Chapter 5: The Skeletal System
... Identify on a skeleton or diagram the bones of the shoulder and pelvic girdles and their attached limbs. Shoulder (pectoral) girdle = clavicle and scapula Clavicle = collarbone; doubly curved; attaches to manubrium of sternum and scapula; acts as a brace; ...
... Identify on a skeleton or diagram the bones of the shoulder and pelvic girdles and their attached limbs. Shoulder (pectoral) girdle = clavicle and scapula Clavicle = collarbone; doubly curved; attaches to manubrium of sternum and scapula; acts as a brace; ...
Spring 02
... a) the oblique popliteal ligament is located on the anterior aspect of the knee joint b) the medial collateral ligament is also called the tibial collateral ligament c) it is a synovial, double condyloid, biaxial joint d) if the knee is hyperextended, the femur will rotate medially if the foot is pl ...
... a) the oblique popliteal ligament is located on the anterior aspect of the knee joint b) the medial collateral ligament is also called the tibial collateral ligament c) it is a synovial, double condyloid, biaxial joint d) if the knee is hyperextended, the femur will rotate medially if the foot is pl ...
general osteology
... directed medially • Inferior facets directed laterally • Flexion/extension, some lateral flexion, rotation prevented ...
... directed medially • Inferior facets directed laterally • Flexion/extension, some lateral flexion, rotation prevented ...
07. General osteology
... directed medially • Inferior facets directed laterally • Flexion/extension, some lateral flexion, rotation prevented ...
... directed medially • Inferior facets directed laterally • Flexion/extension, some lateral flexion, rotation prevented ...
Skeletal System note outline
... See pg. 140-143 Bone is formed from a template of __________________________. Cartilage can be found in the following places: List and briefly describe the six types of fractures ...
... See pg. 140-143 Bone is formed from a template of __________________________. Cartilage can be found in the following places: List and briefly describe the six types of fractures ...
massage therapist study guide - Advanced Massage Education
... 10. b - Fascia is the connective tissue that extends from head to toe, surrounding all our muscles, nerves and blood vessels and binds all of our tissues together. There are several layers of fascia including, superficial fascia, deep fascia and subserous or visceral fascia which covers and connect ...
... 10. b - Fascia is the connective tissue that extends from head to toe, surrounding all our muscles, nerves and blood vessels and binds all of our tissues together. There are several layers of fascia including, superficial fascia, deep fascia and subserous or visceral fascia which covers and connect ...
Slide 1
... Polio, Standard & the Howland laryngoscopes. • The short handle is helpful, when Intubating Obese or Patients with Large Breast ...
... Polio, Standard & the Howland laryngoscopes. • The short handle is helpful, when Intubating Obese or Patients with Large Breast ...
Management of the hemiplegic upper limb Trunk Control Alignment
... – Occurs due to prolonged downward pull by gravity on the arm against which hypotonic muscles offer little resistance (Chaco and Wolf 1971). Results in overstretching of the glenohumeral capsule (especially its superior aspect) and hypotonic supraspinatus and deltoid muscles (Basmajian and Bazant 19 ...
... – Occurs due to prolonged downward pull by gravity on the arm against which hypotonic muscles offer little resistance (Chaco and Wolf 1971). Results in overstretching of the glenohumeral capsule (especially its superior aspect) and hypotonic supraspinatus and deltoid muscles (Basmajian and Bazant 19 ...
Skull Worksheet
... 4) ______________________Bones – fingernail-sized bones that form part of the medial walls of the eye sockets 5) ______________________Bones – rectangular bones that form the bridge of the nose 6) ______________________Bone – single bone that forms most of the nasal septum 7) Inferior ______________ ...
... 4) ______________________Bones – fingernail-sized bones that form part of the medial walls of the eye sockets 5) ______________________Bones – rectangular bones that form the bridge of the nose 6) ______________________Bone – single bone that forms most of the nasal septum 7) Inferior ______________ ...
