Key Concepts in B cell Activation-I
... 4. T cell signal “Attenuation”: Roles of inhibitory receptors & Protein degradation ...
... 4. T cell signal “Attenuation”: Roles of inhibitory receptors & Protein degradation ...
Specific Immune Response (Chapter 17) Response in highly specific
... Use in diagnostic tests and in therapy: Mono Abs to suppress T cells in transplant patient Treat specific illnesses (leukemia, Crohn’s, RA) Combine mono Abs with radioisotope to target cancer cells Cell Mediated Immunity: T cells Dependent on cytokines: chemical messengers within the immune system ( ...
... Use in diagnostic tests and in therapy: Mono Abs to suppress T cells in transplant patient Treat specific illnesses (leukemia, Crohn’s, RA) Combine mono Abs with radioisotope to target cancer cells Cell Mediated Immunity: T cells Dependent on cytokines: chemical messengers within the immune system ( ...
PFIZER’S CENTERS FOR THERAPEUTIC INNOVATION (CTI) CTI:
... either harness the immune system for tumor eradication or, conversely, targeted therapies to provide selective immunosuppression or immunoregulation for autoimmune diseases ...
... either harness the immune system for tumor eradication or, conversely, targeted therapies to provide selective immunosuppression or immunoregulation for autoimmune diseases ...
TOPIC 6.3
... • Antibiotics are chemicals that work against living bacterial cells, but do not affect our body cells • Bacteria are prokaryotic, body cells are eukaryotic – Different biochemical rxs and pathways – Protein synthesis not exactly the same – Bacteria have a cell wall, body cells don’t ...
... • Antibiotics are chemicals that work against living bacterial cells, but do not affect our body cells • Bacteria are prokaryotic, body cells are eukaryotic – Different biochemical rxs and pathways – Protein synthesis not exactly the same – Bacteria have a cell wall, body cells don’t ...
Sanquin Cellular Therapy Services
... been destroyed by high doses of chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy. The stem cells can be derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood or umbilical cord blood. Within the Laboratory for Stem Cell Transplantation, blood and bone marrow is processed for patients who are in need of stem cell transplan ...
... been destroyed by high doses of chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy. The stem cells can be derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood or umbilical cord blood. Within the Laboratory for Stem Cell Transplantation, blood and bone marrow is processed for patients who are in need of stem cell transplan ...
Key Concepts in B cell Activation-I
... 4. T cell signal “Attenuation”: Roles of inhibitory receptors & Protein degradation ...
... 4. T cell signal “Attenuation”: Roles of inhibitory receptors & Protein degradation ...
insights - The Journal of Experimental Medicine
... The development of drug resistance is a major problem in combating malaria caused by Plasmodium falciparum, the most deadly human malaria parasite. Resistance to artemisinin, the key component of current treatment regimens, is now being reported in parts of Asia. In this issue, Zenonos et al. report ...
... The development of drug resistance is a major problem in combating malaria caused by Plasmodium falciparum, the most deadly human malaria parasite. Resistance to artemisinin, the key component of current treatment regimens, is now being reported in parts of Asia. In this issue, Zenonos et al. report ...
Lymphatic and Immune System Information Sheet
... thoracic duct is much larger as it receives the lymph from the rest of the body and empties into the left subclavian vein. The enlarged pouch-like storage area for purified lymph before it returns to the blood is located at the start of the thoracic duct and is called cisterna chyli. Lacteals found ...
... thoracic duct is much larger as it receives the lymph from the rest of the body and empties into the left subclavian vein. The enlarged pouch-like storage area for purified lymph before it returns to the blood is located at the start of the thoracic duct and is called cisterna chyli. Lacteals found ...
Cells
... Interaction of molecules with water Important factor for determining the molecular organization within a cell Hydrophilic (water soluble) or Hydrophobic (water insoluble) • Congregation of hydrophilic parts with other hydrophilic parts • Congregation of hydrophobic parts with other hydrophobic ...
... Interaction of molecules with water Important factor for determining the molecular organization within a cell Hydrophilic (water soluble) or Hydrophobic (water insoluble) • Congregation of hydrophilic parts with other hydrophilic parts • Congregation of hydrophobic parts with other hydrophobic ...
CELLS AND TISSUES OF THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNE SYSTEM
... Lymphocytes are the only cells in the body capable of specifically recognizing and distinguishing different antigenic determinants and are responsible for the two defining characteristics of the adaptive immune response, specificity and memory ...
... Lymphocytes are the only cells in the body capable of specifically recognizing and distinguishing different antigenic determinants and are responsible for the two defining characteristics of the adaptive immune response, specificity and memory ...
Disease as a Failure of Homeostasis
... ANTIBODIES and having the WBC’s ATTACK the invader Some WBC’s SPECIFIC for this pathogen remain in the body for a long time to continue PROTECTION from future attacks. ...
... ANTIBODIES and having the WBC’s ATTACK the invader Some WBC’s SPECIFIC for this pathogen remain in the body for a long time to continue PROTECTION from future attacks. ...
Chapter 5 Tissues
... Exocrine glands-secretes its products into a duct or onto a body surface 3 types 1. Merocrine glands-secretes a fluid without losing cytoplasm 2.Apocrine glands-secretions contain parts of secretory cells 3. Holocrine glands-secretion contains entire secretory cells Endocrine glands-secretes hormone ...
