Frontal bone - PA
... superior and lateral part of the skull. They join together at a suture on the midline and also join with the frontal bones. The word "parietal" means wall and these bones form much of the lateral "walls" of the skull. • 3. Temporal bones - These bones make up the "temple" region of the skull superio ...
... superior and lateral part of the skull. They join together at a suture on the midline and also join with the frontal bones. The word "parietal" means wall and these bones form much of the lateral "walls" of the skull. • 3. Temporal bones - These bones make up the "temple" region of the skull superio ...
Fun Facts
... has been done to test this theory—both physically and psychologically, and for human faces and manmade objects—but there is no known scientific basis to support this claim. The degree to which an object or human face conforms to the Golden Ratio can be used only as a subjective measure of aesthetic ...
... has been done to test this theory—both physically and psychologically, and for human faces and manmade objects—but there is no known scientific basis to support this claim. The degree to which an object or human face conforms to the Golden Ratio can be used only as a subjective measure of aesthetic ...
PowerPoint Sunusu
... • Pronation rotates the radius medially so that the palm of the hand faces posteriorly and its dorsum faces anteriorly. When the elbow joint is flexed, pronation moves the hand so that the palm faces inferiorly (e.g., placing the palms flat on a table). • Supination is the opposite rotational movem ...
... • Pronation rotates the radius medially so that the palm of the hand faces posteriorly and its dorsum faces anteriorly. When the elbow joint is flexed, pronation moves the hand so that the palm faces inferiorly (e.g., placing the palms flat on a table). • Supination is the opposite rotational movem ...
Document
... HIPPOCRATES(460-377BC) Greek physician Father of Medicine His name is memorialized in the Hippocratic oath Humoral theory : Four body humors – -blood ...
... HIPPOCRATES(460-377BC) Greek physician Father of Medicine His name is memorialized in the Hippocratic oath Humoral theory : Four body humors – -blood ...
Introduction of Anatomy
... HIPPOCRATES(460-377BC) Greek physician Father of Medicine His name is memorialized in the Hippocratic oath Humoral theory : Four body humors – -blood ...
... HIPPOCRATES(460-377BC) Greek physician Father of Medicine His name is memorialized in the Hippocratic oath Humoral theory : Four body humors – -blood ...
ch 5 day 7
... The ilium , which connects posteriorly with the sacrum at the sacroiliac joint, is a large, flaring bone that forms most of the hip bone. When you put your hands on your hips, they are resting over the alae, or winglike portions, of the ilia. The ischium is the “sit-down bone,” so called because it ...
... The ilium , which connects posteriorly with the sacrum at the sacroiliac joint, is a large, flaring bone that forms most of the hip bone. When you put your hands on your hips, they are resting over the alae, or winglike portions, of the ilia. The ischium is the “sit-down bone,” so called because it ...
Moghadame
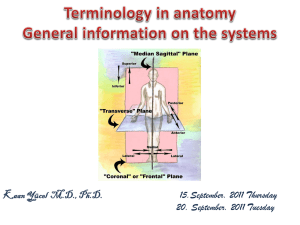
... – Systematic anatomy: organized by systems, e.g., digestive, nervous, endocrine, etc. – Regional anatomy: study of all structures in an area of the body, e.g., upper extremity bones, muscles, blood vessels, etc. ...
... – Systematic anatomy: organized by systems, e.g., digestive, nervous, endocrine, etc. – Regional anatomy: study of all structures in an area of the body, e.g., upper extremity bones, muscles, blood vessels, etc. ...
Appendicular - advbiology227
... Coxal Bones: The hipbones that are made of three fused bones – Ilium: superior; – Ischium: inferior and posterior – Pubis: inferior and anterior ...
... Coxal Bones: The hipbones that are made of three fused bones – Ilium: superior; – Ischium: inferior and posterior – Pubis: inferior and anterior ...
Chapter 5: Skeletal System The Appendicular Skeleton
... Coxal Bones: The hipbones that are made of three fused bones – Ilium: superior; – Ischium: inferior and posterior – Pubis: inferior and anterior ...
... Coxal Bones: The hipbones that are made of three fused bones – Ilium: superior; – Ischium: inferior and posterior – Pubis: inferior and anterior ...
Comparative anatomy
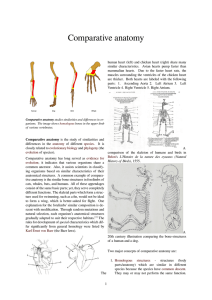
... evolution of species). comparison of the skeleton of humans and birds in Comparative anatomy has long served as evidence for Belon's L'Histoire de la nature des oyseaux (Natural evolution; it indicates that various organisms share a History of Birds), 1555. common ancestor. Also, it assists scientis ...
... evolution of species). comparison of the skeleton of humans and birds in Comparative anatomy has long served as evidence for Belon's L'Histoire de la nature des oyseaux (Natural evolution; it indicates that various organisms share a History of Birds), 1555. common ancestor. Also, it assists scientis ...
10.Anatomy-MBBS
... the neck, which moved upward during swallowing. It was diagnosed as a tumour of the thyroid gland for which she was operated. But she developed husky voice. Why does the thyroid gland move up with swallowing? Describe the different parts, relations and blood supply of the gland. Using your knowledge ...
