anatomy of the knee - Nashville Knee and Shoulder
... notch is generally rounded but in some patients the notch has a triangular, stenotic configuration that may place them at risk for injuring the ACL. The upper end of the tibia is formed by the medial and lateral tibial plateaus. Two tibial spines are located in the central portion between the tibial ...
... notch is generally rounded but in some patients the notch has a triangular, stenotic configuration that may place them at risk for injuring the ACL. The upper end of the tibia is formed by the medial and lateral tibial plateaus. Two tibial spines are located in the central portion between the tibial ...
Mechanics and Pathomechanics of the Muscles of the Face and Eyes
... swallowing. This unit is divided rather artificially by function, and the structures most associated with each function are described within the context of that function. However, the reader must recognize that many anatomical components participate in multiple functions. For example, the lips parti ...
... swallowing. This unit is divided rather artificially by function, and the structures most associated with each function are described within the context of that function. However, the reader must recognize that many anatomical components participate in multiple functions. For example, the lips parti ...
Document
... Each bone consists of a body, a proximal end and distal end. The distal ends or heads of the metacarpals articulate with the proximal phalanges and form the knuckles of the fist. The proximal ends or bases of the metacarpals articulate with the carpal ...
... Each bone consists of a body, a proximal end and distal end. The distal ends or heads of the metacarpals articulate with the proximal phalanges and form the knuckles of the fist. The proximal ends or bases of the metacarpals articulate with the carpal ...
Icd10 femoral neck fracture
... Icd10 femoral neck fracture Icd10 femoral neck fracture Femoral neck fractures have proven to be serious injuries that are associated with high mortality and significant morbidity in the geriatric population. Background Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) is a commonly used treatment for fra ...
... Icd10 femoral neck fracture Icd10 femoral neck fracture Femoral neck fractures have proven to be serious injuries that are associated with high mortality and significant morbidity in the geriatric population. Background Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) is a commonly used treatment for fra ...
Ch9.Joints.Lecture
... Glenoid cavity Glenoid labrum Tendon of long head of biceps brachii muscle Glenohumeral ligaments ...
... Glenoid cavity Glenoid labrum Tendon of long head of biceps brachii muscle Glenohumeral ligaments ...
educational models for teaching pelvic floor disorders
... adduction to the leg. Can be injured during pelvic surgery. pudendal nerve: starts at the roots of S2-S4, passes out the greater sciatic notch between the piriformis and the coccygeus running behind the sacrospinous ligament at the ischial spine, back through the lesser sciatic foramen through the i ...
... adduction to the leg. Can be injured during pelvic surgery. pudendal nerve: starts at the roots of S2-S4, passes out the greater sciatic notch between the piriformis and the coccygeus running behind the sacrospinous ligament at the ischial spine, back through the lesser sciatic foramen through the i ...
Splinting?
... of posterior arm. It attaches to the olecranon process when all 3 heads of the muscle ...
... of posterior arm. It attaches to the olecranon process when all 3 heads of the muscle ...
neon - ulrich medical USA
... The neon hooks extend the instrumentation options of this versatile system. ...
... The neon hooks extend the instrumentation options of this versatile system. ...
Thigh and Knee
... joint with the knee extended and explore them with the knee slightly flexed. The medial head of the gastrocnemius arises at a more proximal level from the femoral condyle than does the lateral head, and the groove it forms with the semimembranosus forms a safe and comparatively avascular approach to ...
... joint with the knee extended and explore them with the knee slightly flexed. The medial head of the gastrocnemius arises at a more proximal level from the femoral condyle than does the lateral head, and the groove it forms with the semimembranosus forms a safe and comparatively avascular approach to ...
VASCULAR APPLIED ANATOMY OF UPPER LIMB
... from lateral border of first rib to lower border of teres major muscle Division ( In to 3 parts) by pectoralis minor Branches From 1st part Superior Thyroid artery From 2nd part 1.Thoracoacromial 2. Lateral thoracic artery rd From 3 part 1. Subscapular artery 2. Ant. humeral circumflex 3. Post. hume ...
... from lateral border of first rib to lower border of teres major muscle Division ( In to 3 parts) by pectoralis minor Branches From 1st part Superior Thyroid artery From 2nd part 1.Thoracoacromial 2. Lateral thoracic artery rd From 3 part 1. Subscapular artery 2. Ant. humeral circumflex 3. Post. hume ...
Ch9.Joints.Lecture_1
... Glenoid cavity Glenoid labrum Tendon of long head of biceps brachii muscle Glenohumeral ligaments ...
... Glenoid cavity Glenoid labrum Tendon of long head of biceps brachii muscle Glenohumeral ligaments ...
MECH5221M Spinal Biomechanics and Instrumentation Unit 1
... are responsible for transmission of most of the compressive load within the spinal column, while the posterior processes mainly provide attachment points for the muscles and ligaments that control the movements of the spine. Under changes in posture the degree to which load is partition between the ...
... are responsible for transmission of most of the compressive load within the spinal column, while the posterior processes mainly provide attachment points for the muscles and ligaments that control the movements of the spine. Under changes in posture the degree to which load is partition between the ...
Human Dissection Anatomy
... point approximately 5 cm above the patella, where the deep fascia becomes continuous with the knee joint capsule. Run your hand laterally under the deep fascia to separate it from the muscles of the anterior compartment. If you extend your hand deep enough you will reach the lateral intermuscular se ...
... point approximately 5 cm above the patella, where the deep fascia becomes continuous with the knee joint capsule. Run your hand laterally under the deep fascia to separate it from the muscles of the anterior compartment. If you extend your hand deep enough you will reach the lateral intermuscular se ...
