A4.2.2.TeacherResource
... Students may have seen the pull-down pulley system in the gym that allows a person to isolate and train this portion of the muscle. 9. Students will now create the largest portion of the muscle – the sternal or sternocostalis head. Write the name of the muscle on the board. Given the name only, ask ...
... Students may have seen the pull-down pulley system in the gym that allows a person to isolate and train this portion of the muscle. 9. Students will now create the largest portion of the muscle – the sternal or sternocostalis head. Write the name of the muscle on the board. Given the name only, ask ...
Bone
... Ask the patient to stick out his/her tongue. The tongue will deviate to the side of the nerve with the lesion (b/c of unilateral paralysis of the genioglossus muscle, which protracts the tongue). 11. All of the “glossus” muscles are innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) except ________, which ...
... Ask the patient to stick out his/her tongue. The tongue will deviate to the side of the nerve with the lesion (b/c of unilateral paralysis of the genioglossus muscle, which protracts the tongue). 11. All of the “glossus” muscles are innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) except ________, which ...
Assignment 4.2.2
... Students may have seen the pull-down pulley system in the gym that allows a person to isolate and train this portion of the muscle. 9. Students will now create the largest portion of the muscle – the sternal or sternocostalis head. Write the name of the muscle on the board. Given the name only, ask ...
... Students may have seen the pull-down pulley system in the gym that allows a person to isolate and train this portion of the muscle. 9. Students will now create the largest portion of the muscle – the sternal or sternocostalis head. Write the name of the muscle on the board. Given the name only, ask ...
Anatomy UE Forum 2011
... – Deep Radial (interossei, lumbricals, deep muscles) • Superficial branch splits into common digital arteries, which go up to become the proper digital arteries ...
... – Deep Radial (interossei, lumbricals, deep muscles) • Superficial branch splits into common digital arteries, which go up to become the proper digital arteries ...
Bone Grafting
... Pubis and ischium form incomplete bony wall for pelvic cavity, their outer surface gives attachment to the thigh muscles The ilium forms a brim between the hip joint and the joint with the sacrum ...
... Pubis and ischium form incomplete bony wall for pelvic cavity, their outer surface gives attachment to the thigh muscles The ilium forms a brim between the hip joint and the joint with the sacrum ...
Dr. Weyrich G04: Anterior Thoracic Wall, Breast and Lymphatic
... -Sternocostal head – sternum, superior 6 costal cartilages, and aponeurosis of external oblique m. Lateral attachments -Intertubercular groove of humerus Innervation -Lateral and medial pectoral nerves Main actions -Adducts and medially rotates humerus -Draws scapula anteriorly and inferiorly ...
... -Sternocostal head – sternum, superior 6 costal cartilages, and aponeurosis of external oblique m. Lateral attachments -Intertubercular groove of humerus Innervation -Lateral and medial pectoral nerves Main actions -Adducts and medially rotates humerus -Draws scapula anteriorly and inferiorly ...
MBBS first Prof. Syllabus, uploaded on 2014-05-17
... extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus, joints- shoulder, elbow and wrist, flexor and extensor retinaculam, arteries- axillary, brachial, radial, ulnar, superficial and deep palmar arches, nerves- median, radial, ulnar. HEAD & NECK Laryngeal prominence, cricoid cartilage, tracheal rin ...
... extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus, joints- shoulder, elbow and wrist, flexor and extensor retinaculam, arteries- axillary, brachial, radial, ulnar, superficial and deep palmar arches, nerves- median, radial, ulnar. HEAD & NECK Laryngeal prominence, cricoid cartilage, tracheal rin ...
synovial (joint)
... Articulating bones: formed by the head of the humerus and the glenoid cavity of the scapula Movements The shoulder joint allows flexion, extension, hyperextension, abduction, adduction, medial rotation, lateral rotation, and circumduction of the arm ...
... Articulating bones: formed by the head of the humerus and the glenoid cavity of the scapula Movements The shoulder joint allows flexion, extension, hyperextension, abduction, adduction, medial rotation, lateral rotation, and circumduction of the arm ...
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 242
... lamellae, circumferential lamellae, osteon, lacuna, canaliculi, cancellous bone, trabeculae, organic matrix (collagen fibers); mineral matrix (hydroxyapatite). Page 179. ...
... lamellae, circumferential lamellae, osteon, lacuna, canaliculi, cancellous bone, trabeculae, organic matrix (collagen fibers); mineral matrix (hydroxyapatite). Page 179. ...
The transverses abdominus is the deepest of the abdominal
... Martini,Frederic, H. Fundementals of Anatomy & Physiology.California. Martini. 2004 ...
... Martini,Frederic, H. Fundementals of Anatomy & Physiology.California. Martini. 2004 ...
UPPER LIMB INJURIES
... In patients over the age of 40 years, rotator cuff tears and nerve injury are more frequent. Greater tuberosity fractures or rotator cuff tears are present in 10-30% of glenohumeral dislocations. They are more common in older patients. Nerve injuries (most commonly the axillary nerve) can be treated ...