Lab Objectives
... Glenohumeral Joint (Shoulder) Glenoid fossa of scapula and head of humerus ...
... Glenohumeral Joint (Shoulder) Glenoid fossa of scapula and head of humerus ...
Movements
... shaft with relatively wide, protruding ends Shaft contains the medullary canal Ex. Phalanges, metatarsals, metacarpals, tibia, fibula, femur, radius, ulna, & humerus Function: Levers ...
... shaft with relatively wide, protruding ends Shaft contains the medullary canal Ex. Phalanges, metatarsals, metacarpals, tibia, fibula, femur, radius, ulna, & humerus Function: Levers ...
Skull
... – Squamosal suture (between temporal & parietal bone) – External auditory/acoustic meatus (ear canal in temporal bone) – Mandibular fossae (articulate with mandible) – Mastoid process (attaches to neck muscles; a spongy bone that projects from the temporal) – Styloid process (anchors muscles, tongue ...
... – Squamosal suture (between temporal & parietal bone) – External auditory/acoustic meatus (ear canal in temporal bone) – Mandibular fossae (articulate with mandible) – Mastoid process (attaches to neck muscles; a spongy bone that projects from the temporal) – Styloid process (anchors muscles, tongue ...
Back
... pairs of foramina for sacral nerves (D) Fracture of the transverse process of the atlas may impair functions of the superior and inferior obliquus capitis muscles (E) The posterior longitudinal ligament is penetrated by the needle during lumbar puncture Match each of the following description with t ...
... pairs of foramina for sacral nerves (D) Fracture of the transverse process of the atlas may impair functions of the superior and inferior obliquus capitis muscles (E) The posterior longitudinal ligament is penetrated by the needle during lumbar puncture Match each of the following description with t ...
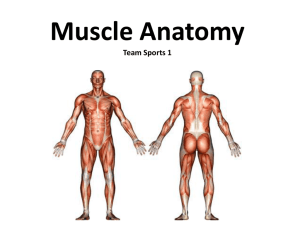
Muscle Anatomy Team Sports 1
... muscle fibers occur in muscles which are attached to the skeleton. Those muscles that can be moved by our thoughts and actions. • Smooth/Involuntary MuscleMuscles that moves internal organs, such as the bowels, and vessels. Reflex action is made without our thought. • Cardiac- The muscle of the hear ...
... muscle fibers occur in muscles which are attached to the skeleton. Those muscles that can be moved by our thoughts and actions. • Smooth/Involuntary MuscleMuscles that moves internal organs, such as the bowels, and vessels. Reflex action is made without our thought. • Cardiac- The muscle of the hear ...
1. The general name for an alternate pathway of blood flow in or
... The accessory nerve innervates the trapezius which is the muscle responsible for elevating the acromion of the scapula, also known as the tip of the shoulder. If a patient has damaged her accessory nerve, she will be unable to elevate her acromion. The dorsal scapular nerve innervates three muscles: ...
... The accessory nerve innervates the trapezius which is the muscle responsible for elevating the acromion of the scapula, also known as the tip of the shoulder. If a patient has damaged her accessory nerve, she will be unable to elevate her acromion. The dorsal scapular nerve innervates three muscles: ...
Analysis of force vectors and torques generated by rotator cuff
... Notably, in the present study, dynamic glenohumeral stability provided by the teres minor and subscapuris decreased significantly when the arm moves from the scapular plane to coronal plane (p<.05). The maximum muscle force may be estimated from the physiological cross-sectional area of each muscle ...
... Notably, in the present study, dynamic glenohumeral stability provided by the teres minor and subscapuris decreased significantly when the arm moves from the scapular plane to coronal plane (p<.05). The maximum muscle force may be estimated from the physiological cross-sectional area of each muscle ...
HEALTH SCIENCES 365
... O. Posterior surface of lateral condyle of humerus I. Posterolateral surface of olecranon process and upper posterior ulna A. _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ N. Radial Pronator Teres O. Medial supracondylar ridge of ...
