also stimulate killer T cells and macrophages. 3. Afterwards, some B cells remain as memory cells. 4. If the antigen is presented to them again, they produce plasma cells. 5. ...
... 2. Helper T cells recognise the antigens as foreign. a) They stimulate B cells (plasma cells) to produce antibodies. b) They also stimulate killer T cells and macrophages. 3. Afterwards, some B cells remain as memory cells. 4. If the antigen is presented to them again, they produce plasma cells. 5. ...
Poster
... binding groove thanks to Tyr-22, Leu-53, Arg-70 and Lys-71, resulting in a HLADQ2-gliadin complex. This complex may be recognized by T helper cells as “non-self,’ with subsequent activation and initiation of an autoimmune response. The ensuing inflammation causes disruption of the structure and func ...
... binding groove thanks to Tyr-22, Leu-53, Arg-70 and Lys-71, resulting in a HLADQ2-gliadin complex. This complex may be recognized by T helper cells as “non-self,’ with subsequent activation and initiation of an autoimmune response. The ensuing inflammation causes disruption of the structure and func ...