Chapter 8: The Appendicular Skeleton
... - The components of the appendicular skeleton. - The components of the pectoral girdle and their relationship to the axial skeleton. - The components of the upper limbs and their relationship to the pectoral girdle. - The components of the pelvic girdle and their relationship to the axial skeleton. ...
... - The components of the appendicular skeleton. - The components of the pectoral girdle and their relationship to the axial skeleton. - The components of the upper limbs and their relationship to the pectoral girdle. - The components of the pelvic girdle and their relationship to the axial skeleton. ...
SKELETAL SYSTEM An Introduction to the Human Adult and Fetal
... include the femur, humerus, bones of the antebrachium and phalanges. Short bones are about the same length as width; these include bones of the carpals, tarsals and patella. Flat bones include the sternum and cranium. Irregular bones include vertebrae and many facial bones. As with other body system ...
... include the femur, humerus, bones of the antebrachium and phalanges. Short bones are about the same length as width; these include bones of the carpals, tarsals and patella. Flat bones include the sternum and cranium. Irregular bones include vertebrae and many facial bones. As with other body system ...
The skeletal system: the axial skeleton
... *articulate with every bone in face except the mandible form part of floor of orbits, parts of nasal cavity, & most of the hard palate (bony roof of mouth) each one has large maxillary sinus alveolar process is small arch that contains the alveolar sockets for upper set of teeth ...
... *articulate with every bone in face except the mandible form part of floor of orbits, parts of nasal cavity, & most of the hard palate (bony roof of mouth) each one has large maxillary sinus alveolar process is small arch that contains the alveolar sockets for upper set of teeth ...
Skeletal System
... Occurs when the knee is locked with the foot planted and the knee is twisted quickly. The bones are more likely to rub against each other (chronic ACL deficiency). Can also damage the cartilage that covers the ends of the bones and can trap and tear the menisci. Left untreated it can lead to osteoar ...
... Occurs when the knee is locked with the foot planted and the knee is twisted quickly. The bones are more likely to rub against each other (chronic ACL deficiency). Can also damage the cartilage that covers the ends of the bones and can trap and tear the menisci. Left untreated it can lead to osteoar ...
Long bones
... connective tissue cells) become more specialized and differentiate into osteoblasts, which produce bone matrix. From each center of ossification, bone growth radiates outward as calcium salts are deposited. This process is not complete at birth; a baby has areas of fibrous connective tissue remainin ...
... connective tissue cells) become more specialized and differentiate into osteoblasts, which produce bone matrix. From each center of ossification, bone growth radiates outward as calcium salts are deposited. This process is not complete at birth; a baby has areas of fibrous connective tissue remainin ...
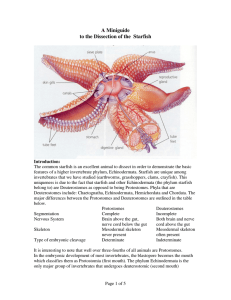
A Miniguide to the Dissection of the Starfish
... the stomach, two from each arm. Now snip out the stomach at its opening to the oral surface, the mouth. This will reveal pairs of gonads in each arm, lying under the hepatic caeca, alongside the ambulacral groove, and yet close to the disk (Figures 1,3). The size of the gonads depends upon the phase ...
... the stomach, two from each arm. Now snip out the stomach at its opening to the oral surface, the mouth. This will reveal pairs of gonads in each arm, lying under the hepatic caeca, alongside the ambulacral groove, and yet close to the disk (Figures 1,3). The size of the gonads depends upon the phase ...
vertebrate body systems -
... NOTE - page numbers for chap 20-26 have not been updated for text version 6 I. Homeostasis: vertebrate bodies are organized into various organs and systems which help the body maintain a stable internal environment. (see p. 425-426, fig. 20.12B and 20.13) II. Circulatory system (click for animation) ...
