Chapter 13 Radioactive Decay
... defining the activity, A(t), and its initial value, A0 . Activity is usually what is measured, since N0 and N(t) are usually unknown, nor of particular interest in many applications. What is generally of real interest is the activity of a source, and, consequently, the ability of the radiation from ...
... defining the activity, A(t), and its initial value, A0 . Activity is usually what is measured, since N0 and N(t) are usually unknown, nor of particular interest in many applications. What is generally of real interest is the activity of a source, and, consequently, the ability of the radiation from ...
Electronic structure, plane waves and pseudopotentials
... Compared to electrons, nuclei are massive and slow. This has two consequences: Whenever a nucleus moves, the electrons react so quickly that it may as well be instant. The wavefunctions for the nuclei are zero except in a very small region – we may as well forget the wavefunction and just say ‘there ...
... Compared to electrons, nuclei are massive and slow. This has two consequences: Whenever a nucleus moves, the electrons react so quickly that it may as well be instant. The wavefunctions for the nuclei are zero except in a very small region – we may as well forget the wavefunction and just say ‘there ...
Dephasing of electrons in mesoscopic metal wires * F. Pierre, A. B. Gougam,
... phase coherence time tends to saturate at low temperature, typically below 0.5 K, in apparent contradiction with theoretical predictions. That same year, measurements of the energy exchange rate between electrons in copper wires8 were found to be at odds, both qualitatively and quantitatively, with ...
... phase coherence time tends to saturate at low temperature, typically below 0.5 K, in apparent contradiction with theoretical predictions. That same year, measurements of the energy exchange rate between electrons in copper wires8 were found to be at odds, both qualitatively and quantitatively, with ...
From a few to many electrons in quantum dots under strong
... strongly deviates from the rigid classical value, a fact that endows the REM with supersolidlike characteristics 共in the sense of the appearance of a nonclassical rotational inertia, but without implying the presence of a superfluid component兲. Furthermore, the REM at high B can be naturally viewed ...
... strongly deviates from the rigid classical value, a fact that endows the REM with supersolidlike characteristics 共in the sense of the appearance of a nonclassical rotational inertia, but without implying the presence of a superfluid component兲. Furthermore, the REM at high B can be naturally viewed ...
No Slide Title
... moles to obtain the simplest whole number ratio. 4. If whole numbers are not obtained* in step 3), multiply through by the smallest number that will give all whole numbers ...
... moles to obtain the simplest whole number ratio. 4. If whole numbers are not obtained* in step 3), multiply through by the smallest number that will give all whole numbers ...
Document
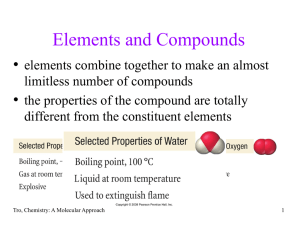
... Balance O by adding H2O: H2O(l) + SO32-(aq) → SO42-(aq) + 2 e-(aq) 5 e-(aq) +MnO4-(aq) → Mn2+(aq) + 4 H2O(l) Balance hydrogen by adding H+: H2O(l) + SO32-(aq) → SO42-(aq) + 2 e-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) 8 H+(aq) + 5 e-(aq) +MnO4-(aq) → Mn2+(aq) + 4 H2O(l) ...
... Balance O by adding H2O: H2O(l) + SO32-(aq) → SO42-(aq) + 2 e-(aq) 5 e-(aq) +MnO4-(aq) → Mn2+(aq) + 4 H2O(l) Balance hydrogen by adding H+: H2O(l) + SO32-(aq) → SO42-(aq) + 2 e-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) 8 H+(aq) + 5 e-(aq) +MnO4-(aq) → Mn2+(aq) + 4 H2O(l) ...
Water deuteration and ortho-to-para nuclear spin ratio of H2 in
... To simulate the formation and physical evolution of a molecular cloud, we use the one-dimensional shock model developed by B04 and H10. Here we briefly outline the model, while more details can be found in the original papers. The model describes the evolution of post-shock materials in a plane-para ...
... To simulate the formation and physical evolution of a molecular cloud, we use the one-dimensional shock model developed by B04 and H10. Here we briefly outline the model, while more details can be found in the original papers. The model describes the evolution of post-shock materials in a plane-para ...
Performance of Many–Body Perturbation Theory
... From this they got sharp current peaks indicating electron tunneling events. These peaks were not equidistant indicating that the energy it costs to inject an electron into the dot (chemical potential) varies with the particle number. Through this procedure they for the first time experimentally sho ...
... From this they got sharp current peaks indicating electron tunneling events. These peaks were not equidistant indicating that the energy it costs to inject an electron into the dot (chemical potential) varies with the particle number. Through this procedure they for the first time experimentally sho ...
chem 13 news 2010 - University of Waterloo
... 10 Which of the following will react appreciably with water at room temperature and pressure to produce hydrogen? ...
... 10 Which of the following will react appreciably with water at room temperature and pressure to produce hydrogen? ...