POPLITEAL FOSSA
... Subcutaneous tissue overlying the fascia contains fat, the small saphenous vein & 3 cutaneous nerves posterior cutaneous of the thigh medial cutaneous sural nerve lateral cutaneous sural nerve The deep fascia forms a protective sheet overlying the neurovascular structures; it is continuous wit ...
... Subcutaneous tissue overlying the fascia contains fat, the small saphenous vein & 3 cutaneous nerves posterior cutaneous of the thigh medial cutaneous sural nerve lateral cutaneous sural nerve The deep fascia forms a protective sheet overlying the neurovascular structures; it is continuous wit ...
POPLITEAL FOSSA
... Subcutaneous tissue overlying the fascia contains fat, the small saphenous vein & 3 cutaneous nerves posterior cutaneous of the thigh medial cutaneous sural nerve lateral cutaneous sural nerve The deep fascia forms a protective sheet overlying the neurovascular structures; it is continuous wit ...
... Subcutaneous tissue overlying the fascia contains fat, the small saphenous vein & 3 cutaneous nerves posterior cutaneous of the thigh medial cutaneous sural nerve lateral cutaneous sural nerve The deep fascia forms a protective sheet overlying the neurovascular structures; it is continuous wit ...
INTRODUCTION
... Posterior tubercle is the origin of the deep component of the posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (PITFL). The more superficial fibers of the posterior tibiofibular ligaments are also attached to the posterior tubercle and are typically not injured in trimalleolar fractures and indirect reducti ...
... Posterior tubercle is the origin of the deep component of the posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (PITFL). The more superficial fibers of the posterior tibiofibular ligaments are also attached to the posterior tubercle and are typically not injured in trimalleolar fractures and indirect reducti ...
Anatomy of the Temporal Bone
... the squama, where it lies below and lateral to the orifice of the auditory tube. Posteriorly, it blends with the squama and mastoid part, and forms the anterior boundary of the tympanomastoid fissure. Its upper border fuses laterally with the back of the postglenoid process, while medially it bounds ...
... the squama, where it lies below and lateral to the orifice of the auditory tube. Posteriorly, it blends with the squama and mastoid part, and forms the anterior boundary of the tympanomastoid fissure. Its upper border fuses laterally with the back of the postglenoid process, while medially it bounds ...
I. Lung and its pleura
... pass through the pleura or the lung tissue. 2. Stab wounds in the mid-axillary line a. Above the 8th rib, they lead to injury of the lung and pleura. b. Between the 10th and 8th rib, they lead to injury of the pleura. 3. Injury of the pleura leads to the followings: a. Entry of air into the pleural ...
... pass through the pleura or the lung tissue. 2. Stab wounds in the mid-axillary line a. Above the 8th rib, they lead to injury of the lung and pleura. b. Between the 10th and 8th rib, they lead to injury of the pleura. 3. Injury of the pleura leads to the followings: a. Entry of air into the pleural ...
Match the action described with the muscle given below
... Contraction of the palmar interosseous muscle between the fourth and fifth fingers results in A. abduction of the fourth finger. B. adduction of the fourth finger. C. adduction of the fifth finger. D. flexion of the interphalangeal joints of the fourth finger. E. flexion of the interphalangeal joint ...
... Contraction of the palmar interosseous muscle between the fourth and fifth fingers results in A. abduction of the fourth finger. B. adduction of the fourth finger. C. adduction of the fifth finger. D. flexion of the interphalangeal joints of the fourth finger. E. flexion of the interphalangeal joint ...
Deep Cervical Fascia
... • Its fibers arise in deep fascia covering superior parts of deltoid & pectoralis major muscles • sweep superomedially over clavicle to inferior border of mandible. anterior borders of the two muscles decussate over chin blend with facial muscles. Inferiorly, fibers diverge, leaving a gap anterior ...
... • Its fibers arise in deep fascia covering superior parts of deltoid & pectoralis major muscles • sweep superomedially over clavicle to inferior border of mandible. anterior borders of the two muscles decussate over chin blend with facial muscles. Inferiorly, fibers diverge, leaving a gap anterior ...
KNEE JOINT
... • Superiorly: Attached to the femur, just proximal to the articular margins of the condyles • Inferiorly: Attached to the articular margin of the tibia. • Posteriorly: Attached to the Intercondylar line • Laterally: Deficient on the lateral condyle, allowing the tendon of the popliteus muscle to pas ...
... • Superiorly: Attached to the femur, just proximal to the articular margins of the condyles • Inferiorly: Attached to the articular margin of the tibia. • Posteriorly: Attached to the Intercondylar line • Laterally: Deficient on the lateral condyle, allowing the tendon of the popliteus muscle to pas ...
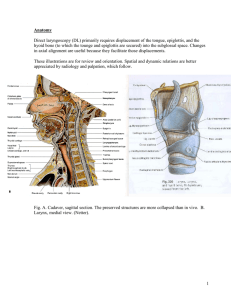
1 Anatomy Direct laryngoscopy (DL) primarily requires displacement
... laryngeal displacement forward but that effect is countered by the lower compliance of the mediastinum at the sternal notch. The compliance limitation is reduced as the neck structures move above the sternal notch. When passive support of the upper trunk has not been placed in advance and difficult ...
... laryngeal displacement forward but that effect is countered by the lower compliance of the mediastinum at the sternal notch. The compliance limitation is reduced as the neck structures move above the sternal notch. When passive support of the upper trunk has not been placed in advance and difficult ...
Scapula
In anatomy, the scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas) or shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones the scapulae are paired, with the scapula on the left side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the right scapula. In early Roman times, people thought the bone resembled a trowel, a small shovel. The shoulder blade is also called omo in Latin medical terminology.The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage.











![[edit]Pelvic cavity - Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000164092_1-0bf08b2d7896fb51bd702acf95617848-300x300.png)