... NOTE - page numbers for chap 20-26 have not been updated for text version 6 I. Homeostasis: vertebrate bodies are organized into various organs and systems which help the body maintain a stable internal environment. (see p. 425-426, fig. 20.12B and 20.13) II. Circulatory system (click for animation) ...
introduction to digestive system anatomy
... responsible for mixing the masticated (chewed) food mass with gastric juices. It is also responsible for emptying the contents of the stomach into the duodenum. Absorption of chemical compounds occurs principally in the small intestine. It is a 5- to 6-m-long tube. It is shorter in life, when tonus ...
... responsible for mixing the masticated (chewed) food mass with gastric juices. It is also responsible for emptying the contents of the stomach into the duodenum. Absorption of chemical compounds occurs principally in the small intestine. It is a 5- to 6-m-long tube. It is shorter in life, when tonus ...
Lower Respiratory Tract Anatomy - Scottish Universities Medical
... The principle route of lymphatic drainage for the body is through the thoracic duct. This extends from vertebral level L2 to the root of the neck. It begins superior to the confluence of several lymph ducts, known as the cisterna chyli, which drains the abdomen, pelvis and lower ...
... The principle route of lymphatic drainage for the body is through the thoracic duct. This extends from vertebral level L2 to the root of the neck. It begins superior to the confluence of several lymph ducts, known as the cisterna chyli, which drains the abdomen, pelvis and lower ...
general osteology
... • Cranial base forms the skull’s inferior aspect • Three prominent ridges divide the base into fossae • The brain rests on these cranial fossae completely enclosed by the cranial vault • The brain occupies the cranial cavity ...
... • Cranial base forms the skull’s inferior aspect • Three prominent ridges divide the base into fossae • The brain rests on these cranial fossae completely enclosed by the cranial vault • The brain occupies the cranial cavity ...
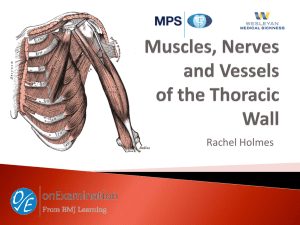
Pectoralis Major - University of Nottingham Surgical Society
... Moore and Agur, ‘Essential Clinical Anatomy’ 4th edition Drake and Vogl, ‘Gray’s Atlas of Anatomy’ Drake and Vogl, ‘Gray’s Anatomy for Students’ 1st edition ...
... Moore and Agur, ‘Essential Clinical Anatomy’ 4th edition Drake and Vogl, ‘Gray’s Atlas of Anatomy’ Drake and Vogl, ‘Gray’s Anatomy for Students’ 1st edition ...
Axial Skeleton Power Point
... Also called the spine or backbone Composed of vertebrae Functions as strong flexible rod that can rotate and move in all directions Encloses and protects spinal cord Supports the skull Point of attachment for ribs, pelvic girdle, and ...
... Also called the spine or backbone Composed of vertebrae Functions as strong flexible rod that can rotate and move in all directions Encloses and protects spinal cord Supports the skull Point of attachment for ribs, pelvic girdle, and ...
Bone Grafting
... using a maxillofacial surgery periosteal elevator rather than Doyen rib stripper ...
... using a maxillofacial surgery periosteal elevator rather than Doyen rib stripper ...
BIO 218 52999 F 2014 MTX 1 Q 140912.4
... Or as a draft Letter to your Dean, or your Mom, or President Obama, about how difficult this course is, and how and why it should be “dumbed” down for poor and struggling PRE-MED students like you………….and that there are just too many parts to the Human Body to memorize ….and its too complicated to u ...
... Or as a draft Letter to your Dean, or your Mom, or President Obama, about how difficult this course is, and how and why it should be “dumbed” down for poor and struggling PRE-MED students like you………….and that there are just too many parts to the Human Body to memorize ….and its too complicated to u ...
hapch5skeletal systemnotes
... retain normal proportions and strength and bones become thicker and form large projections to increase their strength where muscle is bulky….here _______________________lay down new matrix and become trapped w/in it….now,trapped,they become osteocytes-mature bone cells ...
