presentation source
... All states of the system generated by: (1 1 )( 2 2 )(3 3 )......( N N ) -->generating function Total number of states: 2N ; N+1 possible values of the total magnetic moment: M=Nm, (N-2)m, (N-4)m, ...-Nm number of states >> possible values of total magnetic moments (if N>>1) if the ...
... All states of the system generated by: (1 1 )( 2 2 )(3 3 )......( N N ) -->generating function Total number of states: 2N ; N+1 possible values of the total magnetic moment: M=Nm, (N-2)m, (N-4)m, ...-Nm number of states >> possible values of total magnetic moments (if N>>1) if the ...
Chemistry I Honors – Semester Exam Review – Fall 2000
... d. Substances containing these bonds do not conduct electricity and have low melting points. e. Compounds containing these bonds have a crystal lattice structure. f. These bonds are formed by sharing electrons. Nuclear Chemistry – Ch. 21 or 22 Match each description with the appropriate type of radi ...
... d. Substances containing these bonds do not conduct electricity and have low melting points. e. Compounds containing these bonds have a crystal lattice structure. f. These bonds are formed by sharing electrons. Nuclear Chemistry – Ch. 21 or 22 Match each description with the appropriate type of radi ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... positive charge (δ+) and the other has a negative charge(δ-), the molecule is polar. (polar covalent bonds) When molecules have a more uniform distribution of charges they are called nonpolar molecules. (nonpolar covalent bonds) ...
... positive charge (δ+) and the other has a negative charge(δ-), the molecule is polar. (polar covalent bonds) When molecules have a more uniform distribution of charges they are called nonpolar molecules. (nonpolar covalent bonds) ...
Atomic Physics - SFSU Physics & Astronomy
... • Lowest energy state = “ground state” • Higher states = “excited states” • Photon energy equals difference in state energies • Hydrogen atom example – Energy levels – Line spectra ...
... • Lowest energy state = “ground state” • Higher states = “excited states” • Photon energy equals difference in state energies • Hydrogen atom example – Energy levels – Line spectra ...
希臘 - 中正大學化生系
... first modern chemist, and therefore one of the founders of modern chemistry, and one of the pioneers of modern experimental scientific method. 2. He endorsed the view of elements as the undecomposable constituents of material bodies; and made the distinction between mixtures and compounds. ...
... first modern chemist, and therefore one of the founders of modern chemistry, and one of the pioneers of modern experimental scientific method. 2. He endorsed the view of elements as the undecomposable constituents of material bodies; and made the distinction between mixtures and compounds. ...
Chemical Principles – by Steven Zumdahl (5 ) Chapter 1
... Solid State: Attractive forces between particles are so strong that individual particles occupy fixed positions which are close together. Liquid State: Attractive forces between particles are strong enough so that individual particles are close to each other, but not fixed in position. Gaseous State ...
... Solid State: Attractive forces between particles are so strong that individual particles occupy fixed positions which are close together. Liquid State: Attractive forces between particles are strong enough so that individual particles are close to each other, but not fixed in position. Gaseous State ...
AP Chemistry 2013 Semester 1 Final Exam Review Problems
... oxalic acid, H2C2O4, to give solid calcium oxalate, CaC2O4, carbon dioxide and water. The mass of the calcium oxalate produced is 472mg. Write a balanced equation for this reaction. What is the mass percentage of calcium carbonate in this limestone? 8. Potassium superoxide, KO2, is employed in a sel ...
... oxalic acid, H2C2O4, to give solid calcium oxalate, CaC2O4, carbon dioxide and water. The mass of the calcium oxalate produced is 472mg. Write a balanced equation for this reaction. What is the mass percentage of calcium carbonate in this limestone? 8. Potassium superoxide, KO2, is employed in a sel ...
atoms
... Ionic bonds • An ion is an atom that has gained or lost an electron. – Ions have a charge due to the unequal number of protons and electrons ...
... Ionic bonds • An ion is an atom that has gained or lost an electron. – Ions have a charge due to the unequal number of protons and electrons ...
投影片 - 中正大學化生系
... first modern chemist, and therefore one of the founders of modern chemistry, and one of the pioneers of modern experimental scientific method. 2. He endorsed the view of elements as the undecomposable constituents of material bodies; and made the distinction between mixtures and compounds. ...
... first modern chemist, and therefore one of the founders of modern chemistry, and one of the pioneers of modern experimental scientific method. 2. He endorsed the view of elements as the undecomposable constituents of material bodies; and made the distinction between mixtures and compounds. ...
Chemistry Vocab for Quiz 12/21 or 12/22 Atom – The smallest
... material but does not make the material into a different substance. Chemical change – A change in matter that produces a new substance. Solution – A well mixed mixture. Solubility – A measure of how well a solute can be dissolved at a given temperature. Solvent – The part of the solution present in ...
... material but does not make the material into a different substance. Chemical change – A change in matter that produces a new substance. Solution – A well mixed mixture. Solubility – A measure of how well a solute can be dissolved at a given temperature. Solvent – The part of the solution present in ...
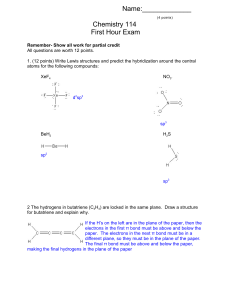
Name:______ Chemistry 114 First Hour Exam
... 3. One of the compounds you have met in the lab is NO gas, the nasty smelling brown gas that can come out of an internal combustion engine and that forms the brown haze of air pollution around big cities. NO uses the same series of molecular orbitals as C2 or N2. Show the occupied and unoccupied mo ...
