The Very Basics of Geometric Optics 5.1.2 Basic Geometric Optics
... The NA for a single lens is roughly the quotient of (possibly aperture defined) diameter / focal length; i.e. a crude measure of the size of the lens; see the picture below. Of course, lenses with small NA will not suffer much from spherical aberration but will also not transmit much light and thus ...
... The NA for a single lens is roughly the quotient of (possibly aperture defined) diameter / focal length; i.e. a crude measure of the size of the lens; see the picture below. Of course, lenses with small NA will not suffer much from spherical aberration but will also not transmit much light and thus ...
Fluoroscopic Unit (Bushong, chapter 21)
... Explain multifield image intensification. How does vigneting occur? b. Multifield Image Intensification: flexibility w/fluoro; standard w/digital fluoro. dual-focus: diameter of input phosphor of II tube = 25 cm/17cm trifocus: diameter of input phosphor of II tube = 25/17/12 or 23/15/10. @ 2 ...
... Explain multifield image intensification. How does vigneting occur? b. Multifield Image Intensification: flexibility w/fluoro; standard w/digital fluoro. dual-focus: diameter of input phosphor of II tube = 25 cm/17cm trifocus: diameter of input phosphor of II tube = 25/17/12 or 23/15/10. @ 2 ...
PPT - Tensors for Tots
... Dispersion and Refraction Prisms display the phenomena called dispersion by separating white light into components of different wavelength (different colors). The different colors refract at different angles, splitting white light into a rainbow. When light passes through a prism, it is refracted t ...
... Dispersion and Refraction Prisms display the phenomena called dispersion by separating white light into components of different wavelength (different colors). The different colors refract at different angles, splitting white light into a rainbow. When light passes through a prism, it is refracted t ...
ultra bright and compact
... The LV-S3 projector has the “Genuine Canon Optics” delivers quality image. In addition, LV-S3 can replicate progressive scan quality with interlaced video signals (480i, 480p, 575i, 575p, 720p, 1035i and 1080i) “Progressive scanning” draws the entire frame continuously from top to the bottom that gr ...
... The LV-S3 projector has the “Genuine Canon Optics” delivers quality image. In addition, LV-S3 can replicate progressive scan quality with interlaced video signals (480i, 480p, 575i, 575p, 720p, 1035i and 1080i) “Progressive scanning” draws the entire frame continuously from top to the bottom that gr ...
Prof. Lan Yang - Microlasers for Nanoscale
... for ultra-sensitive self-referencing detection and sizing of single virion, dielectric and metallic nanoparticles. I will also discuss using optical gains in a microlaser to improve the detection limit beyond the reach of a passive microresonator. These recent advancements in WGM microresonators wil ...
... for ultra-sensitive self-referencing detection and sizing of single virion, dielectric and metallic nanoparticles. I will also discuss using optical gains in a microlaser to improve the detection limit beyond the reach of a passive microresonator. These recent advancements in WGM microresonators wil ...
2 s -1 PAR - The University of Maine In
... Phototropism is plant growth towards a light source. Photomorphogenesis is the light-induced control of plant growth and differentiation. Certain wave lengths function as a signal causing the generation of an information within the cell that is used for the selective activation of certain genes. Pho ...
... Phototropism is plant growth towards a light source. Photomorphogenesis is the light-induced control of plant growth and differentiation. Certain wave lengths function as a signal causing the generation of an information within the cell that is used for the selective activation of certain genes. Pho ...
CT_optics
... A group of sprinters gather at point P on a parking lot bordering a beach. They must run across the parking lot to a point Q on the beach as quickly as possible. Which path from P to Q takes the least time? You should consider the relative speeds of the sprinters on the hard surface of the parking ...
... A group of sprinters gather at point P on a parking lot bordering a beach. They must run across the parking lot to a point Q on the beach as quickly as possible. Which path from P to Q takes the least time? You should consider the relative speeds of the sprinters on the hard surface of the parking ...
The long march of slow photonics
... for readers the issues that must be taken into account when comparing the performance of slow-light devices. Too often the group velocity reduction (that is, the slow-down factor) is assumed to be the most important criterion, but using this alone can drive non-specialists to misleading conclusions. ...