... the neck, which moved upward during swallowing. It was diagnosed as a tumour of the thyroid gland for which she was operated. But she developed husky voice. Why does the thyroid gland move up with swallowing? Describe the different parts, relations and blood supply of the gland. Using your knowledge ...
Pectoral Girdle
... clavicles and the posterior scapulae • They attach the upper limbs to the axial skeleton • The way its set upallows for maximum movement • They provide attachment points for muscles that move the upper limbs ...
... clavicles and the posterior scapulae • They attach the upper limbs to the axial skeleton • The way its set upallows for maximum movement • They provide attachment points for muscles that move the upper limbs ...
bones anatomy day 1 skull
... Appendicular Consists of bones of the upper and lower limbs and the bones that anchor the limbs to the axial skeleton. ...
... Appendicular Consists of bones of the upper and lower limbs and the bones that anchor the limbs to the axial skeleton. ...
Anatomy & Physiology
... Skull, thoracic cage and vertebrae Skull: 8 cranial (cranium or “braincase”) and 14 facial bones (face) Skull also: 6 auditory ossicles and hyoid bone 24 vertebrae and sacrum and coccyx 24 ribs and sternum Know #’s on page 199 Know vertebrae ...
... Skull, thoracic cage and vertebrae Skull: 8 cranial (cranium or “braincase”) and 14 facial bones (face) Skull also: 6 auditory ossicles and hyoid bone 24 vertebrae and sacrum and coccyx 24 ribs and sternum Know #’s on page 199 Know vertebrae ...
ANIMAL BIOLOGY (1604) LABORATORY Week of
... • Body perforated by numerous pores for water flow Scypha: longitudinal and cross-section slides (Figs. 5.1, 5.2) Identify the following structures: • Apopyles • Canals • Choanocytes ...
... • Body perforated by numerous pores for water flow Scypha: longitudinal and cross-section slides (Figs. 5.1, 5.2) Identify the following structures: • Apopyles • Canals • Choanocytes ...
Unit 4 - Skeletal System Review
... Step 2 - Cell division occurs and migrates to the fracture area, hard skin forms, internal callus organizes, broken ends are temporarily stabilized Step 3 - Osteoblasts replace central cartilage with spongy bone, calluses form a brace at the fracture site, if there was a cast, it can be removed at t ...
... Step 2 - Cell division occurs and migrates to the fracture area, hard skin forms, internal callus organizes, broken ends are temporarily stabilized Step 3 - Osteoblasts replace central cartilage with spongy bone, calluses form a brace at the fracture site, if there was a cast, it can be removed at t ...
Introduction
... e. Each thoracic vertebra has articulated facets for the ________________________ 5. Vertebral column as a whole articulated with the head, ribs, and iliac ________________________ 6. Individual vertebrae articulate with each other in ________________________ between their bodies and between their a ...
... e. Each thoracic vertebra has articulated facets for the ________________________ 5. Vertebral column as a whole articulated with the head, ribs, and iliac ________________________ 6. Individual vertebrae articulate with each other in ________________________ between their bodies and between their a ...
Skeletal System Notes
... Scapula = flat, triangular bone at the back of the shoulder, also called shoulder blade Sternum = long flat bone in the middle of the upper chest; chest bone Clavicle = long slender bone that extends from the shoulder to the sternum Ribcage = structure formed by the thoracic vertebrae, ribs, and ste ...
... Scapula = flat, triangular bone at the back of the shoulder, also called shoulder blade Sternum = long flat bone in the middle of the upper chest; chest bone Clavicle = long slender bone that extends from the shoulder to the sternum Ribcage = structure formed by the thoracic vertebrae, ribs, and ste ...
figure 98-1
... veins. C, The anterior inferior portion of the left major fissure may be developed by connecting the dissection around the pulmonary arteries (A) with the ...
... veins. C, The anterior inferior portion of the left major fissure may be developed by connecting the dissection around the pulmonary arteries (A) with the ...
Bone Diversity
... Cranium – Frontal Bone (#1) • Shell-shaped frontal bone, anterior to parietal (coronal) sutures • Makes up superior wall of orbits ...
... Cranium – Frontal Bone (#1) • Shell-shaped frontal bone, anterior to parietal (coronal) sutures • Makes up superior wall of orbits ...
GAIT AND POSTURE IN THE BIPED
... Habitually quadrupedal apes can stand on two legs for short periods, but as facultative bipeds they expend a considerable amount of energy to achieve two-legged stance and make progress in this manner. Human beings, however, are obligate bipeds, designed for habitual vertical stance and bipedal gait ...
... Habitually quadrupedal apes can stand on two legs for short periods, but as facultative bipeds they expend a considerable amount of energy to achieve two-legged stance and make progress in this manner. Human beings, however, are obligate bipeds, designed for habitual vertical stance and bipedal gait ...
Skull Bones - Obsessed With Skulls
... walls of orbitals A. Cristi galli – “cock’s comb”; projection on superior surface to which outermost ...
... walls of orbitals A. Cristi galli – “cock’s comb”; projection on superior surface to which outermost ...
Body snatching
Body snatching is the secret disinterment of corpses from graveyards or other burial sites. A common purpose of body snatching, especially in the 19th century, was to sell the corpses for dissection or anatomy lectures in medical schools. Those who practiced body snatching were often called ""resurrectionists"" or ""resurrection-men"". A related act is grave robbery, uncovering a tomb or crypt to steal artifacts or personal effects rather than corpses.