... Exocrine glands-secretes its products into a duct or onto a body surface 3 types 1. Merocrine glands-secretes a fluid without losing cytoplasm 2.Apocrine glands-secretions contain parts of secretory cells 3. Holocrine glands-secretion contains entire secretory cells Endocrine glands-secretes hormone ...
Immune Response 1. Cells involved in the Immune response #1. B
... the thalamus and later can develop into a plasma cell that produces antibodies. Develops from stem cells in the bone marrow. Resides in lymphoid tissue. Found in lymph nodes and other locations (ex. Tonsillar tissues). There are two types of B lymphocytes: plasma cells and B memory cells. 2. Cells i ...
... the thalamus and later can develop into a plasma cell that produces antibodies. Develops from stem cells in the bone marrow. Resides in lymphoid tissue. Found in lymph nodes and other locations (ex. Tonsillar tissues). There are two types of B lymphocytes: plasma cells and B memory cells. 2. Cells i ...
positive selection - immunology.unideb.hu
... Effector functions are inhibited by regulatory T cells ...
... Effector functions are inhibited by regulatory T cells ...
Define: Cell, Tissue, organ, and organ system
... 4. Create a flow chart illustrating relationship between cells, tissues, organs, systems and organisms (PK) ...
... 4. Create a flow chart illustrating relationship between cells, tissues, organs, systems and organisms (PK) ...
Blood Whole blood has two components
... that contains dissolved substances, and (2) formed elements, which are cells and cell fragments. Blood is about 45% formed elements and 55% plasma. Normally more than 99% of the formed elements are red-colored red blood cells. Pale colorless white blood cells and platelets occupy less than 1% of tot ...
... that contains dissolved substances, and (2) formed elements, which are cells and cell fragments. Blood is about 45% formed elements and 55% plasma. Normally more than 99% of the formed elements are red-colored red blood cells. Pale colorless white blood cells and platelets occupy less than 1% of tot ...
AP Biology Cell Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling Webquest
... watching them, attempt to answer the questions written below AND any questions/self-quizzes at the website. Note that most of the McGraw Hill animations are followed by a self-check set of multiple choice questions. I will not collect this sheet, so I trust you to write as little as much as you like ...
... watching them, attempt to answer the questions written below AND any questions/self-quizzes at the website. Note that most of the McGraw Hill animations are followed by a self-check set of multiple choice questions. I will not collect this sheet, so I trust you to write as little as much as you like ...
Rotation Final Report
... cell bind to an area on the antigen called the epitope. Once the B cell binds to the antigen, the B cell is activated and begins to engulf the pathogen; the pathogen gets digested and the resulting peptides are presented on the cell surface using MHC (Major Histocompatibility complex) class II prote ...
... cell bind to an area on the antigen called the epitope. Once the B cell binds to the antigen, the B cell is activated and begins to engulf the pathogen; the pathogen gets digested and the resulting peptides are presented on the cell surface using MHC (Major Histocompatibility complex) class II prote ...
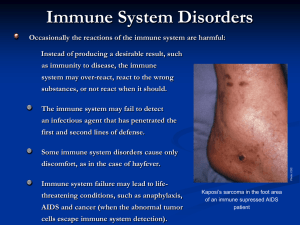
Immune System Disorders
... discomfort, as in the case of hayfever. Immune system failure may lead to lifethreatening conditions, such as anaphylaxis, AIDS and cancer (when the abnormal tumor cells escape immune system detection). ...
... discomfort, as in the case of hayfever. Immune system failure may lead to lifethreatening conditions, such as anaphylaxis, AIDS and cancer (when the abnormal tumor cells escape immune system detection). ...
Immunity Talk selected slides
... A substance (usually protein) recognised as 'foreign' that stimulate antibody formation ...
... A substance (usually protein) recognised as 'foreign' that stimulate antibody formation ...
Document
... • Your body’s immune response T cells start working to identify the pathogen and B cells make antibodies to immobilize it. This immobilization process can take a week and then you feel better. • Viruses can’t be killed with antibiotics since they are not living. You can take medicines like acetamino ...
... • Your body’s immune response T cells start working to identify the pathogen and B cells make antibodies to immobilize it. This immobilization process can take a week and then you feel better. • Viruses can’t be killed with antibiotics since they are not living. You can take medicines like acetamino ...
Exam in Infection and Immunity 1BI004, November 1, 2013. Total 27
... determinants. This information code for virulence factors, such as bacterial adhesins or toxins, that makes the bacterium pathogenic. 20. Bacterial adhesion is quite a prerequisite for their ability to colonize mucosal membranes. This is usually achieved through the expression of bacterial adhesins ...
... determinants. This information code for virulence factors, such as bacterial adhesins or toxins, that makes the bacterium pathogenic. 20. Bacterial adhesion is quite a prerequisite for their ability to colonize mucosal membranes. This is usually achieved through the expression of bacterial adhesins ...
Immunology - TeacherWeb
... • Activity Immunity – your own immune system responds • Pasive Immunity – transfer of antibodies – Rabies Treatment – Mother’s Milk ...
... • Activity Immunity – your own immune system responds • Pasive Immunity – transfer of antibodies – Rabies Treatment – Mother’s Milk ...