Word - TYC Physics Workshop Project
... Our intrepid hunter was asked by the instructor to point his pencil-spear directly at the image of Frederica that he saw. Everyone observed that the pencil was pointing well above and past the actual location of the fish, as viewed from the side. Does your ray diagram demonstrate this fact? If not, ...
... Our intrepid hunter was asked by the instructor to point his pencil-spear directly at the image of Frederica that he saw. Everyone observed that the pencil was pointing well above and past the actual location of the fish, as viewed from the side. Does your ray diagram demonstrate this fact? If not, ...
3. How to - TYC Physics Workshop Project
... Our intrepid hunter was asked by the instructor to point his pencil-spear directly at the image of Frederica that he saw. Everyone observed that the pencil was pointing well above and past the actual location of the fish, as viewed from the side. Does your ray diagram demonstrate this fact? If not, ...
... Our intrepid hunter was asked by the instructor to point his pencil-spear directly at the image of Frederica that he saw. Everyone observed that the pencil was pointing well above and past the actual location of the fish, as viewed from the side. Does your ray diagram demonstrate this fact? If not, ...
Physics Tute Sheet-6 - College of Engineering Roorkee
... 5. Calculate the thickness of a calcite plate which would convert plane polarized light into elliptically polarized light. The principal refractive indices are μo= 1.66 and μe=1.49 for the wavelength 5890A. Ans. 8.66x10-5cm & its odd multiple. 6. Calculate the thickness of a doubly refracting crysta ...
... 5. Calculate the thickness of a calcite plate which would convert plane polarized light into elliptically polarized light. The principal refractive indices are μo= 1.66 and μe=1.49 for the wavelength 5890A. Ans. 8.66x10-5cm & its odd multiple. 6. Calculate the thickness of a doubly refracting crysta ...
An Optical ‘‘Janus’’ Device for Integrated Photonics By Xiang Zhang*
... loss and reflection from the device boundary, the overall functionality is preserved. In addition to the hole pattern for the metadevice, four grating couplers are fabricated where a typical geometry for the total structure is shown as an scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image in Figure 2c. The gr ...
... loss and reflection from the device boundary, the overall functionality is preserved. In addition to the hole pattern for the metadevice, four grating couplers are fabricated where a typical geometry for the total structure is shown as an scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image in Figure 2c. The gr ...
Geometric optics
... • It is difficult at Swarthmore to begin the laboratories the first week of class due to our system for registering students for classes, so our labs generally cover material after it has been discussed in class. Putting optics at the beginning of the semester therefore allows us to offer more optic ...
... • It is difficult at Swarthmore to begin the laboratories the first week of class due to our system for registering students for classes, so our labs generally cover material after it has been discussed in class. Putting optics at the beginning of the semester therefore allows us to offer more optic ...
General Physical Science
... Muscles in the eye change the thickness of the lens so we can focus on objects at different distances. ...
... Muscles in the eye change the thickness of the lens so we can focus on objects at different distances. ...
7.8 Polarized light - one more excursion into optics 7.8.1 The
... through half of the plate, i. e. through the equivalent of a λ/4 plate, the beam will be elliptically polarised, as indicated in the middle of the figure. The total phase shift after passage through the λ/2 plate is π, i. e. the electric vector along the slow axis is reversed with respect to the fa ...
... through half of the plate, i. e. through the equivalent of a λ/4 plate, the beam will be elliptically polarised, as indicated in the middle of the figure. The total phase shift after passage through the λ/2 plate is π, i. e. the electric vector along the slow axis is reversed with respect to the fa ...
9-26 Geometrical Optics
... Fermat’s principle can be used to derive the shape of a boundary that images light from one side of the boundary to another. This shape is a cartesian oval and is used for aspheric lenses Spherical lenses can well approximate the ideal shape of an aspherical lens for paraxial beams and are usually m ...
... Fermat’s principle can be used to derive the shape of a boundary that images light from one side of the boundary to another. This shape is a cartesian oval and is used for aspheric lenses Spherical lenses can well approximate the ideal shape of an aspherical lens for paraxial beams and are usually m ...
Transient Voltage Surge Suppression Design
... • Output V slightly higher than other MOVs • Handles more energy • Ringing less due to transorb ...
... • Output V slightly higher than other MOVs • Handles more energy • Ringing less due to transorb ...