... 3. One of the compounds you have met in the lab is NO gas, the nasty smelling brown gas that can come out of an internal combustion engine and that forms the brown haze of air pollution around big cities. NO uses the same series of molecular orbitals as C2 or N2. Show the occupied and unoccupied mo ...
cell molecules
... near pH 7. • To maintain cellular pH values at a constant level, biological fluids have buffers. • Buffers resist changes to the pH of a solution when H+ or OH- is added to the solution. – Buffers accept hydrogen ions from the solution when they are in excess and donate hydrogen ions when they have ...
... near pH 7. • To maintain cellular pH values at a constant level, biological fluids have buffers. • Buffers resist changes to the pH of a solution when H+ or OH- is added to the solution. – Buffers accept hydrogen ions from the solution when they are in excess and donate hydrogen ions when they have ...
Chapter 8 Study Guide
... 2. What was Dalton’s 5 part atomic theory of matter and his model of the atom? a. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms, which cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. b. Atoms of a given element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. c. Atoms of diff ...
... 2. What was Dalton’s 5 part atomic theory of matter and his model of the atom? a. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms, which cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. b. Atoms of a given element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. c. Atoms of diff ...
Atomic Structure Study Guide
... Philosophers have hypothesized that matter was made up of tiny particles called ______ since the times of _____________________. However, these speculations were not scientific theories, because they were not based on any experimental ____________. The first scientific theory of atoms was developed ...
... Philosophers have hypothesized that matter was made up of tiny particles called ______ since the times of _____________________. However, these speculations were not scientific theories, because they were not based on any experimental ____________. The first scientific theory of atoms was developed ...
Atomic Theory - WaylandHighSchoolChemistry
... Schrödinger and Heisenberg, and many, many more. Used their brains to venture in the realm of inner space and found the world of the atom was a weird and wondrous place. ...
... Schrödinger and Heisenberg, and many, many more. Used their brains to venture in the realm of inner space and found the world of the atom was a weird and wondrous place. ...
Basic Atomic Theory
... • The energy of the orbiting electrons as depicted in Bohr model is restricted to certain discrete values. • The energy is therefore “quantized” – Only certain orbits with certain radii are possible – Orbits in between discrete value not possible ...
... • The energy of the orbiting electrons as depicted in Bohr model is restricted to certain discrete values. • The energy is therefore “quantized” – Only certain orbits with certain radii are possible – Orbits in between discrete value not possible ...
Chapter 2 Study Guides
... 7. Before a chemical reaction can start, ____________________ must be absorbed by the reactants. The amount that must be absorbed to start the reaction is called the ...
... 7. Before a chemical reaction can start, ____________________ must be absorbed by the reactants. The amount that must be absorbed to start the reaction is called the ...
Chapter 7, 8, and 9 Exam 2014 Name I. 50% of your grade will come
... Select the one lettered choice that best fits each statement and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, more than once, or not at all in each set. Questions 1–4 refer to the following types of energy. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) ...
... Select the one lettered choice that best fits each statement and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, more than once, or not at all in each set. Questions 1–4 refer to the following types of energy. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) ...
Elements, mixtures and compounds lecture
... A. exists as only one type of atom: it is, therefore a pure substance (This does not often occur in nature); gold necklace? Oxygen is the most common pure element on Earth (occurs as a dioxide: O2 , what does “di” mean?) B. cannot be broken down by chemical reactions: burning/acids/eating (but nucle ...
... A. exists as only one type of atom: it is, therefore a pure substance (This does not often occur in nature); gold necklace? Oxygen is the most common pure element on Earth (occurs as a dioxide: O2 , what does “di” mean?) B. cannot be broken down by chemical reactions: burning/acids/eating (but nucle ...
Matter and Energy
... always degraded to lower-quality, more dispersed (higher entropy), less-useful energy. Entropy is a measure of disorder. Therefore, it is always increasing. “Entropy always wins.” 3rd Law – The entropy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero is exactly equal to zero. Zeroth Law – if two systems are bo ...
... always degraded to lower-quality, more dispersed (higher entropy), less-useful energy. Entropy is a measure of disorder. Therefore, it is always increasing. “Entropy always wins.” 3rd Law – The entropy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero is exactly equal to zero. Zeroth Law – if two systems are bo ...
Chemistry of life
... • Many of our everyday experiences depend upon chemistry. – For example: Making kool aid or sweet tea. ...
... • Many of our everyday experiences depend upon chemistry. – For example: Making kool aid or sweet tea. ...
3rd of September, 2008 1. A suspension of tiny charged particles in
... Find the electric potential around a colloidal particle! Consider the concentration of positive and negative ions to be the same n 0 far away from the particle. You will need the formula for the Boltzmann-distribution: particles in a potential are distributed in such a way that the number of particl ...
... Find the electric potential around a colloidal particle! Consider the concentration of positive and negative ions to be the same n 0 far away from the particle. You will need the formula for the Boltzmann-distribution: particles in a potential are distributed in such a way that the number of particl ...
Bonding Challenge
... C2 Cl3F3, C2HCl, C2F3Cl 4) Put the following in order of increasing C-C bond strength: C2 Cl3F3, C2HCl, C2F3Cl 5) Using principles of chemical bonding and molecular geometry explain each of the following observations. Lewis electron-dot diagrams and sketches of molecules may be helpful as part of yo ...
... C2 Cl3F3, C2HCl, C2F3Cl 4) Put the following in order of increasing C-C bond strength: C2 Cl3F3, C2HCl, C2F3Cl 5) Using principles of chemical bonding and molecular geometry explain each of the following observations. Lewis electron-dot diagrams and sketches of molecules may be helpful as part of yo ...