... for readers the issues that must be taken into account when comparing the performance of slow-light devices. Too often the group velocity reduction (that is, the slow-down factor) is assumed to be the most important criterion, but using this alone can drive non-specialists to misleading conclusions. ...
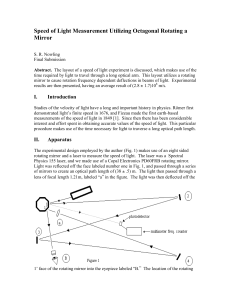
Speed of Light Measurement Utilizing Octagonal
... lens ÒaÓ was the most important factor in the entire experiment. If the lens was placed after the rotating mirror no shifts will ever be seen. This is because the shifts are so small that they are well within the paraxial approximation. The lens therefore sends all of the ÒparallelÓ rays to the sam ...
... lens ÒaÓ was the most important factor in the entire experiment. If the lens was placed after the rotating mirror no shifts will ever be seen. This is because the shifts are so small that they are well within the paraxial approximation. The lens therefore sends all of the ÒparallelÓ rays to the sam ...
Minerals and Their Physical Properties
... The speed of light in a vacuum is always faster than in any other medium so all RI values are >1 ...
... The speed of light in a vacuum is always faster than in any other medium so all RI values are >1 ...
Minerals and Their Physical Properties
... The speed of light in a vacuum is always faster than in any other medium so all RI values are >1 ...
... The speed of light in a vacuum is always faster than in any other medium so all RI values are >1 ...
optics(conceptuals)
... What is the phase difference between two particles on a wavefront? (i) A plane wavefront is incident normally on a convex lens. Draw the refracted wavefront. (ii) Draw the wavefronts emerging out of a convex lens when a point source of light is placed at its focus. Sketch the variation of intensity ...
... What is the phase difference between two particles on a wavefront? (i) A plane wavefront is incident normally on a convex lens. Draw the refracted wavefront. (ii) Draw the wavefronts emerging out of a convex lens when a point source of light is placed at its focus. Sketch the variation of intensity ...
Paraxial Formulas - CVI Laser Optics
... determine paraxial image location and magnification. This graphical approach relies on two simple properties of an optical system. First, a ray that enters the system parallel to the optical axis crosses the optical axis at the focal point. Second, a ray that enters the first principal point of the ...
... determine paraxial image location and magnification. This graphical approach relies on two simple properties of an optical system. First, a ray that enters the system parallel to the optical axis crosses the optical axis at the focal point. Second, a ray that enters the first principal point of the ...
Optics-Optical Instruments_ppt_RevW10
... objective mirror. The first real image is then viewed with a second short focal length (high diopter power) eyepiece lens • The first real image is brought to the side by means of a small flat mirror so that the eyepiece and observer can be out of the way of the incoming light ...
... objective mirror. The first real image is then viewed with a second short focal length (high diopter power) eyepiece lens • The first real image is brought to the side by means of a small flat mirror so that the eyepiece and observer can be out of the way of the incoming light ...
mirrors and lenses - Appoquinimink High School
... where the index of refraction is less (water into air for example), the light bends away from the normal. At a particular incident angle, the angle of refraction will be 90 degrees. This is called the critical angle. ...
... where the index of refraction is less (water into air for example), the light bends away from the normal. At a particular incident angle, the angle of refraction will be 90 degrees. This is called the critical angle. ...
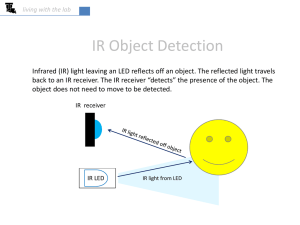
living with the lab
... Install an LED Shield It is important to install the LED in an enclosure to properly direct the IR light. Your kit includes the black pieces shown. Insert the legs of the LED through the holes in the longer black cylinder, and then install the smaller top piece over the exposed end of the LED. If yo ...
... Install an LED Shield It is important to install the LED in an enclosure to properly direct the IR light. Your kit includes the black pieces shown. Insert the legs of the LED through the holes in the longer black cylinder, and then install the smaller top piece over the exposed end of the LED. If yo ...
Light microscopy
... 2. Insert the eyepiece graticule (transparent disc with accurately spaced marks) in the eyepiece. Screw the top lens back in place and replace the eyepiece. ...
... 2. Insert the eyepiece graticule (transparent disc with accurately spaced marks) in the eyepiece. Screw the top lens back in place and replace the eyepiece. ...