... O. Posterior surface of lateral condyle of humerus I. Posterolateral surface of olecranon process and upper posterior ulna A. _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ N. Radial Pronator Teres O. Medial supracondylar ridge of ...
skeletal
... The clavicles are slender, doubly curved long bones lying across the superior thorax The acromial (lateral) end articulates with the scapula, and the sternal (medial) end articulates with the sternum They provide attachment points for numerous muscles, and act as braces to hold the scapulae an ...
... The clavicles are slender, doubly curved long bones lying across the superior thorax The acromial (lateral) end articulates with the scapula, and the sternal (medial) end articulates with the sternum They provide attachment points for numerous muscles, and act as braces to hold the scapulae an ...
Pathology Codes - Museum of London
... Vertebrae: There has been fusion across the centra of at least seven consecutive thoracic vertebrae (T3-T9). The fusion is the result of large smoothed vertical osteophytes running along the anterior right aspect of the vertebral bodies, which have a characteristic ‘candlewax’ appearance. The interv ...
... Vertebrae: There has been fusion across the centra of at least seven consecutive thoracic vertebrae (T3-T9). The fusion is the result of large smoothed vertical osteophytes running along the anterior right aspect of the vertebral bodies, which have a characteristic ‘candlewax’ appearance. The interv ...
Building the Muscles of the Chest
... - Pectoralis Minor - Pectoralis Major (three major pieces or “heads” of this muscle) Some of these muscles will be created using spaghetti strands while others will be made with larger balls of clay. Before the lesson, make terra cotta spaghetti strands for the students or have students do the prepa ...
... - Pectoralis Minor - Pectoralis Major (three major pieces or “heads” of this muscle) Some of these muscles will be created using spaghetti strands while others will be made with larger balls of clay. Before the lesson, make terra cotta spaghetti strands for the students or have students do the prepa ...
241Supplement Bones
... (1) Draw a typical long bone and label it with periosteum, diaphysis, articular cartilage, epiphyseal plate, medullary cavity and endosteum. (2) Develop an acronym or ridiculous poem for the bones of the skull. It is easier in groups! (3) Develop an acronym or ridiculous poem for the bones of the up ...
... (1) Draw a typical long bone and label it with periosteum, diaphysis, articular cartilage, epiphyseal plate, medullary cavity and endosteum. (2) Develop an acronym or ridiculous poem for the bones of the skull. It is easier in groups! (3) Develop an acronym or ridiculous poem for the bones of the up ...
241Supplement Bones
... (1) Draw a typical long bone and label it with periosteum, diaphysis, articular cartilage, epiphyseal plate, medullary cavity and endosteum. (2) Develop an acronym or ridiculous poem for the bones of the skull. It is easier in groups! (3) Develop an acronym or ridiculous poem for the bones of the up ...
... (1) Draw a typical long bone and label it with periosteum, diaphysis, articular cartilage, epiphyseal plate, medullary cavity and endosteum. (2) Develop an acronym or ridiculous poem for the bones of the skull. It is easier in groups! (3) Develop an acronym or ridiculous poem for the bones of the up ...
Original Article
... Fig.3: The caudal (anconal) view of the upper arm skeleton of the right wing with M. triceps brachii (left end), and the cranial and caudal views of the proximal humerus. Fig.3: 1: Insertion of M. subscapularis. 2: Insertion of M. coracobrachialis caudalis [M. coracobrachialis posterior]. 3: An acce ...
... Fig.3: The caudal (anconal) view of the upper arm skeleton of the right wing with M. triceps brachii (left end), and the cranial and caudal views of the proximal humerus. Fig.3: 1: Insertion of M. subscapularis. 2: Insertion of M. coracobrachialis caudalis [M. coracobrachialis posterior]. 3: An acce ...
Scapula
In anatomy, the scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas) or shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones the scapulae are paired, with the scapula on the left side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the right scapula. In early Roman times, people thought the bone resembled a trowel, a small shovel. The shoulder blade is also called omo in Latin medical terminology.The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage.