Notes-Undergrad-Child-Psychopath-Wk1Day2
... Epidemiology is concerned with the ways in which clinical disorders and diseases occur in human populations, and with factors that influence these patterns of occurrence. Three interrelated components of epidemiological research involve: 1. Assessing the occurrence of new cases (incidence rate) or e ...
... Epidemiology is concerned with the ways in which clinical disorders and diseases occur in human populations, and with factors that influence these patterns of occurrence. Three interrelated components of epidemiological research involve: 1. Assessing the occurrence of new cases (incidence rate) or e ...
Psych 305A: Lecture 14 The Cognitive Approach Part I Learning and
... The Essence of Behaviorism • "The consequences of behavior determine the probability that the behavior will occur again” – BF Skinner •Anyone’s personality can be formed or changed through patterns of reinforcement and punishment •If you are extraverted, that’s because extraverted behaviors ...
... The Essence of Behaviorism • "The consequences of behavior determine the probability that the behavior will occur again” – BF Skinner •Anyone’s personality can be formed or changed through patterns of reinforcement and punishment •If you are extraverted, that’s because extraverted behaviors ...
Psychiatric Disorders, Diseases, and Drugs 1 Running Head
... benzodiazepines but eliminate the sedation and impaired motor functioning side effects of those drugs (Pinel, 2007). Each psychiatric disorder and disease is characterized by its own set of unique symptoms. Causes and contributing factors of these disorders and diseases include genetics, neurodevelo ...
... benzodiazepines but eliminate the sedation and impaired motor functioning side effects of those drugs (Pinel, 2007). Each psychiatric disorder and disease is characterized by its own set of unique symptoms. Causes and contributing factors of these disorders and diseases include genetics, neurodevelo ...
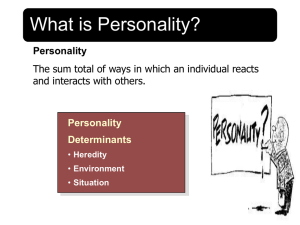
Personality
... For the idea that people are inherently good For placing importance on conscious mental experience For the idea that the self-concept is the heart of personality ...
... For the idea that people are inherently good For placing importance on conscious mental experience For the idea that the self-concept is the heart of personality ...
Cognitive Approaches
... weight determined by number of fat cells. Fat cells expand as we gain weight and contracts as we lose weight. When we lose weight, it is difficult to get below set point. Our bodies interpret starvation and respond by storing fat. If we gain weight over time, set-point may increase. ...
... weight determined by number of fat cells. Fat cells expand as we gain weight and contracts as we lose weight. When we lose weight, it is difficult to get below set point. Our bodies interpret starvation and respond by storing fat. If we gain weight over time, set-point may increase. ...
Psychological Disorders
... include clinical disorders, personality disorders, general medical conditions, psychosocial and environmental problems, and a global assessment of functioning. • Over one-fifth of all adults over age 18 suffer from a mental disorder in any given year. • Major depression is one of the most common psy ...
... include clinical disorders, personality disorders, general medical conditions, psychosocial and environmental problems, and a global assessment of functioning. • Over one-fifth of all adults over age 18 suffer from a mental disorder in any given year. • Major depression is one of the most common psy ...
File - BBA Group A 2010
... 1. are always moving, walking, and eating rapidly; 2. feel impatient with the rate at which most events take place; 3. strive to think or do two or more things at once; 4. cannot cope with leisure time; 5. are obsessed with numbers, measuring their success in terms of how many or how much of everyth ...
... 1. are always moving, walking, and eating rapidly; 2. feel impatient with the rate at which most events take place; 3. strive to think or do two or more things at once; 4. cannot cope with leisure time; 5. are obsessed with numbers, measuring their success in terms of how many or how much of everyth ...
Theory Application Paper Sarah Merve Ahmad Koç University
... to Freud we might claim that X fails to complete psychosexual stages successfully and also this could be the reason why fixation occur and in result becoming over-weight boy. I also want to point out that three major system which constitutes the total personality and called id, ego and superego fai ...
... to Freud we might claim that X fails to complete psychosexual stages successfully and also this could be the reason why fixation occur and in result becoming over-weight boy. I also want to point out that three major system which constitutes the total personality and called id, ego and superego fai ...
Course review terms and concepts
... Constructive coping Defense mechanisms Factor analysis Five factor model (The Big 5) Fight or flight response Frustration General adaptation syndrome Influence of Id, Ego and Superego Adler’s Inferiority complex Learned helplessness Psychosomatic diseases Carl Roger’s theory of Self Maslow’s self-ac ...
... Constructive coping Defense mechanisms Factor analysis Five factor model (The Big 5) Fight or flight response Frustration General adaptation syndrome Influence of Id, Ego and Superego Adler’s Inferiority complex Learned helplessness Psychosomatic diseases Carl Roger’s theory of Self Maslow’s self-ac ...
Chapter 2
... theories. Each can be traced back to Sigmund Freud. • Personality is characterized by a dynamic struggle between elements of the personality. ...
... theories. Each can be traced back to Sigmund Freud. • Personality is characterized by a dynamic struggle between elements of the personality. ...
General Psychology Notes - Theories of Personality
... 2) through experiences with the world the self emerges 3) unconditional positive regard (accepting & valuing person regardless of behavior) 4) positive self-concept emerges when we have unconditional positive regard & empathy 5) genuine relationships needed 6) healthy - congruence between the sum of ...
... 2) through experiences with the world the self emerges 3) unconditional positive regard (accepting & valuing person regardless of behavior) 4) positive self-concept emerges when we have unconditional positive regard & empathy 5) genuine relationships needed 6) healthy - congruence between the sum of ...
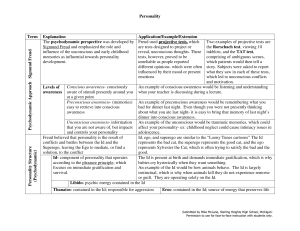
Personality Term Explanation Application/Example
... are capable of doing things on their own and are not dependent on them and overcome childhood inferiorities hence inferior. Adler also believed that people brag to cover up to make through being superior in life during other people forget or not notice their inferiorities. adulthood Horney thought t ...
... are capable of doing things on their own and are not dependent on them and overcome childhood inferiorities hence inferior. Adler also believed that people brag to cover up to make through being superior in life during other people forget or not notice their inferiorities. adulthood Horney thought t ...
Chapter 16 Review Notes
... associated with schizophrenia, and discuss the possible link between prenatal viral infections and schizophrenia. Researchers have linked certain forms of schizophrenia with brain abnormalities such as increased receptors for the neurotransmitter dopamine and impaired glutamate activity. Modern brai ...
... associated with schizophrenia, and discuss the possible link between prenatal viral infections and schizophrenia. Researchers have linked certain forms of schizophrenia with brain abnormalities such as increased receptors for the neurotransmitter dopamine and impaired glutamate activity. Modern brai ...
Abnormal Psychology
... Know what hallucinations & delusions are & the different types Know the psychomotor symptoms Understand the diathesis-stress model of schizophrenia Know what neurotransmitter has been implicated with schizophrenia Understand the research on viral infections & schizophrenia Ch15 What is the social br ...
... Know what hallucinations & delusions are & the different types Know the psychomotor symptoms Understand the diathesis-stress model of schizophrenia Know what neurotransmitter has been implicated with schizophrenia Understand the research on viral infections & schizophrenia Ch15 What is the social br ...
History and Approaches of Psychology
... Thought other approaches were “dehumanizing” and suggested people weren’t masters of their own destinies People have a basic need to continue to evolve and fulfill their potential; many psychological disturbances are due to thwarting these needs Abraham Maslow: Hierarchy of Needs - each level of nee ...
... Thought other approaches were “dehumanizing” and suggested people weren’t masters of their own destinies People have a basic need to continue to evolve and fulfill their potential; many psychological disturbances are due to thwarting these needs Abraham Maslow: Hierarchy of Needs - each level of nee ...
File
... disorder from two of the following groups: anxiety disorders, affective disorders, eating disorders. Analyze etiologies (in terms of biological, cognitive, and sociocultural factors) of one disorder from two of the following groups: anxiety disorders, affective disorders, eating disorders. ...
... disorder from two of the following groups: anxiety disorders, affective disorders, eating disorders. Analyze etiologies (in terms of biological, cognitive, and sociocultural factors) of one disorder from two of the following groups: anxiety disorders, affective disorders, eating disorders. ...
Freud`s Psychoanalytic Theory
... • Positive psychology – Movement within psychology focusing on the desirable aspects of human functioning, as opposed to an emphasis on psychopathology. ...
... • Positive psychology – Movement within psychology focusing on the desirable aspects of human functioning, as opposed to an emphasis on psychopathology. ...
Personality Types
... having experiences in mastering new skills and overcoming obstacles having successful and competent role models in one's life receiving feedback and encouragement from others self awareness and management of one's inner state (thoughts and emotions). ...
... having experiences in mastering new skills and overcoming obstacles having successful and competent role models in one's life receiving feedback and encouragement from others self awareness and management of one's inner state (thoughts and emotions). ...
personal construct theory personality
... list has grown considerably since then. The underlying assumptions common to all definitions are that people have more or less stable patterns of behaviour across certain situations, and that these behaviour patterns differ from one person to the next. Whereas most areas of psychological research ar ...
... list has grown considerably since then. The underlying assumptions common to all definitions are that people have more or less stable patterns of behaviour across certain situations, and that these behaviour patterns differ from one person to the next. Whereas most areas of psychological research ar ...
Intro to Psychological Disorders
... There is no one absolute definition of psychological disorders; moreover, a continuum exists between mental health on the one hand and pathology on the other. Some proposed definitions include: ...
... There is no one absolute definition of psychological disorders; moreover, a continuum exists between mental health on the one hand and pathology on the other. Some proposed definitions include: ...
BCLMA Small Firm Thursday June 22 2017
... responsibilities, successful change management, a culture of client value through collaboration and so much more! The benefits of having helpful tips that take the mystery out of how to communicate with people from other personality types is endless. ...
... responsibilities, successful change management, a culture of client value through collaboration and so much more! The benefits of having helpful tips that take the mystery out of how to communicate with people from other personality types is endless. ...
Слайд 1 - sechenov.ru
... The First Sechenov Moscow State Medical University under Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation ...
... The First Sechenov Moscow State Medical University under Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation ...
Eating Disorders - Primary Mental Health
... Bulimia Nervosa – more common BUT less severe NZ Community Sample – lifetime risk using formal diagnostic criteria - 1.5-3.0% Secondary school girls – rates of binge eating/vomiting high – up to 20% - mostly self-limiting/does not progress to full disorder Female risk 10x male risk Co-morb ...
... Bulimia Nervosa – more common BUT less severe NZ Community Sample – lifetime risk using formal diagnostic criteria - 1.5-3.0% Secondary school girls – rates of binge eating/vomiting high – up to 20% - mostly self-limiting/does not progress to full disorder Female risk 10x male risk Co-morb ...