Part 1
... You use a lens with a focal length of +5 cm as a magnifying glass to look at a 1 cm-long bug. (a) How far is the lens from the bug if you get the maximum useful angular mag? (b) What is the maximum useful mag? (c) What is the lateral mag? (d) How long does the bug look to you? Suppose you now move t ...
... You use a lens with a focal length of +5 cm as a magnifying glass to look at a 1 cm-long bug. (a) How far is the lens from the bug if you get the maximum useful angular mag? (b) What is the maximum useful mag? (c) What is the lateral mag? (d) How long does the bug look to you? Suppose you now move t ...
Chapter 19 Reading Quiz
... the focal length of the objective lens is increased. the focal length of the objective lens is decreased. the focal length of the eyepiece is increased. the distance between the objective lens and eyepiece is decreased. ...
... the focal length of the objective lens is increased. the focal length of the objective lens is decreased. the focal length of the eyepiece is increased. the distance between the objective lens and eyepiece is decreased. ...
Diffraction-of-light
... In the atmosphere, diffracted light is actually bent around atmospheric particles—most commonly, the atmospheric particles are tiny water droplets found in clouds. Diffracted light can produce fringes of light, dark or colored bands.. The illustration above shows how light (from either the sun or t ...
... In the atmosphere, diffracted light is actually bent around atmospheric particles—most commonly, the atmospheric particles are tiny water droplets found in clouds. Diffracted light can produce fringes of light, dark or colored bands.. The illustration above shows how light (from either the sun or t ...
Semiconductor Devices
... the NDR region to produce a Gunn-domain. Once a domain has formed, the electric field in the rest of the sample falls below the NDR region and will therefore inhibit the formation of a second Gunn-domain. As soon as the domain is absorbed by the anode contact region, the average electric field in th ...
... the NDR region to produce a Gunn-domain. Once a domain has formed, the electric field in the rest of the sample falls below the NDR region and will therefore inhibit the formation of a second Gunn-domain. As soon as the domain is absorbed by the anode contact region, the average electric field in th ...
Optics - Tensors for Tots
... Dispersion and Refraction Prisms display the phenomena called dispersion by separating white light into components of different wavelength (different colors). The different colors refract at different angles, splitting white light into a rainbow. When light passes through a prism, it is refracted t ...
... Dispersion and Refraction Prisms display the phenomena called dispersion by separating white light into components of different wavelength (different colors). The different colors refract at different angles, splitting white light into a rainbow. When light passes through a prism, it is refracted t ...
Document
... and the much higher potential processing speed - under current technology, a tenfold increase in processing power would not be justified by the size of the 'chip'. Such a chip would be constrained by the speed of numerous electronic interfaces and controllers but, if these could be removed, the pote ...
... and the much higher potential processing speed - under current technology, a tenfold increase in processing power would not be justified by the size of the 'chip'. Such a chip would be constrained by the speed of numerous electronic interfaces and controllers but, if these could be removed, the pote ...
Parts of the Microscope and Their Function
... Ocular Holds the objective lenses and can turn to change the objective lens in use. Revolving nosepiece Low power objective lens. High power objective lens. ...
... Ocular Holds the objective lenses and can turn to change the objective lens in use. Revolving nosepiece Low power objective lens. High power objective lens. ...
Night vision device

A night vision device (NVD) is an optoelectronic device that allows images to be produced in levels of light approaching total darkness. The image may be a conversion to visible light of both visible light and near-infrared, while by convention detection of thermal infrared is denoted thermal imaging. The image produced is typically monochrome, e.g. shades of green. NVDs are most often used by the military and law enforcement agencies, but are available to civilian users. The term usually refers to a complete unit, including an image intensifier tube, a protective and generally water-resistant housing, and some type of mounting system. Many NVDs also include optical components such as a sacrificial lens, or telescopic lenses or mirrors. An NVD may have an IR illuminator, making it an active as opposed to passive night vision device.Night vision devices were first used in World War II, and came into wide use during the Vietnam War. The technology has evolved greatly since their introduction, leading to several ""generations"" of night vision equipment with performance increasing and price decreasing. Consequently, they are available for a wide range of applications, e.g. for gunners, drivers and aviators. Another term is ""night optical/observation device"" or NOD.