... In patients over the age of 40 years, rotator cuff tears and nerve injury are more frequent. Greater tuberosity fractures or rotator cuff tears are present in 10-30% of glenohumeral dislocations. They are more common in older patients. Nerve injuries (most commonly the axillary nerve) can be treated ...
Biology 231
... scoliosis – lateral curvature Parts of Typical Vertebra vertebral body – anterior portion; thick disc that bears weight; have intervertebral discs between vertebral arch – extends posteriorly from body and surrounds spinal cord pedicles – form anterior margin of arch laminae – form posterior margin ...
... scoliosis – lateral curvature Parts of Typical Vertebra vertebral body – anterior portion; thick disc that bears weight; have intervertebral discs between vertebral arch – extends posteriorly from body and surrounds spinal cord pedicles – form anterior margin of arch laminae – form posterior margin ...
FEMUR (osteology) OBJECTIVES At the end of the session, the
... at the junction of the neck with the upper part of the shaft Directed a little laterally and backward About 1 cm. lower than the head in the adult It has two surfaces and four borders. ...
... at the junction of the neck with the upper part of the shaft Directed a little laterally and backward About 1 cm. lower than the head in the adult It has two surfaces and four borders. ...
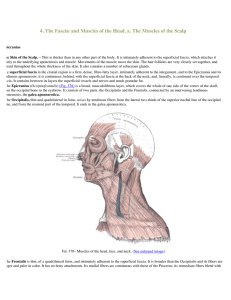
4. The Fascię and Muscles of the Head. a. The Muscles of the Scalp
... The orbital portion is thicker and of a reddish color; its fibers form a complete ellipse without interruption at the lateral palpebral commissure; the upper fibers of this portion blend with the Frontalis and Corrugator. The lacrimal part (Tensor tarsi) is a small, thin muscle, about 6 mm. in bread ...
... The orbital portion is thicker and of a reddish color; its fibers form a complete ellipse without interruption at the lateral palpebral commissure; the upper fibers of this portion blend with the Frontalis and Corrugator. The lacrimal part (Tensor tarsi) is a small, thin muscle, about 6 mm. in bread ...
Cranial Bone Features
... Squamous (flat) and Petrous (rocky) portions Styloid process (GK: stylos = needle + oid = like, i.e. the stylus of your record player ?) StyloMastoid foramen (CN VII) Tympanic canaliculus (for passage of lesser petrosal nerve from CN IX to tympanic plexus) Zygomatic process ...
... Squamous (flat) and Petrous (rocky) portions Styloid process (GK: stylos = needle + oid = like, i.e. the stylus of your record player ?) StyloMastoid foramen (CN VII) Tympanic canaliculus (for passage of lesser petrosal nerve from CN IX to tympanic plexus) Zygomatic process ...
nasal cavity paranasal sinuses
... Open into lateral wall of nasal cavity. Innervated by branches of the trigeminal nerve. The maxillary and sphenoidal are rudimentary at birth. They enlarge after the 8th year. ...
... Open into lateral wall of nasal cavity. Innervated by branches of the trigeminal nerve. The maxillary and sphenoidal are rudimentary at birth. They enlarge after the 8th year. ...
2401_Ch8.pdf
... (rotator cuff muscles) and one tendon Review ligaments of shoulder from table 8.2 – The tendon of the biceps brachii holds the anterior face of the humerus. ...
... (rotator cuff muscles) and one tendon Review ligaments of shoulder from table 8.2 – The tendon of the biceps brachii holds the anterior face of the humerus. ...
The Spine
... There is also a small ligament called ligamentum teres or the ligament of the head of the femur. The ligament is a triangularly shaped band with its base on both sides of peripheral edge of acetabular notch. This structure is not that important as a ligament but can often be vitally important as a c ...
... There is also a small ligament called ligamentum teres or the ligament of the head of the femur. The ligament is a triangularly shaped band with its base on both sides of peripheral edge of acetabular notch. This structure is not that important as a ligament but can often be vitally important as a c ...
Action of the Diaphragm
... • It is the broad end of thorax • Surrounds the upper part of abdominal cavity • Separates the thoracic from abdominal cavity by diaphragm ...
... • It is the broad end of thorax • Surrounds the upper part of abdominal cavity • Separates the thoracic from abdominal cavity by diaphragm ...
7 - Anatomy and Physiology
... • Cone-shaped sternal (medial) end articulates with the sternum • Act as braces to hold the scapulae and arms out laterally ...
... • Cone-shaped sternal (medial) end articulates with the sternum • Act as braces to hold the scapulae and arms out laterally ...
Scapula
In anatomy, the scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas) or shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones the scapulae are paired, with the scapula on the left side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the right scapula. In early Roman times, people thought the bone resembled a trowel, a small shovel. The shoulder blade is also called omo in Latin medical terminology.The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage.