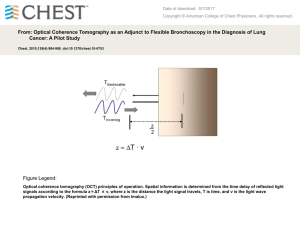
High Resolution Biomedical Imaging with Light and Sound
... illuminates tissue, where optical absorption and transient thermal expansion leads to ultrasound emission. Image contrast is based on the naturally occurring (endogenous) optical absorption in tissue. Spatial resolution and penetration depth are determined by the ultrasonic properties of tissue. Per ...
... illuminates tissue, where optical absorption and transient thermal expansion leads to ultrasound emission. Image contrast is based on the naturally occurring (endogenous) optical absorption in tissue. Spatial resolution and penetration depth are determined by the ultrasonic properties of tissue. Per ...
unit –iii fiber optics and applications part-a 2
... (b) Hetero junction laser (c)Injection laser diode. 18. Why is laser much preferred then LED as an optical source? Laser light is much preferred than LED because it is more directional , highly coherent, faster rise time and narrow spectral width than LED. 19. What is meant by LED / give its princi ...
... (b) Hetero junction laser (c)Injection laser diode. 18. Why is laser much preferred then LED as an optical source? Laser light is much preferred than LED because it is more directional , highly coherent, faster rise time and narrow spectral width than LED. 19. What is meant by LED / give its princi ...
What are Fiber Optics
... LOSSES IN OPTICAL FIBER CABLES The predominant losses in optic Fibers are: absorption losses due to impurities in the Fiber material wavelength dispersion because of the use of a non- ...
... LOSSES IN OPTICAL FIBER CABLES The predominant losses in optic Fibers are: absorption losses due to impurities in the Fiber material wavelength dispersion because of the use of a non- ...
Lecture 9 - web page for staff
... ATM cells can be combined or multiplexed for transmission over SONET/SDH. Note: SDH (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy) – ...
... ATM cells can be combined or multiplexed for transmission over SONET/SDH. Note: SDH (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy) – ...
Introduction
... • Similarly in acoustic communications, the deep water environment will be different than the shallow water environment, purely from the geometric effects of multiple reflections from the bottom and surface. • For acoustic single transducers the emitter can be considered omni ...
... • Similarly in acoustic communications, the deep water environment will be different than the shallow water environment, purely from the geometric effects of multiple reflections from the bottom and surface. • For acoustic single transducers the emitter can be considered omni ...
Photo Contest Winners Member Lens:
... bowl, where they combine to form white light. “This image beautifully demonstrates total internal reflection and three-color mixing, creating a visceral, interactive tutorial for optical fiber technology, modern display technology, Rayleigh scattering, and even integrating sphere technology,” says j ...
... bowl, where they combine to form white light. “This image beautifully demonstrates total internal reflection and three-color mixing, creating a visceral, interactive tutorial for optical fiber technology, modern display technology, Rayleigh scattering, and even integrating sphere technology,” says j ...
CHAPTER 3
... 1- Impurities in fiber material - occurs due to electronic transitions between the energy levels and because of charge transitions from one ion to another. A major source of attenuation is from transition of metal impurity ions such as iron, chromium, cobalt, and copper 2- Intrinsic absorption- Intr ...
... 1- Impurities in fiber material - occurs due to electronic transitions between the energy levels and because of charge transitions from one ion to another. A major source of attenuation is from transition of metal impurity ions such as iron, chromium, cobalt, and copper 2- Intrinsic absorption- Intr ...
Introduction to Optical Networks
... • Deliver new and flexible types of services – Bandwidth on demand – Restorable connections with different restoration guarantees ...
... • Deliver new and flexible types of services – Bandwidth on demand – Restorable connections with different restoration guarantees ...
SET 3742 Light and Optical Fiber Interaction
... to construct a simple, remote passive optical detection sensor. Light which is collected by the fiber will be converted into an electrical signal by photodetector and then amplified. This amplified signal will be converted to an audible signal by the speaker on the Lab Module. We will output the amp ...
... to construct a simple, remote passive optical detection sensor. Light which is collected by the fiber will be converted into an electrical signal by photodetector and then amplified. This amplified signal will be converted to an audible signal by the speaker on the Lab Module. We will output the amp ...
Document
... Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS) 1) Effect and consequences SRS causes a signal wavelength to behave as a “pump” for longer wavelengths, either other signal channels or spontaneously scattered Raman-shifted light. The shorter wavelengths is attenuated by this process, which amplifies longer wavele ...
... Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS) 1) Effect and consequences SRS causes a signal wavelength to behave as a “pump” for longer wavelengths, either other signal channels or spontaneously scattered Raman-shifted light. The shorter wavelengths is attenuated by this process, which amplifies longer wavele ...
Optical fiber sensors
... Optical Fiber Sensor Optical fiber sensor: A sensor that measures a physical quantity based on its modulation on the intensity, spectrum, phase, or polarization of light traveling through an optical fiber. Advantages of optical fiber sensors ...
... Optical Fiber Sensor Optical fiber sensor: A sensor that measures a physical quantity based on its modulation on the intensity, spectrum, phase, or polarization of light traveling through an optical fiber. Advantages of optical fiber sensors ...
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE)
... Abstract: Radio over fiber is an analog transmission in which radio frequency is modulated with laser diode. It is an integration of wireless and fiber optic network .Today the peek requirement is capacity of the channel so optical communication has come in picture. The future provision of multimedi ...
... Abstract: Radio over fiber is an analog transmission in which radio frequency is modulated with laser diode. It is an integration of wireless and fiber optic network .Today the peek requirement is capacity of the channel so optical communication has come in picture. The future provision of multimedi ...
Lect 4 - Components - Sonoma State University
... • The incident light is transmitted through the slits • Due to diffraction (narrow slits) the light is transmitted in all direction • Each Slit becomes a secondary source of light • A constructive interference will be created on the image plane only for specific WLs that are in phase high light in ...
... • The incident light is transmitted through the slits • Due to diffraction (narrow slits) the light is transmitted in all direction • Each Slit becomes a secondary source of light • A constructive interference will be created on the image plane only for specific WLs that are in phase high light in ...
mar9-94 as a Word 6.0 doc - Lyle School of Engineering
... 15. How is a soliton different from conventional optical pulses that propagate on optical fibers? a) Only one soliton pulse can be in a fiber at a time. b) A soliton pulse does not spread. c) A soliton pulse travels at the same speed as a conventional pulse but contains more information. d) A solito ...
... 15. How is a soliton different from conventional optical pulses that propagate on optical fibers? a) Only one soliton pulse can be in a fiber at a time. b) A soliton pulse does not spread. c) A soliton pulse travels at the same speed as a conventional pulse but contains more information. d) A solito ...
may10-94 as a Word 6.0 doc - Lyle School of Engineering
... 2) Some of the multiple choice questions may have more than one correct answer listed. If so, circle all of the correct responses for the question. 3) Please print your name at the bottom of the remaining pages. 4) The last three pages of this exam contain supplementary figures and information that ...
... 2) Some of the multiple choice questions may have more than one correct answer listed. If so, circle all of the correct responses for the question. 3) Please print your name at the bottom of the remaining pages. 4) The last three pages of this exam contain supplementary figures and information that ...
Low Signal Latency in Optical Fiber Networks
... Latency is the elapsed time between sending and receiving a message in an actionable form. Low latency is important whenever action on the message is time sensitive. The most common low latency application today is high frequency trading by the financial services industry where trades are initiated ...
... Latency is the elapsed time between sending and receiving a message in an actionable form. Low latency is important whenever action on the message is time sensitive. The most common low latency application today is high frequency trading by the financial services industry where trades are initiated ...
blood group detection using fiber optics
... Determination of blood groups of a human being is a vital factor. Man by nature has any one of the blood groups namely A, B, AB and O. The blood group “AB” is called the “Universal acceptor” and the people with the “O” group are called “Universal donors”. During blood transfusion any mismatch can le ...
... Determination of blood groups of a human being is a vital factor. Man by nature has any one of the blood groups namely A, B, AB and O. The blood group “AB” is called the “Universal acceptor” and the people with the “O” group are called “Universal donors”. During blood transfusion any mismatch can le ...
Why Optical Communications?
... • The Fiber – that carries the light – Single Mode Fiber (only one EM mode exists), offers the highest bit rate, most widely used – Multi Mode Fiber (multiple EM modes exist), hence higher dispersion (due to multiple modes) cheaper than SMF, used in local area networks – Step Index Fiber – two disti ...
... • The Fiber – that carries the light – Single Mode Fiber (only one EM mode exists), offers the highest bit rate, most widely used – Multi Mode Fiber (multiple EM modes exist), hence higher dispersion (due to multiple modes) cheaper than SMF, used in local area networks – Step Index Fiber – two disti ...
Fiber Optic
... i) Responsitivity: Responsitivity is a measure of the conversion efficiency of a photodetector. ii ) Dark current: Dark current is the leakage current that flows through a photodiode with no light input. iii ) Transit time: Transit time is the time it takes a light-induced carrier to travel across t ...
... i) Responsitivity: Responsitivity is a measure of the conversion efficiency of a photodetector. ii ) Dark current: Dark current is the leakage current that flows through a photodiode with no light input. iii ) Transit time: Transit time is the time it takes a light-induced carrier to travel across t ...
Fiber-optic communication

Fiber-optic communication is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending pulses of light through an optical fiber. The light forms an electromagnetic carrier wave that is modulated to carry information. First developed in the 1970s, fiber-optic communication systems have revolutionized the telecommunications industry and have played a major role in the advent of the Information Age. Because of its advantages over electrical transmission, optical fibers have largely replaced copper wire communications in core networks in the developed world. Optical fiber is used by many telecommunications companies to transmit telephone signals, Internet communication, and cable television signals. Researchers at Bell Labs have reached internet speeds of over 100 petabit×kilometer per second using fiber-optic communication.The process of communicating using fiber-optics involves the following basic steps: Creating the optical signal involving the use of a transmitter, relaying the signal along the fiber, ensuring that the signal does not become too distorted or weak, receiving the optical signal, and converting it into an electrical signal.