N15_Geom_Optics - University of Arizona
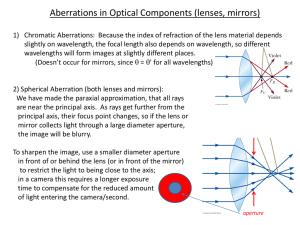
... prisms, blue light bends more than red light. So the same effect must happen in lenses—where one assumes that ray paths are independent of color. The first picture below shows how lenses will have slightly different focal lengths for different colors. This effect is called “chromatic aberration” and ...
... prisms, blue light bends more than red light. So the same effect must happen in lenses—where one assumes that ray paths are independent of color. The first picture below shows how lenses will have slightly different focal lengths for different colors. This effect is called “chromatic aberration” and ...
Adiabatic far-field sub-diffraction imaging ARTICLE Hu Cang *, Alessandro Salandrino
... lthough a tsunami is devastating near land, it is barely noticeable in the open ocean. This is because the sea floor near the land slows down the tsunami, compressing its wavelength from hundreds of kilometres1 to metres and rapidly increasing its amplitude to be destructive. Recently, a similar opti ...
... lthough a tsunami is devastating near land, it is barely noticeable in the open ocean. This is because the sea floor near the land slows down the tsunami, compressing its wavelength from hundreds of kilometres1 to metres and rapidly increasing its amplitude to be destructive. Recently, a similar opti ...
CT_dc_circuits
... ISBN 0-13-565441-6 No portion of the file may be distributed, transmitted in any form, or included in other documents without express written permission from the publisher. ...
... ISBN 0-13-565441-6 No portion of the file may be distributed, transmitted in any form, or included in other documents without express written permission from the publisher. ...
Digital X-Ray Imaging - Experimental Elementary Particle Physics
... material, caused by the presence of the dopant. Such traps are metastable so that a latent image is built up consisting of electrons trapped at the F-centres. Once the exposure is complete, the plate is stimulated by irradiating with laser light of the right frequency. This frees the electrons from ...
... material, caused by the presence of the dopant. Such traps are metastable so that a latent image is built up consisting of electrons trapped at the F-centres. Once the exposure is complete, the plate is stimulated by irradiating with laser light of the right frequency. This frees the electrons from ...
February 6 pptx
... on the CCD/film as long as the image distance p >> f. (i.e. 1/q = 1/f – 1/p 1/f if p >> f) (In the limit, D 0, you don’t even need a lens: the camera is a pin-hole camera: only “one ray” from each point on the object reaches the CCD/film. These are sometimes used for surveillance, because difficu ...
... on the CCD/film as long as the image distance p >> f. (i.e. 1/q = 1/f – 1/p 1/f if p >> f) (In the limit, D 0, you don’t even need a lens: the camera is a pin-hole camera: only “one ray” from each point on the object reaches the CCD/film. These are sometimes used for surveillance, because difficu ...
Images in Lenses
... other parts of the illustration. Ask students questions such as, Is this incident ray parallel or angled? Where is the light source now? What happens when it emerges and why? • As you work through the illustrations with students, ask them to note the size of the image, its attitude or orientation, a ...
... other parts of the illustration. Ask students questions such as, Is this incident ray parallel or angled? Where is the light source now? What happens when it emerges and why? • As you work through the illustrations with students, ask them to note the size of the image, its attitude or orientation, a ...
LED Characteristic Measurement Methods
... calculate the thermal resistance, which normally gives the characteristics shown in Figure 8. ...
... calculate the thermal resistance, which normally gives the characteristics shown in Figure 8. ...
LM Ch 4: Optics
... The curved surface of a lens affects how much a ray of light will be deflected. This is called refraction. For example take two parallel rays of light, one hitting the center of the lens normal to the lens surface and the other hitting the edge of the lens. The center ray will not be refracted by th ...
... The curved surface of a lens affects how much a ray of light will be deflected. This is called refraction. For example take two parallel rays of light, one hitting the center of the lens normal to the lens surface and the other hitting the edge of the lens. The center ray will not be refracted by th ...
Intense switchable fluorescence in light wave coupled electrowetting
... then propagates within the waveguide 共nsp ⬃ 1.46兲 via internal reflection. Violet light also propagates in all layers contacting the waveguide that have refractive indices greater than or equal that of the waveguide. Layers meeting this criteria for propagation include the ITO electrode 共n ⬇ 1.95兲, ...