... retain normal proportions and strength and bones become thicker and form large projections to increase their strength where muscle is bulky….here _______________________lay down new matrix and become trapped w/in it….now,trapped,they become osteocytes-mature bone cells ...
hapch5skeletal systemnotes
... retain normal proportions and strength and bones become thicker and form large projections to increase their strength where muscle is bulky….here _______________________lay down new matrix and become trapped w/in it….now,trapped,they become osteocytes-mature bone cells ...
... retain normal proportions and strength and bones become thicker and form large projections to increase their strength where muscle is bulky….here _______________________lay down new matrix and become trapped w/in it….now,trapped,they become osteocytes-mature bone cells ...
File - South Sevier High School
... The basic structure of a cell (Figure 3-1) includes three parts: 1. The cell membrane is the outer covering of the cell. It holds substances inside the cell while helping the cell maintain its shape. It also regulates substances that are allowed to pass in and out of the cell. 2. The nucleus is the ...
... The basic structure of a cell (Figure 3-1) includes three parts: 1. The cell membrane is the outer covering of the cell. It holds substances inside the cell while helping the cell maintain its shape. It also regulates substances that are allowed to pass in and out of the cell. 2. The nucleus is the ...
Chapter 7
... a. Fontanels are dense connective tissue membrane-filled spaces between the cranial bones of fetuses and infants. They remain unossified at birth but close early in a child’s life (Figure 7.14). b. The major fontanels are the anterior, posterior, anterolaterals, and posterolaterals . c. Fontanels h ...
... a. Fontanels are dense connective tissue membrane-filled spaces between the cranial bones of fetuses and infants. They remain unossified at birth but close early in a child’s life (Figure 7.14). b. The major fontanels are the anterior, posterior, anterolaterals, and posterolaterals . c. Fontanels h ...
The Skeletal System (Axial Skeleton)
... 1. The skull forms the large cranial cavity and smaller cavities, including the nasal cavity and orbits (eye sockets). 2. Certain skull bones contain mucous membrane lined cavities called paranasal sinuses. (Figure7.13) 3. The only moveable bone of the skull, other than the ear ossicles within the t ...
... 1. The skull forms the large cranial cavity and smaller cavities, including the nasal cavity and orbits (eye sockets). 2. Certain skull bones contain mucous membrane lined cavities called paranasal sinuses. (Figure7.13) 3. The only moveable bone of the skull, other than the ear ossicles within the t ...
- DUNE - University of New England
... neighbors in the abdomen, a posterior approach to dissect the kidney prior to the abdominal dissection seemed to be the best solution to this problem. It was important to preserve the renal system’s structural and functional relationships to the abdominal and pelvic contents for future study. As stu ...
... neighbors in the abdomen, a posterior approach to dissect the kidney prior to the abdominal dissection seemed to be the best solution to this problem. It was important to preserve the renal system’s structural and functional relationships to the abdominal and pelvic contents for future study. As stu ...
SELECTIVE NECK DISSECTION
... 1. A horizontal incision from the anterior border of the SCM to the midline of the neck just below the level of the hyoid bone is made. 2. Level Ia dissection clears tissue between the anterior bellies of both digastrics and off the mylohyoid muscle. 3. Incising the submandibular capsule horizont ...
... 1. A horizontal incision from the anterior border of the SCM to the midline of the neck just below the level of the hyoid bone is made. 2. Level Ia dissection clears tissue between the anterior bellies of both digastrics and off the mylohyoid muscle. 3. Incising the submandibular capsule horizont ...
Body snatching
Body snatching is the secret disinterment of corpses from graveyards or other burial sites. A common purpose of body snatching, especially in the 19th century, was to sell the corpses for dissection or anatomy lectures in medical schools. Those who practiced body snatching were often called ""resurrectionists"" or ""resurrection-men"". A related act is grave robbery, uncovering a tomb or crypt to steal artifacts or personal effects rather than corpses.