1994 AP Chemistry Multiple Choice
... 38. Concentrations of colored substances are commonly measured by means of a spectrophotometer. Which of the following would ensure that correct values are obtained for the measured absorbance? I. There must be enough sample in the tube to cover the entire light path. II. The instrument must be peri ...
... 38. Concentrations of colored substances are commonly measured by means of a spectrophotometer. Which of the following would ensure that correct values are obtained for the measured absorbance? I. There must be enough sample in the tube to cover the entire light path. II. The instrument must be peri ...
Electron-scattering cross sections for 1
... collisions. Cross sections for electron impact ionization (ICS) have been calculated for energies ranging from the ionization threshold at 9.274 up to 3000 eV. Having in hand the total ECS and the ICS over a wide energy range, we can predict approximate values of the TCS even far beyond the range of ...
... collisions. Cross sections for electron impact ionization (ICS) have been calculated for energies ranging from the ionization threshold at 9.274 up to 3000 eV. Having in hand the total ECS and the ICS over a wide energy range, we can predict approximate values of the TCS even far beyond the range of ...
Syllabys for BSc(Major):
... Unit I: Quantum Theory of Atoms (No. of Lectures: 15) (Marks: 24) Background of Quantum Theory: Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom, origin of spectral lines, Bohr’s correspondence principle, Sommerfeld’s atom model, designation of spectral term symbol. Vector atom model, space quantization, Larmor pr ...
... Unit I: Quantum Theory of Atoms (No. of Lectures: 15) (Marks: 24) Background of Quantum Theory: Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom, origin of spectral lines, Bohr’s correspondence principle, Sommerfeld’s atom model, designation of spectral term symbol. Vector atom model, space quantization, Larmor pr ...
Everything Science Grade 11
... Physical sciences is far more wonderful, exciting and beautiful than magic! It is everywhere. See introductory video by Dr. Mark Horner: ...
... Physical sciences is far more wonderful, exciting and beautiful than magic! It is everywhere. See introductory video by Dr. Mark Horner: ...
Can the Wave Function in Configuration Space Be Replaced by
... pilot-wave theory: in the terminology of Allori, Goldstein, Tumulka and Zanghı̀ (2013), for example, it is not part of the primitive ontology of the theory. But it is still there. Bell for example stressed that (compared to some other interpretations in which the role of the wave function is perhaps ...
... pilot-wave theory: in the terminology of Allori, Goldstein, Tumulka and Zanghı̀ (2013), for example, it is not part of the primitive ontology of the theory. But it is still there. Bell for example stressed that (compared to some other interpretations in which the role of the wave function is perhaps ...
Worked solutions to textbook questions 1 Chapter 14 From organic
... b nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy c mass spectroscopy Heinemann Chemistry 2 (4th edition) Copyright © Pearson Education Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) 2007 ...
... b nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy c mass spectroscopy Heinemann Chemistry 2 (4th edition) Copyright © Pearson Education Australia (a division of Pearson Australia Group Pty Ltd) 2007 ...
Coupling ultracold atoms to mechanical oscillators
... Alternatively, one can increase the effective mass of the atoms by using a large number of them. Such collective enhancement is a promising route to achieve strong coupling mediated by an optical lattice (Sec. 5). For the perspective of creating a coupled quantum system where the mechanical oscillat ...
... Alternatively, one can increase the effective mass of the atoms by using a large number of them. Such collective enhancement is a promising route to achieve strong coupling mediated by an optical lattice (Sec. 5). For the perspective of creating a coupled quantum system where the mechanical oscillat ...
Dissociation energy of the water dimer from Quantum Monte Carlo
... The usual B3LYP functional corresponds to A = 0.2, B = 0.9 and C = 0.81. In principle we could try and minimize the DMC energy with respect to A, B and C, but this would be very expensive. Setting A = 1 in Eq. (8), we have obtained a DMC energy for the water molecule of −76.4218(1) Ha [44], which is ...
... The usual B3LYP functional corresponds to A = 0.2, B = 0.9 and C = 0.81. In principle we could try and minimize the DMC energy with respect to A, B and C, but this would be very expensive. Setting A = 1 in Eq. (8), we have obtained a DMC energy for the water molecule of −76.4218(1) Ha [44], which is ...
FES Question Bank
... Name the characteristics of something (a happening, object, method or subject). Give a concise description of the subject. Give a complete description of the subject. Write down names, facts, items, advantages and/or disadvantages. Do not discuss. Write down names, facts, items, etc. In a specific o ...
... Name the characteristics of something (a happening, object, method or subject). Give a concise description of the subject. Give a complete description of the subject. Write down names, facts, items, advantages and/or disadvantages. Do not discuss. Write down names, facts, items, etc. In a specific o ...
pptx - Departamento de Matemáticas
... transformations in QED,[2] which are the most physically significant, and focused on asymptotic forms of the photon propagator at high energies. They determined the variation of the electromagnetic coupling in QED, by appreciating the simplicity of the scaling structure of that theory. The renormali ...
... transformations in QED,[2] which are the most physically significant, and focused on asymptotic forms of the photon propagator at high energies. They determined the variation of the electromagnetic coupling in QED, by appreciating the simplicity of the scaling structure of that theory. The renormali ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.