... then propagates within the waveguide 共nsp ⬃ 1.46兲 via internal reflection. Violet light also propagates in all layers contacting the waveguide that have refractive indices greater than or equal that of the waveguide. Layers meeting this criteria for propagation include the ITO electrode 共n ⬇ 1.95兲, ...
Convolution in Imaging and the Optical Transfer Function Process
... found from different image compressions using a simple line gradient transfer. Since we don’t have a sophisticated camera to work with – fortunately blur effects can be emulated in programs like Photoshop. Begin by going to this link and downloading the packet: http://voltagemoon.com/opticsfiles/opt ...
... found from different image compressions using a simple line gradient transfer. Since we don’t have a sophisticated camera to work with – fortunately blur effects can be emulated in programs like Photoshop. Begin by going to this link and downloading the packet: http://voltagemoon.com/opticsfiles/opt ...
Slide 1
... Sensors that switch two phase power (208/480) also available Remotely configurable and upgradeable ...
... Sensors that switch two phase power (208/480) also available Remotely configurable and upgradeable ...
Wire Resistance and Ohm`s Law
... Light 1: ________________ Volts Light 2: ________________ Volts Light 3: ________________ Volts Battery: ________________ Volts ...
... Light 1: ________________ Volts Light 2: ________________ Volts Light 3: ________________ Volts Battery: ________________ Volts ...
Worksheets for Unit 4 Light and Matter
... to narrowest. The effect is best when your eye in along the principal axis of the apparatus and you hold the slide directly in-front of the iris of your eye. 4. Observe the optical pattern and the changes in the pattern as the blue light is systematically passed through widest to narrowest of slits. ...
... to narrowest. The effect is best when your eye in along the principal axis of the apparatus and you hold the slide directly in-front of the iris of your eye. 4. Observe the optical pattern and the changes in the pattern as the blue light is systematically passed through widest to narrowest of slits. ...
physics
... formed at the least distance of distinct vision. 7. State and prove Prism Formula. 8. A ray of light falls normally on a refracting face of a prism of refractive index (1.5) . Find the angle of the prism if the ray just fails to emerge from the prism. 9. A diver looks into the external worlds from a ...
... formed at the least distance of distinct vision. 7. State and prove Prism Formula. 8. A ray of light falls normally on a refracting face of a prism of refractive index (1.5) . Find the angle of the prism if the ray just fails to emerge from the prism. 9. A diver looks into the external worlds from a ...
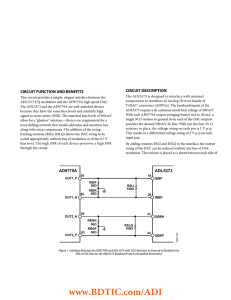
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... (Continued from first page) "Circuits from the Lab" are intended only for use with Analog Devices products and are the intellectual property of Analog Devices or its licensors. While you may use the "Circuits from the Lab" in the design of your product, no other license is granted by implication or ...
... (Continued from first page) "Circuits from the Lab" are intended only for use with Analog Devices products and are the intellectual property of Analog Devices or its licensors. While you may use the "Circuits from the Lab" in the design of your product, no other license is granted by implication or ...
Night vision device

A night vision device (NVD) is an optoelectronic device that allows images to be produced in levels of light approaching total darkness. The image may be a conversion to visible light of both visible light and near-infrared, while by convention detection of thermal infrared is denoted thermal imaging. The image produced is typically monochrome, e.g. shades of green. NVDs are most often used by the military and law enforcement agencies, but are available to civilian users. The term usually refers to a complete unit, including an image intensifier tube, a protective and generally water-resistant housing, and some type of mounting system. Many NVDs also include optical components such as a sacrificial lens, or telescopic lenses or mirrors. An NVD may have an IR illuminator, making it an active as opposed to passive night vision device.Night vision devices were first used in World War II, and came into wide use during the Vietnam War. The technology has evolved greatly since their introduction, leading to several ""generations"" of night vision equipment with performance increasing and price decreasing. Consequently, they are available for a wide range of applications, e.g. for gunners, drivers and aviators. Another term is ""night optical/observation device"" or NOD.